Abstract
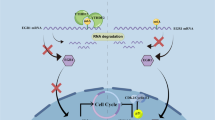
Multiple myeloma (MM) represents the malignant proliferation of terminally differentiated B cells, which, in many cases, is associated with the maintenance of high levels of the oncoprotein c-MYC. Overexpression of the histone methyltransferase MMSET (WHSC1/NSD2), due to t(4;14) chromosomal translocation, promotes the proliferation of MM cells along with global changes in chromatin; nevertheless, the precise mechanisms by which MMSET stimulates neoplasia remain incompletely understood. We found that MMSET enhances the proliferation of MM cells by stimulating the expression of c-MYC at the post-transcriptional level. A microRNA (miRNA) profiling experiment in t(4;14) MM cells identified miR-126* as an MMSET-regulated miRNA predicted to target c-MYC mRNA. We show that miR-126* specifically targets the 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of c-MYC, inhibiting its translation and leading to decreased c-MYC protein levels. Moreover, the expression of this miRNA was sufficient to decrease the proliferation rate of t(4;14) MM cells. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis showed that MMSET binds to the miR-126* promoter along with the KAP1 corepressor and histone deacetylases, and is associated with heterochromatic modifications, characterized by increased trimethylation of H3K9 and decreased H3 acetylation, leading to miR-126* repression. Collectively, this study shows a novel mechanism that leads to increased c-MYC levels and enhanced proliferation of t(4;14) MM, and potentially other cancers with high MMSET expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergsagel PL, Kuehl WM . Chromosome translocations in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 2001; 20: 5611–5622.
Dib A, Gabrea A, Glebov OK, Bergsagel PL, Kuehl WM . Characterization of MYC translocations in multiple myeloma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 2008; 39: 25–31.
Chapman MA, Lawrence MS, Keats JJ, Cibulskis K, Sougnez C, Schinzel AC et al. Initial genome sequencing and analysis of multiple myeloma. Nature 2011; 471: 467–472.
Lin Y, Wong K, Calame K . Repression of c-myc transcription by Blimp-1, an inducer of terminal B cell differentiation. Science 1997; 276: 596–599.
Keats JJ, Reiman T, Maxwell CA, Taylor BJ, Larratt LM, Mant MJ et al. In multiple myeloma, t(4;14)(p16;q32) is an adverse prognostic factor irrespective of FGFR3 expression. Blood 2003; 101: 1520–1529.
Santra M, Zhan F, Tian E, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy J . A subset of multiple myeloma harboring the t(4;14)(p16;q32) translocation lacks FGFR3 expression but maintains an IGH/MMSET fusion transcript. Blood 2003; 101: 2374–2376.
Marango J, Shimoyama M, Nishio H, Meyer JA, Min DJ, Sirulnik A et al. The MMSET protein is a histone methyltransferase with characteristics of a transcriptional corepressor. Blood 2008; 111: 3145–3154.
Kim JY, Kee HJ, Choe NW, Kim SM, Eom GH, Baek HJ et al. Multiple-myeloma-related WHSC1/MMSET isoform RE-IIBP is a histone methyltransferase with transcriptional repression activity. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 2023–2034.
Brito JL, Walker B, Jenner M, Dickens NJ, Brown NJ, Ross FM et al. MMSET deregulation affects cell cycle progression and adhesion regulons in t(4;14) myeloma plasma cells. Haematologica 2009; 94: 78–86.
Nimura K, Ura K, Shiratori H, Ikawa M, Okabe M, Schwartz RJ et al. A histone H3 lysine 36 trimethyltransferase links Nkx2-5 to Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Nature 2009; 460: 287–291.
Martinez-Garcia E, Popovic R, Min DJ, Sweet SM, Thomas PM, Zamdborg L et al. The MMSET histone methyl transferase switches global histone methylation and alters gene expression in t(4;14) multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2011; 117: 211–220.
Kuo AJ, Cheung P, Chen K, Zee BM, Kioi M, Lauring J et al. NSD2 links dimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 36 to oncogenic programming. Mol Cell 2011; 44: 609–620.
Shaffer AL, Emre NC, Lamy L, Ngo VN, Wright G, Xiao W et al. IRF4 addiction in multiple myeloma. Nature 2008; 454: 226–231.
McConnell MJ, Chevallier N, Berkofsky-Fessler W, Giltnane JM, Malani RB, Staudt LM et al. Growth suppression by acute promyelocytic leukemia-associated protein PLZF is mediated by repression of c-myc expression. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 9375–9388.
