Abstract
Objective:
The objective of this study is to analyze the white blood cell changes that occur after a transfusion of red blood cells in order to identify a subclinical inflammatory response in neonates.
Study Design:
Retrospective analysis of infants who received a red blood cell transfusion in an intensive care nursery. White blood cell results within 24 h pre- to 48 h post-transfusion were collected and analyzed. Statistical analysis included ANOVA, T-test, Mann–Whitney U test, Pearson's correlation and multivariable linear regression.
Result:
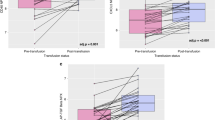
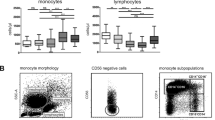
Monocytes (P=0.02) and bands (P=0.035) were increased post-transfusion. There were no differences in monocytes (P=0.46) or bands (P=0.56) between groups who did or did not have blood cultures obtained. There was no difference in monocytes between groups who did or did not have sepsis (P=0.88).
Conclusion:
We identified an elevation in monocytes and bands in the 48 h following a transfusion in premature infants. Our findings support a possible pro-inflammatory response related to transfusion of red blood cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen RD, Lambert DK, Henry E, Wiedmeier SE, Snow GL, Baer VL et al. Is ‘transfusion-associated necrotizing enterocolitis’ an authentic pathogenic entity? Transfusion 2009; 50: 1106–1112.
Demirel G, Celik IH, Aksoy HT, Erdeve O, Oguz SS, Uras N et al. Transfusion-associated necrotising enterocolitis in very low birth weight premature infants. Transfus Med 2012; 22: 332–337.
Paul DA, Mackley A, Novitsky A, Zhao Y, Brooks A, Locke RG . Increased odds of necrotizing enterocolitis after transfusion of red blood cells in premature infants. Pediatrics 2011; 127: 635–641.
Singh R, Visintainer PF, Frantz ID, Shah BL, Meyer KM, Favila SA et al. Association of necrotizing enterocolitis with anemia and packed red blood cell transfusions in preterm infants. J Perinatol 2011; 31: 176–182.
El-Dib M, Narang S, Lee E, Massaro AN, Aly H . Red blood cell transfusion, feeding and necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. J Perinatol 2011; 31: 183–187.
Mohamed A, Shah PS . Transfusion associated necrotizing enterocolitis: a meta-analysis of observational data. Pediatrics 2012; 129: 529–540.
La Gamma EF, Blau J . Transfusion-related acute gut injury: feeding, flora, flow, and barrier defense. Semin Perinatol 2012; 36: 294–305.
Hébert PC, Wells G, Tweeddale M, Martin C, Marshall J, Pham B et al. Does transfusion practice affect mortality in critically ill patients? Transfusion Requirements in Critical Care (TRICC) Investigators and the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997; 155: 1618–1623.
Aiboshi J, Moore EE, Ciesla DJ, Silliman CC . Blood transfusion and the two-insult model of post-injury multiple organ failure. Shock 2001; 15: 302–306.
Tinmouth A, Fergusson D, Yee IC, Hébert PC . Clinical consequences of red cell storage in the critically ill. Transfusion 2006; 46: 2014–2027.
Hotoura E, Giapros V, Kostoula A, Spyrou P, Andronikou S . Pre-inflammatory mediators and lymphocyte subpopulations in preterm neonates with sepsis. Inflammation 2012; 35: 1094–1101.
Groselj-Grenc M, Ihan A, Derganc M . Neutrophil and monocyte CD64 and CD163 expression in critically ill neonates and children with sepsis: comparison of fluorescence intensities and calculated indexes. Mediators Inflamm 2008; 2008: 202646.
Christensen RD, Lambert DK, Gordon PV, Baer VL, Gerday E, Henry E . Neonates presenting with bloody stools and eosinophilia can progress to two different types of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Perinatol 2012; 32: 874–879.
Patel L, Garvey B, Arnon S, Roberts IA . Eosinophilia in newborn infants. Acta Paediatr 1994; 83: 797–801.
Juul SE, Haynes JW, McPherson RJ . Evaluation of eosinophilia in hospitalized preterm infants. J Perinatol 2005; 25: 182–188.
Shannon KM, Keith JF, Mentzer WC, Ehrenkranz RA, Brown MS, Widness JA et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis and reduces erythrocyte transfusions in very low birth weight preterm infants. Pediatrics 1995; 95: 1–8.
Yankowitz J, Weiner CP . Blood transfusion for haemolytic disease as a cause of leukocytosis in the fetus. Prenat Diagn 1996; 16: 719–722.
