Abstract
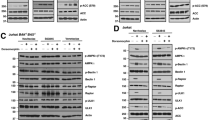
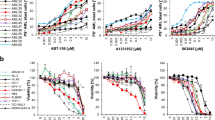
Recently, strategies for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) therapy have been developed that target anti-apoptotic BCL2 family members using BH3-mimetic drugs such as ABT-737. Though effective against BCL2 and BCL-XL, ABT-737 poorly inhibits MCL-1. Here we report that, unexpectedly, ABT-737 induces activation of the extracellular receptor activated kinase and induction of MCL-1 in AML cells. MEK inhibitors such as PD0325901 and CI-1040 have been used successfully to suppress MCL-1. We report that PD0325901 blocked ABT-737-induced MCL-1 expression, and when combined with ABT-737 resulted in potent synergistic killing of AML-derived cell lines, primary AML blast and CD34+38-123+ progenitor/stem cells. Finally, we tested the combination of ABT-737 and CI-1040 in a murine xenograft model using MOLM-13 human leukemia cells.Whereas control mice and CI-1040-treated mice exhibited progressive leukemia growth, ABT-737, and to a significantly greater extent, ABT-737+CI-1040 exerted major anti-leukemia activity. Collectively, results demonstrated unexpected anti-apoptotic interaction between the BCL2 family-targeted BH3-mimetic ABT-737 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in AML cells: the BH3 mimetic is not only restrained in its activity by MCL-1, but also induces its expression. However, concomitant inhibition by BH3 mimetics and MEK inhibitors could abrogate this effect and may be developed into a novel and effective therapeutic strategy for patients with AML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zinkel S, Gross A, Yang E . BCL2 family in DNA damage and cell cycle control. Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 1351–1359.
Letai AG . Diagnosing and exploiting cancer's addiction to blocks in apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 121–132.
Yip KW, Reed JC . Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene 2008; 27: 6398–6406.
Frenzel A, Grespi F, Chmelewskij W, Villunger A . Bcl2 family proteins in carcinogenesis and the treatment of cancer. Apoptosis 2009; 14: 584–596.
Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons MJ, Green DR . The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell 2010; 37: 299–310.
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA et al. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 351–365.
Del Gaizo Moore V, Letai A . Rational design of therapeutics targeting the BCL-2 family: are some cancer cells primed for death but waiting for a final push? Adv Exp Med Biol 2008; 615: 159–175.
Kornblau SM, Thall PF, Estrov Z, Walterscheid M, Patel S, Theriault A et al. The prognostic impact of BCL2 protein expression in acute myelogenous leukemia varies with cytogenetics. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 1758–1766.
Kornblau SM, Vu HT, Ruvolo P, Estrov Z, O'Brien S, Cortes J et al. BAX and PKCalpha modulate the prognostic impact of BCL2 expression in acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 1401–1409.
Del Poeta G, Venditti A, Del Principe MI, Maurillo L, Buccisano F, Tamburini A et al. Amount of spontaneous apoptosis detected by Bax/Bcl-2 ratio predicts outcome in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2003; 101: 2125–2131.
Del Poeta G, Ammatuna E, Lavorgna S, Capelli G, Zaza S, Luciano F et al. The genotype nucleophosmin mutated and FLT3-ITD negative is characterized by high bax/bcl-2 ratio and favourable outcome in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2010; 149: 383–387.
Moreira JN, Santos A, Simoes S . Bcl-2-targeted antisense therapy (Oblimersen sodium): towards clinical reality. Rev Recent Clin Trials 2006; 1: 217–235.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005; 435: 677–681.
Chonghaile TN, Letai A . Mimicking the BH3 domain to kill cancer cells. Oncogene 2008; 27 (Suppl 1): S149–S157.
Vogler M, Dinsdale D, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM . Bcl-2 inhibitors: small molecules with a big impact on cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 360–367.
Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson MG, Chen J, Jin S et al. ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 3421–3428.
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T, Samudio I, Ruvolo PP, Kitada S et al. Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 375–388.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 389–399.
Chen S, Dai Y, Harada H, Dent P, Grant S . Mcl-1 down-regulation potentiates ABT-737 lethality by cooperatively inducing Bak activation and Bax translocation. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 782–791.
Yecies D, Carlson NE, Deng J, Letai A . Acquired resistance to ABT-737 in lymphoma cells that up-regulate MCL-1 and BFL-1. Blood 2010; 115: 3304–3313.
Townsend KJ, Zhou P, Qian L, Bieszczad CK, Lowrey CH, Yen A et al. Regulation of MCL1 through a serum response factor/Elk-1-mediated mechanism links expression of a viability-promoting member of the BCL2 family to the induction of hematopoietic cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 1801–1813.
Domina AM, Vrana JA, Gregory MA, Hann SR, Craig RW . MCL1 is phosphorylated in the PEST region and stabilized upon ERK activation in viable cells, and at additional sites with cytotoxic okadaic acid or taxol. Oncogene 2004; 23: 5301–5315.
Barrett SD, Bridges AJ, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR, Fergus JH, Flamme CM et al. The discovery of the benzhydroxamate MEK inhibitors CI-1040 and PD 0325901. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2008; 18: 6501–6504.
