Abstract
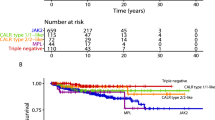
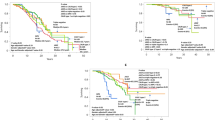
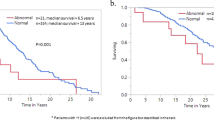
The germline JAK2 haplotype 46/1, tagged by the ‘C’ allele of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs12343867 (C/T), has been associated with JAK2V617F (VF)-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms. SNP rs12343867 was genotyped using bone marrow DNA in 226 consecutive patients with essential thrombocythemia (ET) with concomitant analysis of VF allele burden. The incidence of the 46/1-linked C allele was significantly higher in ET (genotype: CC 15%, CT 52%, TT 33%; C-allele frequency: 41%) than in population controls (P<0.01). Genotype distributions were similar among VF-positive/VF-negative patients (genotype: CC 18/11%, CT 52/53%, TT 30/36%; C-allele: 44/38%; P=0.29). Haplotype 46/1 frequency was remarkably similar when comparing VF-negative patients to those with <10% VF allele burden, but significantly higher in the presence of >10% VF allele burden (genotype: CC 11/13/38%, CT 53/56/38%, TT 36/31/24%; C-allele frequency: 38/41/57%; P<0.01). The clinical features of 46/1-positive and -negative ET were indistinguishable, including blood counts, rate of thrombosis/disease transformation and survival. We conclude that JAK2 haplotype 46/1 confers susceptibility to developing ET independent of VF mutational status and does not seem to further affect the clinical phenotype or prognosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pardanani A . JAK2 inhibitor therapy in myeloproliferative disorders: rationale, preclinical studies and ongoing clinical trials. Leukemia 2008; 22: 23–30.
Levine RL, Pardanani A, Tefferi A, Gilliland DG . Role of JAK2 in the pathogenesis and therapy of myeloproliferative disorders. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 673–683.
Delhommeau F, Dupont S, Della Valle V, James C, Trannoy S, Masse A et al. Mutation in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 2289–2301.
Tefferi A, Pardanani A, Lim KH, Abdel-Wahab O, Lasho TL, Patel J et al. TET2 mutations and their clinical correlates in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia and myelofibrosis. Leukemia 2009; 23: 905–911.
Carbuccia N, Murati A, Trouplin V, Brecqueville M, Adelaide J, Rey J et al. Mutations of ASXL1 gene in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 2009, e-pub ahead of print 16 July 2009; doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.141.
Lasho TL, Pardanani A, McClure RF, Mesa RA, Levine RL, Gilliland DG et al. Concurrent MPL515 and JAK2V617F mutations in myelofibrosis: chronology of clonal emergence and changes in mutant allele burden over time. Br J Haematol 2006; 135: 683–687.
Tiedt R, Hao-Shen H, Sobas MA, Looser R, Dirnhofer S, Schwaller J et al. Ratio of mutant JAK2-V617F to wild-type Jak2 determines the MPD phenotypes in transgenic mice. Blood 2008; 111: 3931–3940.
Pardanani A, Fridley BL, Lasho TL, Gilliland DG, Tefferi A . Host genetic variation contributes to phenotypic diversity in myeloproliferative disorders. Blood 2008; 111: 2785–2789.
Bellanne-Chantelot C, Chaumarel I, Labopin M, Bellanger F, Barbu V, De Toma C et al. Genetic and clinical implications of the Val617Phe JAK2 mutation in 72 families with myeloproliferative disorders. Blood 2006; 108: 346–352.
Saint-Martin C, Leroy G, Delhommeau F, Panelatti G, Dupont S, James C et al. Analysis of the ten-eleven translocation 2 (TET2) gene in familial myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2009; 114: 1628–1632.
Kralovics R, Guan Y, Prchal JT . Acquired uniparental disomy of chromosome 9p is a frequent stem cell defect in polycythemia vera. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 229–236.
Jones AV, Chase A, Silver RT, Oscier D, Zoi K, Wang YL et al. JAK2 haplotype is a major risk factor for the development of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 446–449.
