Abstract
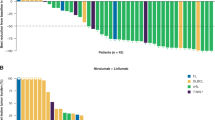
Rituximab has modest activity in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma but is associated with tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) release that can cause CLL proliferation and inhibit apoptosis. We examined whether disruption of TNF-α by etanercept improves response to rituximab in CLL. Eligible patients had previously treated CLL with performance status 0–3. Patients received etanercept 25 mg subcutaneously twice weekly (weeks 1–5) and rituximab 375 mg/m2 intravenously thrice weekly (weeks 2–5) using a phase I/II design. Primary end points were response and toxicity. The 36 enrolled patients had a median of two prior treatments; 50% were fludarabine refractory and 22% had del(17p13.1). Of the 34 response-evaluable patients, 10 (29%) responded, including 9 partial responses and 1 complete remission. Response was not affected by prior rituximab or fludarabine-refractory status, but no patients with del(17p13.1) responded. Median progression-free survival for responders was 9.0 months (range 1–43). Ten patients have had treatment-free intervals exceeding 12 months, including four who have remained untreated for 32, 43, 46 and 56 months. Adverse events were mild, including mild infusion reactions, transient cytopenias and grade 3 infections in 14% of the patients. The combination of etanercept and thrice weekly rituximab produces durable remissions in non-del(17p13.1) CLL patients and is well tolerated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Videbaek A . Some clinical aspects of leukaemia. Acta Haematol 1960; 24: 54–58.
Bigley RH, Koler RD, Pirofsky B, Osgood EE . A comparison of chronic leukemic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic subleukemic lymphocytic leukemia, and lymphocytic sarcoma. Cancer Chemother Rep 1962; 16: 231–234.
Travis LB, Curtis RE, Hankey BF, Fraumeni Jr JF . Second cancers in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992; 84: 1422–1427.
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Dohner H et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (IWCLL) updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group (NCI-WG) 1996 guidelines. Blood 2008; 111: 5446–5456.
Hamblin TJ . Prognostic markers in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Best Pract Res 2007; 20: 455–468.
Gowda A, Byrd JC . Use of prognostic factors in risk stratification at diagnosis and time of treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr Opin Hematol 2006; 13: 266–272.
O’Brien S, del Giglio A, Keating M . Advances in the biology and treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1995; 85: 307–318.
Rai KR, Peterson BL, Appelbaum FR, Kolitz J, Elias L, Shepherd L et al. Fludarabine compared with chlorambucil as primary therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1750–1757.
Leporrier M, Chevret S, Cazin B, Boudjerra N, Feugier P, Desablens B et al. Randomized comparison of fludarabine, CAP, and ChOP in 938 previously untreated stage B and C chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. Blood 2001; 98: 2319–2325.
Johnson S, Smith AG, Loffler H, Osby E, Juliusson G, Emmerich B et al. Multicentre prospective randomised trial of fludarabine versus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CAP) for treatment of advanced-stage chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. The French Cooperative Group on CLL. Lancet 1996; 347: 1432–1438.
Catovsky D, Richards S, Matutes E, Oscier D, Dyer MJ, Bezares RF et al. Assessment of fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (the LRF CLL4 Trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007; 370: 230–239.
Eichhorst BF, Busch R, Hopfinger G, Pasold R, Hensel M, Steinbrecher C et al. Fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide versus fludarabine alone in first-line therapy of younger patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 885–891.
Flinn IW, Neuberg DS, Grever MR, Dewald GW, Bennett JM, Paietta EM et al. Phase III trial of fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide compared with fludarabine for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: US Intergroup Trial E2997. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 793–798.
McLaughlin P, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Link BK, Levy R, Czuczman MS, Williams ME et al. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy for relapsed indolent lymphoma: half of patients respond to a four-dose treatment program. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2825–2833.
Nguyen DT, Amess JA, Doughty H, Hendry L, Diamond LW . IDEC-C2B8 anti-CD20 (rituximab) immunotherapy in patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and lymphoproliferative disorders: evaluation of response on 48 patients. Eur J Haematol 1999; 62: 76–82.
Hainsworth JD, Burris III HA, Morrissey LH, Litchy S, Scullin Jr DC, Bearden III JD et al. Rituximab monoclonal antibody as initial systemic therapy for patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2000; 95: 3052–3056.
Ladetto M, Bergui L, Ricca I, Campana S, Pileri A, Tarella C . Rituximab anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody induces marked but transient reductions of peripheral blood lymphocytes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients. Med Oncol 2000; 17: 203–210.
Huhn D, von Schilling C, Wilhelm M, Ho AD, Hallek M, Kuse R et al. Rituximab therapy of patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2001; 98: 1326–1331.
O’Brien SM, Kantarjian H, Thomas DA, Giles FJ, Freireich EJ, Cortes J et al. Rituximab dose-escalation trial in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 2165–2170.
Byrd JC, Murphy T, Howard RS, Lucas MS, Goodrich A, Park K et al. Rituximab using a thrice weekly dosing schedule in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma demonstrates clinical activity and acceptable toxicity. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 2153–2164.
Byrd JC, Peterson BL, Morrison VA, Park K, Jacobson R, Hoke E et al. Randomized phase 2 study of fludarabine with concurrent versus sequential treatment with rituximab in symptomatic, untreated patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9712 (CALGB 9712). Blood 2003; 101: 6–14.
