Abstract
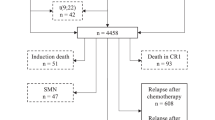
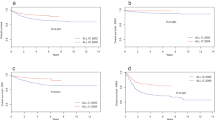
In the management of the childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), 5% of failures are due to induction death and treatment-related deaths in first complete remission. We retrospectively analyzed the incidence, pattern and causes of death and its risk factors for 896 children with ALL enrolled into five Austrian (A) Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster (BFM) trials between 1981 and 1999. The estimated 10-year cumulative incidence of death significantly decreased from 6±1% (n=16/268) in trials ALL-BFM-A 81 and ALL-A 84 to 2±1% (n=15/628) in trials ALL-BFM-A 86, 90 and 95 (P=0.006). A significant reduction of death was evident during induction therapy (2.2% in trials ALL-BFM-A 81 and ALL-A 84 and 0.2% in trials ALL-BFM-A 86, 90 and 95, P=0.001). Of 31 patients, 21 (68%) patients died from infectious and 10 (32%) from noninfectious complications. Treatment in trial ALL-BFM-A 81, infant age and female gender were independent predictors of an enhanced risk for death. Conclusively, we found a progressive reduction of death rates that may be explained by the increasing experience in specialized hemato-oncologic centers and improved supportive and intensive care. We also identified a distinct subset of patients who are especially prone to death and may need a special focus when receiving intense chemotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moricke A, Reiter A, Zimmermann M, Gadner H, Stanulla M, Dordelmann M et al. Risk-adjusted therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia can decrease treatment burden and improve survival: treatment results of 2169 unselected pediatric and adolescent patients enrolled in the trial ALL-BFM 95. Blood 2008; 111: 4477–4489.
Pui CH, Evans WE . Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 166–178.
Pui CH, Sandlund JT, Pei D, Campana D, Rivera GK, Ribeiro RC et al. Improved outcome for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of Total Therapy Study XIIIB at St Jude Children's Research Hospital. Blood 2004; 104: 2690–2696.
Silverman LB, Declerck L, Gelber RD, Dalton VK, Asselin BL, Barr RD et al. Results of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Consortium protocols for children with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (1981–1995). Leukemia 2000; 14: 2247–2256.
Atra A, Richards SM, Chessells JM . Remission death in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a changing pattern. Arch Dis Child 1993; 69: 550–554.
Hargrave DR, Hann II, Richards SM, Hill FG, Lilleyman JS, Kinsey S et al. Progressive reduction in treatment-related deaths in Medical Research Council childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia trials from 1980 to 1997 (UKALL VIII, X and XI). Br J Haematol 2001; 112: 293–299.
Rubnitz JE, Lensing S, Zhou Y, Sandlund JT, Razzouk BI, Ribeiro RC et al. Death during induction therapy and first remission of acute leukemia in childhood: the St. Jude experience. Cancer 2004; 101: 1677–1684.
Wheeler K, Chessells JM, Bailey CC, Richards SM . Treatment related deaths during induction and in first remission in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: MRC UKALL X. Arch Dis Child 1996; 74: 101–107.
Hurwitz CA, Silverman LB, Schorin MA, Clavell LA, Dalton VK, Glick KM et al. Substituting dexamethasone for prednisone complicates remission induction in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2000; 88: 1964–1969.
Liang DC, Hung IJ, Yang CP, Lin KH, Chen JS, Hsiao TC et al. Unexpected mortality from the use of E. coli L-asparaginase during remission induction therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Taiwan Pediatric Oncology Group. Leukemia 1999; 13: 155–160.
Christensen MS, Heyman M, Mottonen M, Zeller B, Jonmundsson G, Hasle H . Treatment-related death in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the Nordic countries: 1992–2001. Br J Haematol 2005; 131: 50–58.
Slats AM, Egeler RM, van der Does-van den Berg A, Korbijn C, Hahlen K, Kamps WA et al. Causes of death—other than progressive leukemia—in childhood acute lymphoblastic (ALL) and myeloid leukemia (AML): the Dutch Childhood Oncology Group experience. Leukemia 2005; 19: 537–544.
Pui CH, Boyett JM, Rivera GK, Hancock ML, Sandlund JT, Ribeiro RC et al. Long-term results of Total Therapy Studies 11, 12 and 13A for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia at St Jude Children's Research Hospital. Leukemia 2000; 14: 2286–2294.
Schrappe M . Risk-adapted stratification and treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Radiat Prot Dosim 2008; 132: 130–133.
Schrappe M, Reiter A, Zimmermann M, Harbott J, Ludwig WD, Henze G et al. Long-term results of four consecutive trials in childhood ALL performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 1995. Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster. Leukemia 2000; 14: 2205–2222.
Te Poele EM, de Bont ES, Marike Boezen H, Revesz T, Bokkerink JP, Beishuizen A et al. Dexamethasone in the maintenance phase of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treatment: is the risk of lethal infections too high? Eur J Cancer 2007; 43: 2532–2536.
Attarbaschi A, Mann G, Dworzak M, Urban C, Fink FM, Dieckmann K et al. Treatment results of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Austria—a report of 20 years' experience. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2002; 114: 148–157.
van der Does-van den Berg A, Bartram CR, Basso G, Benoit YC, Biondi A, Debatin KM et al. Minimal requirements for the diagnosis, classification, and evaluation of the treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in the ‘BFM Family’ Cooperative Group. Med Pediatr Oncol 1992; 20: 497–505.
