Abstract
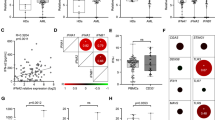
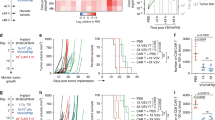
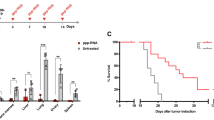
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) harboring the t(4;11) translocation is associated with a very poor prognosis; innovative treatment strategies are required to improve the current 5-year survival rate of 30–40%. Interferon β (IFNβ) has shown promise in the treatment of both solid and hematologic malignancies, although the short half-life and toxicity associated with high doses have limited its clinical utility. To overcome these limitations, we investigated the effect of continuous, gene transfer-mediated delivery of IFNβ using adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated expression, on ALL cells with the t(4;11) translocation. We found that this method of IFNβ delivery resulted in complete remission of leukemia in a murine model. However, leukemic cells eventually became resistant to IFNβ and relapse was observed. Activation of NF-κB was identified as a mechanism for IFNβ resistance, and inhibition of NF-κB activity in resistant cells sensitized cells to IFNβ. IFNβ combined with agents that inhibit NF-κB could have therapeutic potential in the treatment of children with mixed lineage leukemia subtype ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pui CH, Relling MV, Downing JR . Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 1535–1548.
Pui CH, Relling MV, Sandlund JT, Downing JR, Campana D, Evans WE . Rationale and design of Total Therapy Study XV for newly diagnosed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann Hematol 2004; 83 (Suppl 1): S124–S126.
Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Frestedt JL, Liu Q, Crist WM, Downing JR et al. Rearrangement of the MLL gene confers a poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia, regardless of presenting age. Blood 1996; 87: 2870–2877.
Pui CH, Behm FG, Downing JR, Hancock ML, Shurtleff SA, Ribeiro RC et al. 11q23/MLL rearrangement confers a poor prognosis in infants with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 1994; 12: 909–915.
Pui CH, Chessells JM, Camitta B, Baruchel A, Biondi A, Boyett JM et al. Clinical heterogeneity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with 11q23 rearrangements. Leukemia 2003; 17: 700–706.
Pui CH, Gaynon PS, Boyett JM, Chessells JM, Baruchel A, Kamps W et al. Outcome of treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with rearrangements of the 11q23 chromosomal region. Lancet 2002; 359: 1909–1915.
Benjamin R, Khwaja A, Singh N, McIntosh J, Meager A, Wadhwa M et al. Continuous delivery of human type I interferons (alpha/beta) has significant activity against acute myeloid leukemia cells in vitro and in a xenograft model. Blood 2007; 109: 1244–1247.
Streck CJ, Dickson PV, Ng CY, Zhou J, Hall MM, Gray JT et al. Antitumor efficacy of AAV-mediated systemic delivery of interferon-beta. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 99–106.
Streck CJ, Zhang Y, Miyamoto R, Zhou J, Ng CY, Nathwani AC et al. Restriction of neuroblastoma angiogenesis and growth by interferon-alpha/beta. Surgery 2004; 136: 183–189.
Greil J, Gramatzki M, Burger R, Marschalek R, Peltner M, Trautmann U et al. The acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cell line SEM with t(4;11) chromosomal rearrangement is biphenotypic and responsive to interleukin-7. Br J Haematol 1994; 86: 275–283.
Stong RC, Korsmeyer SJ, Parkin JL, Arthur DC, Kersey JH . Human acute leukemia cell line with the t(4;11) chromosomal rearrangement exhibits B lineage and monocytic characteristics. Blood 1985; 65: 21–31.
Yang CH, Murti A, Pfeffer SR, Basu L, Kim JG, Pfeffer LM . IFNalpha/beta promotes cell survival by activating NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 13631–13636.
Davidoff AM, Gray JT, Ng CY, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Spence Y et al. Comparison of the ability of adeno-associated viral vectors pseudotyped with serotype 2, 5, and 8 capsid proteins to mediate efficient transduction of the liver in murine and nonhuman primate models. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 875–888.
Baranzini SE, Mousavi P, Rio J, Caillier SJ, Stillman A, Villoslada P et al. Transcription-based prediction of response to IFNbeta using supervised computational methods. PLoS Biol 2005; 3: e2.
Shang D, Liu Y, Ito N, Kamoto T, Ogawa O . Defective Jak-Stat activation in renal cell carcinoma is associated with interferon-alpha resistance. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 1259–1264.