Salmon P, Trono D . Production and titration of lentiviral vectors. Curr Protoc Hum Genet 2007; Chapter 12: Unit 12.10.
Kim MK, Mason JM, Li CM, Berkofsky-Fessler W, Jiang L, Choubey D et al. A pathologic link between Wilms tumor suppressor gene, WT1, and IFI16. Neoplasia 2008; 10: 69–78.
Kuchenbauer F, Mah SM, Heuser M, McPherson A, Ruschmann J, Rouhi A et al. Comprehensive analysis of mammalian miRNA* species and their role in myeloid cells. Blood 2011; 118: 3350–3358.
Littlewood TD, Hancock DC, Danielian PS, Parker MG, Evan GI . A modified oestrogen receptor ligand-binding domain as an improved switch for the regulation of heterologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 1995; 23: 1686–1690.
Todoerti K, Ronchetti D, Agnelli L, Castellani S, Marelli S, Deliliers GL et al. Transcription repression activity is associated with the type I isoform of the MMSET gene involved in t(4;14) in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 2005; 131: 214–218.
Ayyanathan K, Lechner MS, Bell P, Maul GG, Schultz DC, Yamada Y et al. Regulated recruitment of HP1 to a euchromatic gene induces mitotically heritable, epigenetic gene silencing: a mammalian cell culture model of gene variegation. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 1855–1869.
O’Geen H, Squazzo SL, Iyengar S, Blahnik K, Rinn JL, Chang HY et al. Genome-wide analysis of KAP1 binding suggests autoregulation of KRAB-ZNFs. PLoS Genet 2007; 3: e89.
Peng H, Ivanov AV, Oh HJ, Lau YF, Rauscher FJ . Epigenetic gene silencing by the SRY protein is mediated by a KRAB-O protein that recruits the KAP1 co-repressor machinery. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 35670–35680.
Oswald F, Lovec H, Moroy T, Lipp M . E2F-dependent regulation of human MYC: trans-activation by cyclins D1 and A overrides tumour suppressor protein functions. Oncogene 1994; 9: 2029–2036.
Morgan MA, Magnusdottir E, Kuo TC, Tunyaplin C, Harper J, Arnold SJ et al. Blimp-1/Prdm1 alternative promoter usage during mouse development and plasma cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 5813–5827.
Cobbold LC, Wilson LA, Sawicka K, King HA, Kondrashov AV, Spriggs KA et al. Upregulated c-myc expression in multiple myeloma by internal ribosome entry results from increased interactions with and expression of PTB-1 and YB-1. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2884–2891.
Shi Y, Frost P, Hoang B, Benavides A, Gera J, Lichtenstein A . IL-6-induced enhancement of c-Myc translation in multiple myeloma cells: critical role of cytoplasmic localization of the rna-binding protein hnRNP A1. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 67–78.
Garzon R, Calin GA, Croce CM . MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Med 2009; 60: 167–179.
Pichiorri F, Suh SS, Ladetto M, Kuehl M, Palumbo T, Drandi D et al. MicroRNAs regulate critical genes associated with multiple myeloma pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 12885–12890.
Gutierrez NC, Sarasquete ME, Misiewicz-Krzeminska I, Delgado M, De Las Rivas J, Ticona FV et al. Deregulation of microRNA expression in the different genetic subtypes of multiple myeloma and correlation with gene expression profiling. Leukemia 2010; 24: 629–637.
Lionetti M, Biasiolo M, Agnelli L, Todoerti K, Mosca L, Fabris S et al. Identification of microRNA expression patterns and definition of a microRNA/mRNA regulatory network in distinct molecular groups of multiple myeloma. Blood 2009; 114: e20–e26.
Wong TS, Man OY, Tsang CM, Tsao SW, Tsang RK, Chan JY et al. MicroRNA let-7 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells proliferation through downregulating c-Myc expression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2011; 137: 415–422.
Leucci E, Cocco M, Onnis A, De Falco G, van Cleef P, Bellan C et al. MYC translocation-negative classical Burkitt lymphoma cases: an alternative pathogenetic mechanism involving miRNA deregulation. J Pathol 2008; 216: 440–450.
Bhatia S, Kaul D, Varma N . Potential tumor suppressive function of miR-196b in B-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Cell Biochem 2010; 340: 97–106.
Biasiolo M, Sales G, Lionetti M, Agnelli L, Todoerti K, Bisognin A et al. Impact of host genes and strand selection on miRNA and miRNA* expression. PLoS One 2011; 6: e23854.
Li Z, Chen J . In vitro functional study of miR-126 in leukemia. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 676: 185–195.