Kilpivaara O, Mukherjee S, Schram AM, Wadleigh M, Mullally A, Ebert BL et al. A germline JAK2 SNP is associated with predisposition to the development of JAK2(V617F)-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 455–459.
Olcaydu D, Harutyunyan A, Jager R, Berg T, Gisslinger B, Pabinger I et al. A common JAK2 haplotype confers susceptibility to myeloproliferative neoplasms. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 450–454.
Thiele J, Vardiman JW, Pierre R, Brunning RD, Imbert M, Flandrin G . Chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds). World Health Organization classification of tumors: Tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Press: Lyon, France, 2001, 35–38.
Tefferi A, Lasho TL, Huang J, Finke C, Mesa RA, Li CY et al. Low JAK2V617F allele burden in primary myelofibrosis, compared to either a higher allele burden or unmutated status, is associated with inferior overall and leukemia-free survival. Leukemia 2008; 22: 756–761.
Wolanskyj AP, Lasho TL, Schwager SM, McClure RF, Wadleigh M, Lee SJ et al. JAK2 mutation in essential thrombocythaemia: clinical associations and long-term prognostic relevance. Br J Haematol 2005; 131: 208–213.
Kittur J, Knudson RA, Lasho TL, Finke CM, Gangat N, Wolanskyj AP et al. Clinical correlates of JAK2V617F allele burden in essential thrombocythemia. Cancer 2007; 109: 2279–2284.
Campbell PJ, Scott LM, Buck G, Wheatley K, East CL, Marsden JT et al. Definition of subtypes of essential thrombocythaemia and relation to polycythaemia vera based on JAK2 V617F mutation status: a prospective study. Lancet 2005; 366: 1945–1953.
Scott LM, Scott MA, Campbell PJ, Green AR . Progenitors homozygous for the V617F mutation occur in most patients with polycythemia vera, but not essential thrombocythemia. Blood 2006; 108: 2435–2437.
Pardanani A, Lasho TL, Finke C, Mesa RA, Hogan WJ, Ketterling RP et al. Extending Jak2V617F and MplW515 mutation analysis to single hematopoietic colonies and B and T lymphocytes. Stem Cells 2007; 25: 2358–2362.
Tefferi A, Lasho TL, Patnaik MM, Finke CM, Hussein K, Hogan WJ et al. JAK2 germline genetic variation affects disease susceptibility in primary myelofibrosis regardless of V617F mutational status: nullizygosity for the JAK2 46/1 haplotype is associated with inferior survival, doi: 10.10.1038/leu.2009.225.
Tefferi A, Gangat N, Wolanskyj A . The interaction between leukocytosis and other risk factors for thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia. Blood 2007; 109: 4105.
Olcaydu D, Skoda RC, Looser R, Li S, Cazzola M, Pietra D et al. The ‘GGCC’ haplotype of JAK2 confers susceptibility to JAK2 exon 12 mutation-positive polycythemia vera. Leukemia 2009, e-pub ahead of print 14 May 2009; doi:2010.1038/leu.2009.2110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pardanani, A., Lasho, T., Finke, C. et al. The JAK2 46/1 haplotype confers susceptibility to essential thrombocythemia regardless of JAK2V617F mutational status—clinical correlates in a study of 226 consecutive patients. Leukemia 24, 110–114 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.226
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.226
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Essential thrombocythaemia progression to the fibrotic phase is associated with a decrease in JAK2 and PDL1 levels
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
TERT and JAK2 polymorphisms define genetic predisposition to myeloproliferative neoplasms in Japanese patients
International Journal of Hematology (2019)
-
The JAK2 46/1 haplotype does not predispose to CALR-mutated myeloproliferative neoplasms
Annals of Hematology (2015)
-
Relationship between the 46/1 haplotype of the JAK2 gene and the JAK2 mutational status and allele burden, the initial findings, and the survival of patients with myelofibrosis
Annals of Hematology (2014)
-
The JAK2 46/1 haplotype (GGCC) in myeloproliferative neoplasms and splanchnic vein thrombosis: a pooled analysis of 26 observational studies
Annals of Hematology (2014)