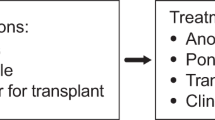
Abstract
For patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who become or are inherently resistant to imatinib therapy, including dose escalation, several important factors must be considered when deciding which strategy to attempt next. The second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) dasatinib and nilotinib offer improved potency and a high likelihood of success for these patients. Overall, the efficacy data are comparable for these two agents, and so physicians should consider the BCR-ABL mutation profile and the patient's history to make an educated decision on the best choice. Only a few BCR-ABL mutations seem to be less responsive to either nilotinib or dasatinib and it is recommended to choose the second-line TKI that has shown clinical activity against the specific mutation in these cases. For patients with all other mutations, and for patients with no mutations, it is recommended to choose the second-generation TKI based on the patient's disease history. It is important to choose an agent that minimizes the likelihood of exacerbating the patient's past tolerability issues to imatinib, or comorbid conditions. Here, we propose a treatment algorithm for imatinib-resistant patients based on BCR-ABL mutation status and patient history.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowley JD . Letter: a new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature 1973; 243: 290–293.
Bartram CR, de Klein A, Hagemeijer A, van Agthoven T, Geurts van Kessel A, Bootsma D et al. Translocation of c-ab1 oncogene correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature 1983; 306: 277–280.
Sawyers CL . Chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 1330–1340.
Sessions J . Chronic myeloid leukemia in 2007. J Manag Care Pharm 2007; 13: 4–7.
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV . The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000; 96: 3343–3356.
Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S, Segal GM, Fanning S et al. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med 1996; 2: 561–566.
Baccarani M, Saglio G, Goldman J, Hochhaus A, Simonsson B, Appelbaum F et al. Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2006; 108: 1809–1820.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN: clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Version (V.1.2010), 2009.
Hochhaus A, O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Druker BJ, Branford S, Foroni L et al. Six-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1054–1061.
O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Goldman JM, Hochhaus A, Hughes T, Radich JP et al. International Randomized Study of Interferon and STI571 (IRIS) 7-year follow-up: sustained survival, low rate of transformation and increased rate of major molecular response (MMR) in patients (pts) with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) treated with imatinib (IM). Blood 2008; 112: 76.
Hochhaus A, Kreil S, Corbin AS, La Rosée P, Müller MC, Lahaye T et al. Molecular and chromosomal mechanisms of resistance to imatinib (STI571) therapy. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2190–2196.
Hochhaus A, La Rosée P . Imatinib therapy in chronic myelogenous leukemia: strategies to avoid and overcome resistance. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1321–1331.
Apperley JF . Part I: mechanisms of resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet Oncol 2007; 8: 1018–1029.
Kantarjian HM, Larson RA, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, Mone M, Rudoltz M et al. Efficacy of imatinib dose escalation in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Cancer 2009; 115: 551–560.
Jabbour E, Kantarjian H, O'Brien S, Wierda W, Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G et al. Imatinib mesylate dose escalation is associated with durable responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia post cytogenetic failure on standard-dose imatinib therapy. Blood 2008; 113: 2154–2160.
Hughes T, Deininger M, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich J, Kaeda J et al. Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors—review and recommendations for ‘harmonizing’ current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 2006; 108: 28–37.
Jabbour E, Cortes J, O'Brien S, Rios MB, Giles F, Kantarjian H . Management of patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia: opportunities and challenges. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 2007; 7 (Suppl 2): S51–S57.
Cortes JE, Baccarani M, Guilhot F, Druker BJ, Branford S, Kim D-W et al. A phase III, randomized, open-label study of 400 versus 800 mg of imatinib mesylate (IM) in patients (pts) with newly diagnosed, previously untreated chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) using molecular endpoints: 1-year results of TOPS (Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Optimization and Selectivity) study. Blood 2008; 112: 130–131.
Baccarani M, Castagnetti F, Simonsson B, Porkka K, Haznedaroglu IC, Nagler A et al. Cytogenetic and molecular response to imatinib in high risk (Sokal) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): results of a European LeukemiaNet prospective study comparing 400 and 800 mg front-line. Blood 2008; 112: 75.
Golemovic M, Verstovsek S, Giles F, Cortes J, Manshouri T, Manley PW et al. AMN107, a novel aminopyrimidine inhibitor of Bcr-Abl, has in vitro activity against imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 4941–4947.
Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W, Bruggen J, Cowan-Jacob SW, Ray A et al. Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr-Abl. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 129–141.
Hantschel O, Rix U, Superti-Furga G . Target spectrum of the BCR-ABL inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib. Leuk Lymphoma 2008; 49: 615–619.
Cortes J, O'Brien S, Jones D, Ferrajoli A, Konopleva M, Borthakur G et al. Efficacy of nilotinib (formerly AMN107) in patients (Pts) with newly diagnosed, previously untreated Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in early chronic phase (CML-CP). Blood 2008; 112: 170.
Rosti G, Castagnetti F, Poerio A, Breccia M, Levato L, Capucci A et al. High and early rates of cytogenetic and molecular response with nilotinib 800 mg daily as first line treatment of Ph-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: results of a phase 2 trial of the GIMEMA CML Working Party. Blood 2008; 112: 73–74.
Shah NP, Tran C, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Sawyers CL . Overriding imatinib resistance with a novel ABL kinase inhibitor. Science 2004; 305: 399–401.
