Abstract
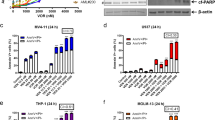
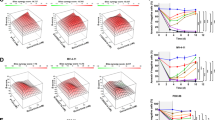
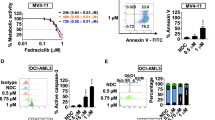
TG02 is a novel pyrimidine-based multi-kinase inhibitor that inhibits CDKs 1, 2, 7 and 9 together with JAK2 and FLT3. It dose-dependently inhibits signaling pathways downstream of CDKs, JAK2 and FLT3 in cancer cells with the main targets being CDKs. TG02 is anti-proliferative in a broad range of tumor cell lines, inducing G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Primary cultures of progenitor cells derived from acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and polycythemia vera patients are very sensitive to TG02. Comparison with reference inhibitors that block only one of the main targets of TG02 demonstrate the benefit of combined CDK and JAK2/FLT3 inhibition in cell lines as well as primary cells. In vivo, TG02 exhibits favorable pharmacokinetics after oral dosing in xenograft models and accumulates in tumor tissues, inducing an effective blockade of both CDK and STAT signaling. TG02 induces tumor regression after oral dosing on both daily and intermittent schedules in a murine model of mutant-FLT3 leukemia (MV4-11) and prolongs survival in a disseminated AML model with wild-type FLT3 and JAK2 (HL-60). These data demonstrate that TG02 is active in various models of leukemia and provide a rationale for the ongoing clinical evaluation of TG02 in patients with advanced leukemias.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker SJ, Reddy EP . Targeted inhibition of kinases in cancer therapy. Mt Sinai J Med 2010; 77: 573–586.
Negrier S, Raymond E . Antiangiogenic treatments and mechanisms of action in renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 2011, e-pub ahead of print, doi: 10.1007/s10637-10011-19677-10636.
Worns MA, Galle PR . Novel inhibitors in development for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2010; 19: 615–629.
Knockaert M, Greengard P, Meijer L . Pharmacological inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2002; 23: 417–425.
Shapiro GI . Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 1770–1783.
Cai D, Latham Jr VM, Zhang X, Shapiro GI . Combined depletion of cell cycle and transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinase activities induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 9270–9280.
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM, Harrison DA . The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 2004; 117 (Part 8): 1281–1283.
Bennett M, Stroncek DF . Recent advances in the bcr-abl negative chronic myeloproliferative diseases. J Transl Med 2006; 4: 41.
Tickenbrock L, Muller-Tidow C, Berdel WE, Serve H . Emerging Flt3 kinase inhibitors in the treatment of leukaemia. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2006; 11: 153–165.
Driggers EM, Hale SP, Lee J, Terrett NK . The exploration of macrocycles for drug discovery—an underexploited structural class. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008; 7: 608–624.
Lapenna S, Giordano A . Cell cycle kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009; 8: 547–566.
Wernig G, Kharas MG, Okabe R, Moore SA, Leeman DS, Cullen DE et al. Efficacy of TG101348, a selective JAK2 inhibitor, in treatment of a murine model of JAK2V617F-induced polycythemia vera. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 311–320.
Atkins M, Jones CA, Kirkpatrick P . Sunitinib maleate. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 279–280.
Jordan CT, Upchurch D, Szilvassy SJ, Guzman ML, Howard DS, Pettigrew AL et al. The interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain is a unique marker for human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1777–1784.
Choudhary C, Brandts C, Schwable J, Tickenbrock L, Sargin B, Ueker A et al. Activation mechanisms of STAT5 by oncogenic Flt3-ITD. Blood 2007; 110: 370–374.
Melzner I, Weniger MA, Bucur AJ, Bruderlein S, Dorsch K, Hasel C et al. Biallelic deletion within 16p13.13 including SOCS-1 in Karpas1106P mediastinal B-cell lymphoma line is associated with delayed degradation of JAK2 protein. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 1941–1944.
Uozumi K, Otsuka M, Ohno N, Moriyama T, Suzuki S, Shimotakahara S et al. Establishment and characterization of a new human megakaryoblastic cell line (SET-2) that spontaneously matures to megakaryocytes and produces platelet-like particles. Leukemia 2000; 14: 142–152.
Grandage VL, Everington T, Linch DC, Khwaja A . Gö6976 is a potent inhibitor of the JAK 2 and FLT3 tyrosine kinases with significant activity in primary acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 2006; 135: 303–316.
Tyner JW, Bumm TG, Deininger J, Wood L, Aichberger KJ, Loriaux MM et al. CYT387, a novel JAK2 inhibitor, induces hematologic responses and normalizes inflammatory cytokines in murine myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2010; 115: 5232–5240.
Conroy A, Stockett DE, Walker D, Arkin MR, Hoch U, Fox JA et al. SNS-032 is a potent and selective CDK 2, 7 and 9 inhibitor that drives target modulation in patient samples. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2009; 64: 723–732.
Hannah AL . Kinases as drug discovery targets in hematologic malignancies. Curr Mol Med 2005; 5: 625–642.
Ikezoe T, Kojima S, Furihata M, Yang J, Nishioka C, Takeuchi A et al. High levels of p-JAK2 are associated with adverse clinical outcome and can be a molecular target in individuals with acute myelogenous leukemia. Int J Cancer 2011;Epub ahead of print.
Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, Kojima S, Takeuchi A, Koeffler HP et al. Inhibition of STAT5 by the inhibitor of janus kinases stimulates dormant human leukemia CD34(+)/CD38(−) cells and sensitizes them to anti-leukemia agents. Int J Cancer 2011; 128: 2317–2325.
Levine RL, Pardanani A, Tefferi A, Gilliland DG . Role of JAK2 in the pathogenesis and therapy of myeloproliferative disorders. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 673–683.
Cai D, Latham Jr VM, Zhang X, Shapiro GI . Combined depletion of cell cycle and transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinase activities induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 9270–9280.
Pesu M, Candotti F, Husa M, Hofmann SR, Notarangelo LD, O’Shea JJ . Jak3, severe combined immunodeficiency, and a new class of immunosuppressive drugs. Immunol Rev 2005; 203: 127–142.
Verstovsek S, Deeg HJ, Odenike O, Zhu J, Kantarjian HM, Estrov Z et al. Phase 1/2 Study of SB1518, a Novel JAK2/FLT3 Inhibitor, In the Treatment of Primary Myelofibrosis. Blood 2010; 116: Abstract 3082.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
FB is an employee of Tragara Pharmaceuticals. All other authors, except KHO, are employees of S*BIO.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goh, K., Novotny-Diermayr, V., Hart, S. et al. TG02, a novel oral multi-kinase inhibitor of CDKs, JAK2 and FLT3 with potent anti-leukemic properties. Leukemia 26, 236–243 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.218
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.218
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MYC: a multipurpose oncogene with prognostic and therapeutic implications in blood malignancies
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
The multi-kinase inhibitor TG02 induces apoptosis and blocks B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia through dual mechanisms of action
Blood Cancer Journal (2021)
-
CDK9 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)
-
Efficacy of RNA polymerase II inhibitors in targeting dormant leukaemia cells
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology (2013)
-
FLT3 inhibition: a moving and evolving target in acute myeloid leukaemia
Leukemia (2013)