Abstract
Objective:
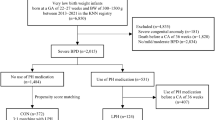
To assess whether mortality in patients with evolving bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD, defined as ⩾28 days of oxygen exposure with lung disease) is independently associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and surgery.
Study Design:
Single institution retrospective birth cohort of preterm infants with gestational age (GA) 230/7 to 366/7 weeks, and evolving BPD delivered between 2001 and 2014. Surgery was classified as minor or major using published criteria. Mortality was analyzed by stepwise logistic regression analysis.
Results:
Among 577 patients with evolving BPD, 33 (6%) died prior to discharge. Mortality decreased with GA (adjusted odds ratio (aOR): 0.69; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.55, 0.87), birth weight Z-score (aOR: 0.69, 95% CI: 0.47, 0.996) and increased with PAH (aOR: 30, 95% CI: 2.1, 415), major surgery (aOR; 2.8, 95% CI: 1.3, 6.3), and PAH and surgery (aOR: 10.3, 95% CI: 2.5, 42.1).
Conclusion:
Among preterm patients with evolving BPD, PAH and surgery are independently associated with mortality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen EA, Schmidt B . Epidemiology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 2014; 100 (3): 145–157.
An HS, Bae EJ, Kim GB, Kwon BS, Beak JS, Kim EK et al. Pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Korean Circ J 2010; 40 (3): 131–136.
Slaughter JL, Pakrashi T, Jones DE, South AP, Shah TA . Echocardiographic detection of pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia requiring prolonged positive pressure ventilation. J Perinatol 2011; 31 (10): 635–640.
Kim DH, Kim HS, Choi CW, Kim EK, Kim BI, Choi JH . Risk factors for pulmonary artery hypertension in preterm infants with moderate or severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Neonatology 2012; 101 (1): 40–46.
Check J, Gotteiner N, Liu X, Su E, Porta N, Steinhorn R et al. Fetal growth restriction and pulmonary hypertension in premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol 2013; 33 (7): 553–557.
Kwon HW, Kim HS, An HS, Kwon BS, Kim GB, Shin SH et al. Long-term outcomes of pulmonary hypertension in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Neonatology 2016; 110 (3): 181–189.
Murthy K, Savani RC, Lagatta JM, Zaniletti I, Wadhawan R, Truog W et al. Predicting death or tracheostomy placement in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol 2014; 34 (7): 543–548.
Memtsoudis SG, Ma Y, Chiu YL, Walz JM, Voswinckel R, Mazumdar M . Perioperative mortality in patients with pulmonary hypertension undergoing major joint replacement. Anesth Analg 2010; 111 (5): 1110–1116.
Shukla AC, Almodovar MC . Anesthesia considerations for children with pulmonary hypertension. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2010; 11 (2 Suppl): S70–S73.
Twite MD, Friesen RH . The anesthetic management of children with pulmonary hypertension in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. Anesthesiol Clin 2014; 32 (1): 157–173.
Salehi A . Pulmonary hypertension: a review of pathophysiology and anesthetic management. Am J Ther 2012; 19 (5): 377–383.
Pilkington SA, Taboada D, Martinez G . Pulmonary hypertension and its management in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery. Anaesthesia 2015; 70 (1): 56–70.
Carmosino MJ, Friesen RH, Doran A, Ivy DD . Perioperative complications in children with pulmonary hypertension undergoing noncardiac surgery or cardiac catheterization. Anesth Analg 2007; 104 (3): 521–527.
Morriss FH Jr, Saha S, Bell EF, Colaizy TT, Stoll BJ, Hintz SR et al. Surgery and neurodevelopmental outcome of very low-birth-weight infants. JAMA Pediatr 2014; 168 (8): 746–754.
Jensen EA, Munson DA, Zhang H, Blinman TA, Kirpalani H . Anti-gastroesophageal reflux surgery in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol 2015; 50 (6): 584–587.
Hintz SR, Van Meurs KP, Perritt R, Poole WK, Das A, Stevenson DK et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of premature infants with severe respiratory failure enrolled in a randomized controlled trial of inhaled nitric oxide. J Pediatr. 2007; 151 (1): 16–22.