Frey B . Transfusion in premature infants impairs production and/or release of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. J Paediatr Child Health 2002; 38: 265–267.
Wright IM, Skinner AM . Post-transfusion white cell count in the sick preterm neonate. J Paediatr Child Health 2001; 37: 44–46.
Fenwick JC, Cameron M, Naiman SC, Haley LP, Ronco JJ, Wiggs BR et al. Blood transfusion as a cause of leucocytosis in critically ill patients. Lancet 1994; 344: 855–856.
Smythies LE, Maheshwari A, Clements R, Eckhoff D, Novak L, Vu HL et al. Mucosal IL-8 and TGF-beta recruit blood monocytes: evidence for cross-talk between the lamina propria stroma and myeloid cells. J Leukoc Biol 2006; 80: 492–499.
Hirano K, Morinobu T, Kim H, Hiroi M, Ban R, Ogawa S et al. Blood transfusion increases radical promoting non-transferrin bound iron in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2001; 84: F188–F193.
Dani C, Martelli E, Bertini G, Pezzati M, Rossetti M, Buonocore G et al. Effect of blood transfusions on oxidative stress in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2004; 89: F408–F411.
Hod EA, Zhang N, Sokol SA, Wojczyk BS, Francis RO, Ansaldi D et al. Transfusion of red blood cells after prolonged storage produces harmful effects that are mediated by iron and inflammation. Blood 2010; 115: 4284–4292.
Stark MJ, Keir AK, Andersen CC . Does non-transferrin bound iron contribute to transfusion related immune-modulation in preterms? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2013; 98: F424–F429.
Remon J, Kampanatkosol R, Kaul RR, Muraskas JK, Christensen RD, Maheshwari A . Acute drop in blood monocyte count differentiates NEC from other causes of feeding intolerance. J Perinatol 2014; 34: 549–554.
MohanKumar K, Kaza N, Jagadeeswaran R, Garzon SA, Bansal A, Kurundkar AR et al. Gut mucosal injury in neonates is marked by macrophage infiltration in contrast to pleomorphic infiltrates in adult: evidence from an animal model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012; 303: G93–G102.
Filias A, Theodorou GL, Mouzopoulou S, Varvarigou AA, Mantagos S, Karakantza M . Phagocytic ability of neutrophils and monocytes in neonates. BMC Pediatr 2011; 11: 29.
Hotoura E, Giapros V, Kostoula A, Spirou P, Andronikou S . Tracking changes of lymphocyte subsets and pre-inflammatory mediators in full-term neonates with suspected or documented infection. Scand J Immunol 2011; 73: 250–255.
Lambert DK, Christensen RD, Baer VL, Henry E, Gordon PV, Besner GE et al. Fulminant necrotizing enterocolitis in a multihospital healthcare system. J Perinatol 2012; 32: 194–198.
Christensen RD, Jensen J, Maheshwari A, Henry E . Reference ranges for blood concentrations of eosinophils and monocytes during the neonatal period defined from over 63 000 records in a multihospital health-care system. J Perinatol 2010; 30: 540–545.
Karayalcin G, Khanijou A, Kim KY, Aballi AJ, Lanzkowsky P . Monocytosis in congenital syphilis. Am J Dis Child 1977; 131: 782–783.
Wolach B, Bogger-Goren S, Whyte R . Perinatal hematological profile of newborn infants with candida antenatal infections. Biol Neonate 1991; 59: 5–12.
Bux J, Kissel K, Nowak K, Spengel U, Mueller-Eckhardt C . Autoimmune neutropenia: clinical and laboratory studies in 143 patients. Ann Hematol 1991; 63: 249–252.
L’Esperance P, Brunning R, Deinard AS, Park BY, Biggar WD, Good RA . Congenital neutropenia: impaired maturation with diminished stem-cell input. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser 1975; 11: 59–65.
Acknowledgements
The findings and outcomes within this manuscript represent original research from the authors. This material has not been previously published and has not been, nor will be, submitted for publication elsewhere; pending consideration from the Journal of Perinatology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellefson, A., Locke, R., Zhao, Y. et al. Increased monocytes and bands following a red blood cell transfusion. J Perinatol 36, 57–60 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2015.153
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2015.153
This article is cited by
-
The role of absolute monocyte counts in predicting severity of necrotizing enterocolitis
Journal of Perinatology (2020)
-
Outcomes after implementing restrictive blood transfusion criteria in extremely premature infants
Journal of Perinatology (2019)