Schrappe M, Reiter A, Ludwig WD, Harbott J, Zimmermann M, Hiddemann W et al. Improved outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia despite reduced use of anthracyclines and cranial radiotherapy: results of trial ALL-BFM 90. German-Austrian-Swiss ALL-BFM Study Group. Blood 2000; 95: 3310–3322.
Grigull L, Beier R, Schrauder A, Kirschner P, Loening L, Jack T et al. Invasive fungal infections are responsible for one-fifth of the infectious deaths in children with ALL. Mycoses 2003; 46: 441–446.
Attarbaschi A, Mann G, Panzer-Grumayer R, Rottgers S, Steiner M, Konig M et al. Minimal residual disease values discriminate between low and high relapse risk in children with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and an intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21: the Austrian and German acute lymphoblastic leukemia Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster (ALL-BFM) trials. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 3046–3050.
Igarashi S, Manabe A, Ohara A, Kumagai M, Saito T, Okimoto Y et al. No advantage of dexamethasone over prednisolone for the outcome of standard- and intermediate-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the Tokyo Children's Cancer Study Group L95-14 protocol. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 6489–6498.
Ito C, Evans WE, McNinch L, Coustan-Smith E, Mahmoud H, Pui CH et al. Comparative cytotoxicity of dexamethasone and prednisolone in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: 2370–2376.
Kager L, Lion T, Attarbaschi A, Koenig M, Strehl S, Haas OA et al. Incidence and outcome of TCF3-PBX1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Austrian children. Haematologica 2007; 92: 1561–1564.
Mitchell CD, Richards SM, Kinsey SE, Lilleyman J, Vora A, Eden TO . Benefit of dexamethasone compared with prednisolone for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results of the UK Medical Research Council ALL97 randomized trial. Br J Haematol 2005; 129: 734–745.
Pui CH, Relling MV, Downing JR . Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 1535–1548.
Belgaumi AF, Al-Bakrah M, Al-Mahr M, Al-Jefri A, Al-Musa A, Saleh M et al. Dexamethasone-associated toxicity during induction chemotherapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia is augmented by concurrent use of daunomycin. Cancer 2003; 97: 2898–2903.
Roberts CW, Walker W, Alexander J . Sex-associated hormones and immunity to protozoan parasites. Clin Microbiol Rev 2001; 14: 476–488.
Dordelmann M, Schrappe M, Reiter A, Zimmermann M, Graf N, Schott G et al. Down's syndrome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: clinical characteristics and treatment outcome in four consecutive BFM trials. Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster Group. Leukemia 1998; 12: 645–651.
Zwaan CM, Kaspers GJ, Pieters R, Hahlen K, Janka-Schaub GE, van Zantwijk CH et al. Different drug sensitivity profiles of acute myeloid and lymphoblastic leukemia and normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells in children with and without Down syndrome. Blood 2002; 99: 245–251.
Acknowledgements
We thank J Regelsberger, N Mühlegger and D Janousek for documentation and data management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Participating centers and investigators
Krankenhaus (KH) Dornbirn: B Ausserer; Landeskrankenhaus (LKH) Feldkirch: U Busch, G Müller; Universitäts-Kinderklinik Graz: R Kurz, Ch Urban; Universitäts-Kinderklinik Innsbruck: H Berger, F-M Fink, B Meister; LKH Klagenfurt: W Kaulfersch, H Messner; LKH Leoben: I Mutz; Allgemeines öffentliches KH der Barmherzigen Schwestern Linz: O Stöllinger; Landeskinderklinik Linz: W Tulzer, K Schmitt, T Ebetsberger; LKH Salzburg: H Grienberger, N and R Jones, J Rücker; Kardinal Schwarzenberg'sches KH Schwarzach: H Haas; LKH Steyr: R Ploier; St Anna Kinderspital Wien: H Gadner, ER Grümayer-Panzer, P Krepler, G Mann; Universitäts-Kinderklinik Wien: E Pichler, O Jürgenssen, I Slavc; Universitätsklinik für Blutgruppenserologie und Transfusionsmedizin Wien: P Höcker.
Immunophenotyping Institute of Immunology, Centre for Physiology, Pathophysiology and Immunology, Medical University of Vienna, Austria: W Knapp, WF Pickl.
Cytogenetic analyses Children's Cancer Research Institute, St Anna Children's Hospital, Vienna, Austria: OA Haas.
Molecular-genetic analyses Children's Cancer Research Institute, St Anna Children's Hospital, Vienna, Austria: Th Lion
Radiotherapy Department of Radiation Oncology, Medical University of Vienna, Austria: KH Kärcher, R Hawlicek, R Pötter and K Dieckmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prucker, C., Attarbaschi, A., Peters, C. et al. Induction death and treatment-related mortality in first remission of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a population-based analysis of the Austrian Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster study group. Leukemia 23, 1264–1269 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Causes of death and treatment-related mortality in newly diagnosed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment with Chinese Children’s Cancer Group study ALL-2015
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Acute pancreatitis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia correlates with L-asparaginase dose intensity
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
FIBCD1 ameliorates weight loss in chemotherapy-induced murine mucositis
Supportive Care in Cancer (2021)
-
The impact of pretreatment serum cobalamin and folate levels on complications and peripheral blood recovery during induction chemotherapy of leukemia: a cross-sectional study
Supportive Care in Cancer (2021)
-
Asparaginase-associated pancreatitis: a study on phenotype and genotype in the NOPHO ALL2008 protocol
Leukemia (2017)