Abstract
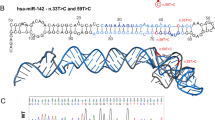
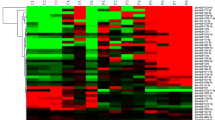
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) control the expression of protein-coding genes in normal hematopoietic cells and, consequently, aberrant expression may contribute to leukemogenesis. To identify miRNAs relevant to pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), we cloned 105 known and 8 new miRNA genes expressed in patients’ leukemia cells. Instead of known miRNA genes, new miRNA genes were not evolutionarily conserved. Quantification of 19 selected miRNA genes revealed an aberrant expression in ALL as compared with normal CD34+ cells (P⩽0.02); both upregulated (14/19) and downregulated (5/19) expressions were observed. Eight miRNAs were differentially expressed between MLL and non-MLL precursor B-ALL cases (P<0.05). Most remarkably, miR-708 was 250- up to 6500-fold higher expressed in 57 TEL-AML1, BCR-ABL, E2A-PBX1, hyperdiploid and B-other cases than in 20 MLL-rearranged and 15 T-ALL cases (0.0001< P<0.01), whereas the expression of miR-196b was 500-fold higher in MLL-rearranged and 800-fold higher in 5 of 15 T-ALL cases as compared with the expression level in the remaining precursor B-ALL cases (P<0.001). The expression did not correlate with the maturation status of leukemia cells based on immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor rearrangements, immunophenotype or MLL-fusion partner. In conclusion, we identified new miRNA genes and showed that miRNA expression profiles are ALL subtype-specific rather than linked to the differentiation stadium associated with these subtypes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–297.
Ambros V . MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 2003; 113: 673–676.
Chen CZ . MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1768–1771.
Available at http://www.sanger.ac.uk/Software/Rfam
Lee Y, Jeon K, Lee JT, Kim S, Kim VN . MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO J 2002; 21: 4663–4670.
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ . Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 2001; 409: 363–366.
Hutvagner G, McLachlan J, Pasquinelli AE, Balint E, Tuschl T, Zamore PD . A cellular function for the RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small temporal RNA. Science 2001; 293: 834–838.
Ketting RF, Fischer SE, Bernstein E, Sijen T, Hannon GJ, Plasterk RH . Dicer functions in RNA interference and in synthesis of small RNA involved in developmental timing in C. Elegans Genes Dev 2001; 15: 2654–2659.
Grishok A, Pasquinelli AE, Conte D, Li N, Parrish S, Ha I et al. Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C elegans developmental timing cell. Genes Dev 2001; 106: 23–34.
Meister G . miRNAs get an early start on translational silencing. Cell 2007; 131: 25–28.
Kim VN . MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 376–385.
He L, Hannon GJ . MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 522–531.
Chen K, Rajewsky N . The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 93–103.
Olsen PH, Ambros V . The lin-4 regulatory RNA controls developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans by blocking LIN-14 protein synthesis after the initiation of translation. Dev Biol 1999; 216: 671–680.
Ambros V . The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004; 431: 350–355.
Takamizawa J, Konishi H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Osada H, Endoh H et al. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 3753–3756.
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pagliarini R, Diaz Jr LA, Sjoblom T et al The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3687–3692.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 15524–15529.
Garzon R, Volinia S, Liu CG, Fernandez-Cymering C, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F et al. MicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 3183–3189.
Jongen-Lavrencic M, Sun SM, Dijkstra MK, Valk PJ, Lowenberg B . MicroRNA expression profiling in relation to the genetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 5078–5085.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005; 435: 828–833.
Pui CH, Evans WE . Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 166–178.
Stam RW, den Boer ML, Schneider P, Nollau P, Horstmann M, Beverloo HB et al. Targeting FLT3 in primary MLL-gene-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2005; 106: 2484–2490.
Jansen MW, Corral L, van der Velden VH, Panzer-Grumayer R, Schrappe M, Schrauder A et al. Immunobiological diversity in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia is related to the occurrence and type of MLL gene rearrangement. Leukemia 2007; 21: 633–641.
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP . An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2001; 294: 858–862.
Available at http://www.tbi.univie.ac.at/~ivo/RNA
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: e179.
Lim LP, Lau NC, Weinstein EG, Abdelhakim A, Yekta S, Rhoades MW et al. The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 991–1008.
Guenther MG, Jenner RG, Chevalier B, Nakamura T, Croce CM, Canaani E et al. Global and Hox-specific roles for the MLL1 methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 8603–8608.
Mullighan CG, Goorha S, Radtke I, Miller CB, Coustan-Smith E, Dalton JD et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic alterations in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2007; 446: 758–764.
van Zelm MC, van der Burg M, de Ridder D, Barendregt BH, de Haas EF, Reinders MJ et al. Ig gene rearrangement steps are initiated in early human precursor B cell subsets and correlate with specific transcription factor expression. J Immunol 2005; 175: 5912–5922.