Cortes J, O'Brien S, Borthakur G, Jones D, Ravandi F, Koller C et al. Efficacy of dasatinib in patients (pts) with previously untreated chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in early chronic phase (CML-CP). Blood 2008; 112: 74.
Sprycel (dasatinib) [package insert]. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Princeton, NJ, 2007.
Sprycel (dasatinib) [package insert]. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Princeton, NJ, 2009.
Hochhaus A, Kantarjian HM, Baccarani M, Lipton JH, Apperley JF, Druker BJ et al. Dasatinib induces notable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of imatinib therapy. Blood 2007; 109: 2303–2309.
Cervantes F, Baccarani M, Lipton J, Matloub Y, Sinha R, Stone RM et al. Dasatinib long-term efficacy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) with resistance or intolerance to imatinib: A two-year update of the START-C study. Haematologica 2008; 93: 372.
Rousselot P, Corm S, Paquette R, Bleickardt E, Dejardin D, Kantarjian H et al. Dasatinib compared with high-dose imatinib in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) after failure of standard-dose imatinib—a two-year update of the START-R study. Haematologica 2008; 93: 48.
Shah NP, Kim DW, Kantarjian HMea . Dasatinib 50 or 70 mg BID compared to 100 or 140 mg QD in patients with CML in chronic phase (CP) who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib: one-year results of CA180034. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 358s.
Tasigna (nilotinib) [package insert] Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: East Hanover, NJ, 2007.
Kantarjian HM, Giles F, Bhalla KN, Larson RA, Gattermann N, Ottmann OG et al. Nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in chronic phase (CML-CP) with imatinib resistance or intolerance: 2-year follow-up results of a phase 2 study. Blood 2008; 112: 1112.
Jabbour E, Kantarjian HM, Baccarani M, le Coutre P, Haque A, Gallagher NJ et al. Minimal cross intolerance between nilotinib and imatinib in patients with imatinib-intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) or accelerated phase (CML-AP). Blood 2008; 112: 1103.
Hochhaus A, Müller MC, Cortes JE, Kim DW, Matloub Y, Ploughman L et al. Dasatinib efficacy after imatinib failure by dosing schedule and baseline BCR-ABL mutation status in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP). Haematologica 2008; 93: 371–372.
Hughes T, Saglio G, Branford S, Soverini S, Kim D, Müller M et al. Impact of baseline BCR-ABL mutations on response to nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in chronic phase (CML-CP). J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 4204–4210.
Bradeen HA, Eide CA, O'Hare T, Johnson KJ, Willis SG, Lee FY et al. Comparison of imatinib mesylate, dasatinib (BMS-354825), and nilotinib (AMN107) in an N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-based mutagenesis screen: high efficacy of drug combinations. Blood 2006; 108: 2332–2338.
Tanaka R, Kimura S . Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors for overriding Bcr-Abl/T315I: from the second to third generation. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2008; 8: 1387–1398.
Cortes J, Khoury HJ, Corm S, Nicolini F, Lipton J, Jones D et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous omacetaxine mepesuccinate in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia patients with the T315I mutation—results of an ongoing multicenter phase 2/3 study. Blood 2008; 112: 1112–1113.
Quintas-Cardama A, Kantarjian H, O'Brien S, Borthakur G, Bruzzi J, Munden R et al. Pleural effusion in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia treated with dasatinib after imatinib failure. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3908–3914.
Lipton JH, Sriharsha L, Bogomilsky S, Casciaro L, Keating A, Messner H et al. Pleural effusions in patients treated with dasatinib: results from two institutions, risk factors and management. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 680s.
Carpiuc KT, Stephens JM, Liou SY, Botteman MF . Incidence of grade 3/4 adverse events in imatinib resistant/intolerant chronic phase CML (CP-CML): a comparison of nilotinib and dasatinib. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 680s.
Hochhaus A, Neubauer A, Mueller MC, Napieralski S, Erben P, Bostel T et al. Sustained molecular responses with interferon alpha 2a maintenance therapy after imatinib plus IFN induction treatment for chronic phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2007; 110: 16a–17a.
Mahon F, Huguet F, Guilhot F, Legros L, Nicolini FE, Charbonnier A et al. Is it possible to stop imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia? An update from a French pilot study and first results from the multicentre ‘Stop Imatinib’ (STIM) study. Blood 2008; 112: 76.
Jain N, Kantarjian HM, Garcia-Manero G, Borthakur G, Ebarb T, Cortes JE . Synthetic tumor-specific breakpoint peptide vaccine in patients (pts) with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and minimal residual disease: a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 386s.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Michael Mandola, PhD (Articulate Science) for medical editorial assistance with this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabbour, E., Hochhaus, A., Cortes, J. et al. Choosing the best treatment strategy for chronic myeloid leukemia patients resistant to imatinib: weighing the efficacy and safety of individual drugs with BCR-ABL mutations and patient history. Leukemia 24, 6–12 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.193
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.193
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Application guide for omics approaches to cell signaling
Nature Chemical Biology (2015)
-
A coiled-coil mimetic intercepts BCR-ABL1 dimerization in native and kinase-mutant chronic myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2015)
-
Causes of resistance and treatment choices of second- and third-line treatment in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients
Annals of Hematology (2015)
-
Bosutinib: A Review of Its Use in Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
BioDrugs (2014)
-
Increased genomic instability may contribute to the development of kinase domain mutations in chronic myeloid leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2014)