Huang X, Gschweng E, Van Handel B, Cheng D, Mikkola HK, Witte ON . Regulated expression of microRNAs-126/126* inhibits erythropoiesis from human embryonic stem cells. Blood 2011; 117: 2157–2165.
Grabher C, Payne EM, Johnston AB, Bolli N, Lechman E, Dick JE et al. Zebrafish microRNA-126 determines hematopoietic cell fate through c-Myb. Leukemia 2011; 25: 506–514.
Zhu N, Zhang D, Xie H, Zhou Z, Chen H, Hu T et al. Endothelial-specific intron-derived miR-126 is down-regulated in human breast cancer and targets both VEGFA and PIK3R2. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 351: 157–164.
Miko E, Margitai Z, Czimmerer Z, Varkonyi I, Dezso B, Lanyi A et al. miR-126 inhibits proliferation of small cell lung cancer cells by targeting SLC7A5. FEBS Lett 2011; 585: 1191–1196.
Otsubo T, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, Shimada S, Goto K, Yuasa Y . MicroRNA-126 inhibits SOX2 expression and contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16617.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 15524–15529.
Rouhi A, Mager DL, Humphries RK, F Kuchenbauer . MiRNAs, epigenetics, and cancer. Mamm Genome 2008; 19: 517–525.
Fazi F, Racanicchi S, Zardo G, Starnes LM, Mancini M, Travaglini L et al. Epigenetic silencing of the myelopoiesis regulator microRNA-223 by the AML1/ETO oncoprotein. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 457–466.
Cammarata G, Augugliaro L, Salemi D, Agueli C, La Rosa M, Dagnino L et al. Differential expression of specific microRNA and their targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol 2010; 85: 331–339.
Li Z, Lu J, Sun M, Mi S, Zhang H, Luo RT et al. Distinct microRNA expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 15535–15540.
Li X, Shen Y, Ichikawa H, Antes T, Goldberg GS . Regulation of miRNA expression by Src and contact normalization: effects on nonanchored cell growth and migration. Oncogene 2009; 28: 4272–4283.
Ezponda T, Popovic R, Shah MY, Martinez-Garcia E, Zheng Y, Min DJ et al. The histone methyltransferase MMSET/WHSC1 activates TWIST1 to promote an epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasive properties of prostate cancer. Oncogene 2012.
Alter MD, Hen R . Putting a KAP on transcription and stress. Neuron 2008; 60: 733–735.
Schrump DS . Cytotoxicity mediated by histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer cells: mechanisms and potential clinical implications. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 3947–3957.
Stimson L, La Thangue NB . Biomarkers for predicting clinical responses to HDAC inhibitors. Cancer Lett 2009; 280: 177–183.
Ellis L, Atadja PW, Johnstone RW . Epigenetics in cancer: targeting chromatin modifications. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 1409–1420.
Mitsiades CS, Davies FE, Laubach JP, Joshua D, San Miguel J, Anderson KC et al. Future directions of next-generation novel therapies, combination approaches, and the development of personalized medicine in myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1916–1923.
Gronbaek K, Hother C, Jones PA . Epigenetic changes in cancer. APMIS 2007; 115: 1039–1059.
Frew AJ, Johnstone RW, Bolden JE . Enhancing the apoptotic and therapeutic effects of HDAC inhibitors. Cancer Lett 2009; 280: 125–133.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Louis Staudt for providing the MMSET-shRNA cells and Dr Marcus Peter for helpful suggestions. This work was supported by NIH Grant CA123204, a Leukemia and Lymphoma Specialized Center of Research grant, a NIH Physical Science Oncology Center Grant U54CA143869 and Epizyme, Inc. (to JDL). EM-G was supported by a European Hematology Association Fellowship, RP by NRSA HL099177 and TE by an Alfonso Martin Escudero fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, DJ., Ezponda, T., Kim, M. et al. MMSET stimulates myeloma cell growth through microRNA-mediated modulation of c-MYC. Leukemia 27, 686–694 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.269
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.269
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Proteosomal degradation of NSD2 by BRCA1 promotes leukemia cell differentiation
Communications Biology (2020)
-
Gm6377 suppressed SP 2/0 xenograft tumor by down-regulating Myc transcription
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2020)
-
Regulatory mechanisms of B cell responses and the implication in B cell-related diseases
Journal of Biomedical Science (2019)
-
The biological significance of histone modifiers in multiple myeloma: clinical applications
Blood Cancer Journal (2018)
-
Role of epigenetics-microRNA axis in drug resistance of multiple myeloma
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2017)