Yu J, Wang F, Yang GH, Wang FL, Ma YN, Du ZW et al. Human microRNA clusters: genomic organization and expression profile in leukemia cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 349: 59–68.
Baskerville S, Bartel DP . Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 2005; 11: 241–247.
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007; 129: 1401–1414.
Lui WO, Pourmand N, Patterson BK, Fire A . Patterns of known and novel small RNAs in human cervical cancer. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6031–6043.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005; 435: 834–838.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Yilmaz OH, Valdez R, Theisen BK, Guo W, Ferguson DO, Wu H et al. Pten dependence distinguishes haematopoietic stem cells from leukaemia-initiating cells. Nature 2006; 441: 475–482.
Fazi F, Racanicchi S, Zardo G, Starnes LM, Mancini M, Travaglini L et al. Epigenetic silencing of the myelopoiesis regulator microRNA-223 by the AML1/ETO oncoprotein. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 457–466.
Nervi C, Fazi F, Grignani F . Oncoproteins, heterochromatin silencing and microRNAs: a new link for leukemogenesis. Epigenetics 2008; 3: 1–4.
Aboobaker AA, Tomancak P, Patel N, Rubin GM, Lai EC . Drosophila microRNAs exhibit diverse spatial expression patterns during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 18017–18022.
Ason B, Darnell DK, Wittbrodt B, Berezikov E, Kloosterman WP, Wittbrodt J et al. Differences in vertebrate microRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 14385–14389.
Kloosterman WP, Wienholds E, de Bruijn E, Kauppinen S, Plasterk RH . In situ detection of miRNAs in animal embryos using LNA-modified oligonucleotide probes. Nat Methods 2006; 3: 27–29.
Wienholds E, Kloosterman WP, Miska E, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Berezikov E, de Bruijn E et al. MicroRNA expression in zebrafish embryonic development. Science 2005; 309: 310–311.
Pieters R, den Boer ML, Durian M, Janka G, Schmiegelow K, Kaspers GJ et al. Relation between age, immunophenotype and in vitro drug resistance in 395 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia—implications for treatment of infants. Leukemia 1998; 12: 1344–1348.
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT . c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005; 435: 839–843.
Yekta S, Shih IH, Bartel DP . MicroRNA-directed cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science 2004; 304: 594–596.
Available at www.microRNA.org.
Available at http://pictar.bio.nyu.edu.
Available at www.targetscan.org.
Buske C, Humphries RK . Homeobox genes in leukemogenesis. Int J Hematol 2000; 71: 301–308.
Molnar A, Georgopoulos K . The Ikaros gene encodes a family of functionally diverse zinc finger DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol 1994; 14: 8292–8303.
Perdomo J, Holmes M, Chong B, Crossley M . Eos and pegasus, two members of the Ikaros family of proteins with distinct DNA binding activities. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 38347–38354.
Winandy S, Wu P, Georgopoulos K . A dominant mutation in the Ikaros gene leads to rapid development of leukemia and lymphoma. Cell 1995; 83: 289–299.
Dalla-Favera R, Bregni M, Erikson J, Patterson D, Gallo RC, Croce CM . Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1982; 79: 7824–7827.
Sheer D, Hiorns LR, Stanley KF, Goodfellow PN, Swallow DM, Povey S et al. Genetic analysis of the 15;17 chromosome translocation associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1983; 80: 5007–5011.
Szczepanski T, van der Velden VH, van Dongen JJ . Classification systems for acute and chronic leukaemias. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2003; 16: 561–582.
Acknowledgements
We highly appreciate the contribution of CZ Chen (Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Stanford University, USA) for sharing knowledge and technologies to clone miRNAs, for performing computational analyses of miRNA structures as well as for discussing study results. We also thank the members of the COALL study group (headed by GE Janka-Schaub, Hamburg, Germany) and the Interfant study group (headed by R Pieters, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, NL) for supporting this study with patient samples. We are grateful to MWJC Jansen (Department of Immunology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, NL) for providing the maturation status of MLL-rearranged cases. This study was financially supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (Program Grant EUR 2005-3662; MLdB/RP), The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO-Vidi Grant; MLdB) and the Baxter foundation (Chen CZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schotte, D., Chau, J., Sylvester, G. et al. Identification of new microRNA genes and aberrant microRNA profiles in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 23, 313–322 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.286
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.286
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The advances of E2A-PBX1 fusion in B-cell acute lymphoblastic Leukaemia
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
miR-1975 serves as an indicator of clinical severity upon influenza infection
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (2021)
-
CCN2 (Cellular Communication Network factor 2) in the bone marrow microenvironment, normal and malignant hematopoiesis
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
MicroRNA-708 is a novel regulator of the Hoxa9 program in myeloid cells
Leukemia (2020)
-
Circulating microRNAs as minimal residual disease biomarkers in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)