Oster ME, Lee KA, Honein MA, Riehle-Colarusso T, Shin M, Correa A . Temporal trends in survival among infants with critical congenital heart defects. Pediatrics 2013; 131 (5): e1502–e1508.
Mourani PM, Sontag MK, Younoszai A, Miller JI, Kinsella JP, Baker CD et al. Early pulmonary vascular disease in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015; 191 (1): 87–95.
Olsen IE, Groveman SA, Lawson ML, Clark RH, Zemel BS . New intrauterine growth curves based on United States data. Pediatrics 2010; 125 (2): e214–e224.
Lillehei CW, Gauvreau K, Jenkins KJ . Risk adjustment for neonatal surgery: a method for comparison of in-hospital mortality. Pediatrics 2012; 130 (3): e568–e574.
Bhat R, Salas AA, Foster C, Carlo WA, Ambalavanan N . Prospective analysis of pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2012; 129 (3): e682–e689.
Khemani E, McElhinney DB, Rhein L, Andrade O, Lacro RV, Thomas KC et al. Pulmonary artery hypertension in formerly premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical features and outcomes in the surfactant era. Pediatrics 2007; 120 (6): 1260–1269.
Hilgendorff A, Apitz C, Bonnet D, Hansmann G . Pulmonary hypertension associated with acute or chronic lung diseases in the preterm and term neonate and infant. The European Paediatric Pulmonary Vascular Disease Network, endorsed by ISHLT and DGPK. Heart 2016; 102 (Suppl 2): ii49–ii56.
Abman SH, Hansmann G, Archer SL, Ivy DD, Adatia I, Chung WK et al. Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension: Guidelines From the American Heart Association and American Thoracic Society. Circulation 2015; 132 (21): 2037–2099.
Nagiub M, Lee S, Guglani L . Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: systematic review of literature and a proposed algorithm for assessment. Echocardiography 2015; 32 (5): 819–833.
Acknowledgements
Author contributions
Lindsay DeVries: She wrote the first draft of the manuscript. She conceptualized and designed the study. She reviewed data from the database, medical records, participated in the interpretation of the data, critically reviewed, revised and approved the final manuscript. Roy J. Heyne: He conceptualized and designed the study. He participated in the interpretation of the data, critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Claudio Ramaciotti: He conceptualized and designed the study. He reviewed and interpreted echocardiograms using pre-specified criteria and echocardiogram readings for patients with unavailable echocardiograms, participated in the interpretation of the data, critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Steven Brown: He conceptualized and designed the study. He completed all statistical analyses, participated in the interpretation of the data and critically reviewed the manuscript. Mambarambath A. Jaleel: He conceptualized and designed the study. He participated in the interpretation of the data, critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Vishal Kapadia: He conceptualized and designed the study. He participated in the interpretation of the data, critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Patti J. Burchfield: She collected and entered data into the database and extracted the data for this study; she participated in the interpretation of the data, critically reviewed the manuscript and approved the final manuscript. Luc P Brion: He conceptualized and designed the study. He participated in the interpretation of the data, critically reviewed, revised and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Preliminary results were presented at the following meetings: DeVries LD, Jaleel M, Kapadia V, Heyne R, Brion LP. Relationship between Pulmonary Hypertension and Outcomes among Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Who Undergo Surgery. (a) Poster presentation at the 86th Perinatal & Developmental Medicine Symposium ‘Perinatal Genomics’ Aspen, Colorado, 4–7 June, 2015. (b) Platform presentation at the AAP Section on Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine 22nd South Central Conference on Perinatal Research, Austin, TX, October 2015. (c) Poster presentation at the 2016 Southern Society for Pediatric Research, New Orleans, LA, USA 18 February 2016. (d) Poster presentation at the 2016 Pediatric Academic Societies Annual Meeting, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3 May 2016.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Perinatology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DeVries, L., Heyne, R., Ramaciotti, C. et al. Mortality among infants with evolving bronchopulmonary dysplasia increases with major surgery and with pulmonary hypertension. J Perinatol 37, 1043–1046 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2017.89
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2017.89