Byrd JC, Rai K, Peterson BL, Appelbaum FR, Morrison VA, Kolitz JE et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine may prolong progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: an updated retrospective comparative analysis of CALGB 9712 and CALGB 9011. Blood 2005; 105: 49–53.
Wierda W, O’Brien S, Wen S, Faderl S, Garcia-Manero G, Thomas D et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab for relapsed and refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 4070–4078.
Shan D, Ledbetter JA, Press OW . Signaling events involved in anti-CD20-induced apoptosis of malignant human B cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2000; 48: 673–683.
Hofmeister JK, Cooney D, Coggeshall KM . Clustered CD20 induced apoptosis: src-family kinase, the proximal regulator of tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium influx, and caspase 3-dependent apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2000; 26: 133–143.
Golay J, Zaffaroni L, Vaccari T, Lazzari M, Borleri GM, Bernasconi S et al. Biologic response of B lymphoma cells to anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in vitro: CD55 and CD59 regulate complement-mediated cell lysis. Blood 2000; 95: 3900–3908.
Tangye SG, Raison RL . Human cytokines suppress apoptosis of leukaemic CD5+ B cells and preserve expression of bcl-2. Immunol Cell Biol 1997; 75: 127–135.
Adami F, Guarini A, Pini M, Siviero F, Sancetta R, Massaia M et al. Serum levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Eur J Cancer 1994; 30A: 1259–1263.
Suffredini AF, Reda D, Banks SM, Tropea M, Agosti JM, Miller R . Effects of recombinant dimeric TNF receptor on human inflammatory responses following intravenous endotoxin administration. J Immunol 1995; 155: 5038–5045.
Tsimberidou AM, Thomas D, O’Brien S, Andreeff M, Kurzrock R, Keating M et al. Recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor (p75) fusion protein Enbrel in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2002; 50: 237–242.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Grever M, Kay N, Keating MJ, O’Brien S et al. National Cancer Institute-sponsored Working Group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 1996; 87: 4990–4997.
Byrd JC, Smith L, Hackbarth ML, Flinn IW, Young D, Proffitt JH et al. Interphase cytogenetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia may predict response to rituximab. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 36–38.
Byrd JC, Gribben JG, Peterson BL, Grever MR, Lozanski G, Lucas DM et al. Select high-risk genetic features predict earlier progression following chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine and rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: justification for risk-adapted therapy. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 437–443.
Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Krober A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Cartron G, Dacheux L, Salles G, Solal-Celigny P, Bardos P, Colombat P et al. Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood 2002; 99: 754–758.
Simon R . Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1989; 10: 1–10.
Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, Chanana AD, Levy RN, Pasternack BS . Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1975; 46: 219–234.
Keating MJ, Flinn I, Jain V, Binet JL, Hillmen P, Byrd J et al. Therapeutic role of alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) in patients who have failed fludarabine: results of a large international study. Blood 2002; 99: 3554–3561.
Weng WK, Levy R . Two immunoglobulin G fragment C receptor polymorphisms independently predict response to rituximab in patients with follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 3940–3947.
Bowles JA, Weiner GJ . CD16 polymorphisms and NK activation induced by monoclonal antibody-coated target cells. J Immunol Methods 2005; 304: 88–99.
Lim LC, Koh LP, Tan P . Fatal cytokine release syndrome with chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in a 71-year-old patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 1962–1963.
Seifert G, Reindl T, Lobitz S, Seeger K, Henze G . Fatal course after administration of rituximab in a boy with relapsed all: a case report and review of literature. Haematologica 2006; 91 (6 Suppl): ECR23.
Byrd JC, Waselenko JK, Maneatis TJ, Murphy T, Ward FT, Monahan BP et al. Rituximab therapy in hematologic malignancy patients with circulating blood tumor cells: association with increased infusion-related side effects and rapid blood tumor clearance. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 791–795.
Cordone I, Masi S, Mauro FR, Soddu S, Morsilli O, Valentini T et al. p53 expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a marker of disease progression and poor prognosis. Blood 1998; 91: 4342–4349.
Grever MR, Lucas DM, Dewald GW, Neuberg DS, Reed JC, Kitada S et al. Comprehensive assessment of genetic and molecular features predicting outcome in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from the US Intergroup Phase III Trial E2997. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 799–804.
Farag SS, Flinn IW, Modali R, Lehman TA, Young D, Byrd JC . Fc gamma RIIIa and Fc gamma RIIa polymorphisms do not predict response to rituximab in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2004; 103: 1472–1474.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute P01 CA9542, The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society and The D Warren Brown Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woyach, J., Lin, T., Lucas, M. et al. A phase I/II study of rituximab and etanercept in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma. Leukemia 23, 912–918 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.385
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.385
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Co-expression of TNF receptors 1 and 2 on melanomas facilitates soluble TNF-induced resistance to MAPK pathway inhibitors
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Cytokine-driven loss of plasmacytoid dendritic cell function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2014)
-
Prognostic factors in CLL
Leukemia Supplements (2012)
-
Rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Advances in Therapy (2011)
-
LMP-420: a novel purine nucleoside analog with potent cytotoxic effects for CLL cells and minimal toxicity for normal hematopoietic cells
Leukemia (2010)