Jordan CT, Upchurch D, Szilvassy SJ, Guzman ML, Howard DS, Pettigrew AL et al. The interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain is a unique marker for human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1777–1784.
Ewings KE, Wiggins CM, Cook SJ . Bim and the pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins: opposites attract, ERK repels. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 2236–2240.
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Ruvolo VR, McQueen T, Evans RL, Bornmann WG et al. Sorafenib induces apoptosis of AML cells via Bim-mediated activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Leukemia 2008; 22: 808–818.
Fox JL, Ismail F, Azad A, Ternette N, Leverrier S, Edelmann MJ et al. Tyrosine dephosphorylation is required for Bak activation in apoptosis. EMBO J 2010; 29: 3853–3868.
Samudio I, Harmancey R, Fiegl M, Kantarjian H, Konopleva M, Korchin B et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of fatty acid oxidation sensitizes human leukemia cells to apoptosis induction. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 142–156.
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Burks JK, Dywer KC, Schober WD, Yang JY et al. Blockade of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase and murine double minute synergistically induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia via BH3-only proteins Puma and Bim. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 2424–2434.
Kang MH, Wan Z, Kang YH, Sposto R, Reynolds CP . Mechanism of synergy of N-(4 hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and ABT-737 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines: Mcl-1inactivation. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008; 100: 580–595.
Ruvolo VR, Karanjeet KB, Schuster TF, Brown R, Deng Y, Hinchcliffe E et al. Role for PKC δ in fenretinide-mediated apoptosis in lymphoid leukemia cells. J Signal Transduct 2010; 2010: 584657.
Thomas LW, Lam C, Edwards SW . Mcl-1; the molecular regulation of protein function. FEBS Lett 2010; 584: 2981–2989.
Chu S, Holtz M, Gupta M, Bhatia R . BCR/ABL kinase inhibition by imatinib mesylate enhances MAP kinase activity in chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ cells. Blood 2004; 103: 3167–3174.
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Rojo F, Salmena L, Alimonti A et al. Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3065–3074.
Lunghi P, Costanzo A, Levrero M, Bonati A . Treatment with arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK1 inhibitor activates the p73-p53AIP1 apoptotic pathway in leukemia cells. Blood 2004; 104: 519–525.
Lunghi P, Tabilio A, Lo-Coco F, Pelicci PG, Bonati A . Arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK1 inhibition synergize to induce apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2005; 19: 234–244.
Lunghi P, Costanzo A, Salvatore L, Noguera N, Mazzera L, Tabilio A et al. MEK1 inhibition sensitizes primary acute myelogenous leukemia to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis. Blood 2006; 107: 4549–4553.
Lunghi P, Giuliani N, Mazzera L, Lombardi G, Ricca M, Corradi A et al. Targeting MEK/MAPK signal transduction module potentiates ATO-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through multiple signaling pathways. Blood 2008; 112: 2450–2462.
Verma A, Mohindru M, Deb DK, Sassano A, Kambhampati S, Ravandi F et al. Activation of Rac1 and the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in response to arsenic trioxide. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 44988–44995.
Kazi A, Sun J, Doi K, Sung SS, Takahashi Y, Yin H et al. The BH3 {alpha}-helical mimic BH3-M6 disrupts Bcl-XL, Bcl-2, and MCL-1 protein-protein interactions with Bax, Bak, Bad, or Bim and induces apoptosis in a Bax- and Bim-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 9382–9392.
Deng J, Carlson N, Takeyama K, Dal Cin P, Shipp M, Letai A . BH3 profiling identifies three distinct classes of apoptotic blocks to predict response to ABT-737 and conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 171–185.
Chen S, Dai Y, Pei XY, Grant S . Bim upregulation by histone deacetylase inhibitors mediates interactions with the Bcl-2 antagonist ABT-737: evidence for distinct roles for Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 6149–6169.
Morales AA, Kurtoglu M, Matulis SM, Liu J, Siefker D, Gutman DM et al. Distribution of Bim determines Mcl-1 dependence or co-dependence with Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 in Mcl-1-expressing myeloma cells. Blood 2011; 118: 1329–1339.
Cragg MS, Jansen ES, Cook M, Harris C, Strasser A, Scott CL . Treatment of B-RAF mutant human tumor cells with a MEK inhibitor requires Bim and is enhanced by a BH3 mimetic. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3651–3659.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (PO1 Grant CA-55164).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konopleva, M., Milella, M., Ruvolo, P. et al. MEK inhibition enhances ABT-737-induced leukemia cell apoptosis via prevention of ERK-activated MCL-1 induction and modulation of MCL-1/BIM complex. Leukemia 26, 778–787 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.287
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.287
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Progress in understanding the mechanisms of resistance to BCL-2 inhibitors
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Targeting Apoptosis in Cancer
Current Oncology Reports (2022)
-
Arsenic trioxide synergistically promotes the antileukaemic activity of venetoclax by downregulating Mcl-1 in acute myeloid leukaemia cells
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
Bayesian multi-source regression and monocyte-associated gene expression predict BCL-2 inhibitor resistance in acute myeloid leukemia
npj Precision Oncology (2021)
-
BH3-only protein expression determines hepatocellular carcinoma response to sorafenib-based treatment
Cell Death & Disease (2021)