Sun WH, Pabon C, Alsayed Y, Huang PP, Jandeska S, Uddin S et al. Interferon-alpha resistance in a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell line is associated with lack of STAT1 expression. Blood 1998; 91: 570–576.
Wong LH, Krauer KG, Hatzinisiriou I, Estcourt MJ, Hersey P, Tam ND et al. Interferon-resistant human melanoma cells are deficient in ISGF3 components, STAT1, STAT2, and p48-ISGF3gamma. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 28779–28785.
Yang CH, Murti A, Pfeffer LM . STAT3 complements defects in an interferon-resistant cell line: evidence for an essential role for STAT3 in interferon signaling and biological activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 5568–5572.
Adams J, Kauffman M . Development of the proteasome inhibitor Velcade (Bortezomib). Cancer Invest 2004; 22: 304–311.
Abramovich C, Shulman LM, Ratovitski E, Harroch S, Tovey M, Eid P et al. Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of the IFNAR chain of the type I interferon receptor and of an associated surface protein in response to IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. EMBO J 1994; 13: 5871–5877.
Brinckmann A, Axer S, Jakschies D, Dallmann I, Grosse J, Patzelt T et al. Interferon-alpha resistance in renal carcinoma cells is associated with defective induction of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 which can be restored by a supernatant of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Br J Cancer 2002; 86: 449–455.
Zitzmann K, Brand S, De Toni EN, Baehs S, Goke B, Meinecke J et al. SOCS1 silencing enhances antitumor activity of type I IFNs by regulating apoptosis in neuroendocrine tumor cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5025–5032.
Bednarski BK, Ding X, Coombe K, Baldwin AS, Kim HJ . Active roles for inhibitory kappaB kinases alpha and beta in nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated chemoresistance to doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 1827–1835.
Cilloni D, Messa F, Arruga F, Defilippi I, Morotti A, Messa E et al. The NF-kappaB pathway blockade by the IKK inhibitor PS1145 can overcome imatinib resistance. Leukemia 2006; 20: 61–67.
Hewamana S, Lin TT, Jenkins C, Burnett AK, Jordan CT, Fegan C et al. The novel nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor LC-1 is equipotent in poor prognostic subsets of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and shows strong synergy with fludarabine. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 8102–8111.
Kunnumakkara AB, Guha S, Krishnan S, Diagaradjane P, Gelovani J, Aggarwal BB . Curcumin potentiates antitumor activity of gemcitabine in an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer through suppression of proliferation, angiogenesis, and inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 3853–3861.
Mi J, Zhang X, Rabbani ZN, Liu Y, Reddy SK, Su Z et al. RNA aptamer-targeted inhibition of NF-kappa B suppresses non-small cell lung cancer resistance to doxorubicin. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 66–73.
Sors A, Jean-Louis F, Begue E, Parmentier L, Dubertret L, Dreano M et al. Inhibition of IkappaB kinase subunit 2 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma down-regulates nuclear factor-kappaB constitutive activation, induces cell death, and potentiates the apoptotic response to antineoplastic chemotherapeutic agents. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 901–911.
Tracey L, Spiteri I, Ortiz P, Lawler M, Piris MA, Villuendas R . Transcriptional response of T cells to IFN-alpha: changes induced in IFN-alpha-sensitive and resistant cutaneous T cell lymphoma. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2004; 24: 185–195.
Wozniak MB, Tracey L, Ortiz-Romero PL, Montes S, Alvarez M, Fraga J et al. Psoralen plus ultraviolet A +/− interferon-alpha treatment resistance in mycosis fungoides: the role of tumour microenvironment, nuclear transcription factor-kappaB and T-cell receptor pathways. Br J Dermatol 2009; 160: 92–102.
Yang CH, Murti A, Pfeffer SR, Kim JG, Donner DB, Pfeffer LM . Interferon alpha/beta promotes cell survival by activating nuclear factor kappa B through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 13756–13761.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Assisi Foundation of Memphis, the National Cancer Institute (R01CA1333222-01A1 and Cancer Center Support CORE grant CA21766), the University of Tennessee Health Science Center (Muirhead Chair Endowment) and the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tracey, L., Streck, C., Du, Z. et al. NF-κB activation mediates resistance to IFNβ in MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 24, 806–812 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pentoxifylline and the proteasome inhibitor MG132 induce apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells through a decrease in the expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL and phosphorylation of p65
Journal of Biomedical Science (2013)
-
Triptolide inhibits the proliferation of cells from lymphocytic leukemic cell lines in association with downregulation of NF-κB activity and miR-16-1*
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2011)
-
Type I IFNs signaling and apoptosis resistance in glioblastoma cells
Apoptosis (2011)