Abstract
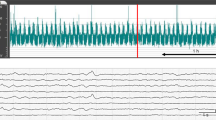
The use of amplitude-integrated electroencephalography (aEEG) to assess brain function and detect seizures has been increasing worldwide. Results from previous studies have demonstrated that seizure patterns can be recognized as transient rises on aEEG traces. We report here a case of an infant with neonatal seizures that showed paradoxical transient drops on aEEG traces. The ictal EEG showed initial low-amplitude fast rhythmic activity followed by epileptic recruiting rhythms and high-voltage slow waves. Therefore, downward patterns on aEEG traces should be recognized as suspected seizure patterns.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hellström-Westas L, Rosén I . Continuous brain-function monitoring: state of the art in clinical practice. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2006; 11 (6): 503–511.
de Vries LS, Toet MC . Amplitude integrated electroencephalography in the full-term newborn. Clin Perinatol 2006; 33 (3): 619–632 vi.
El-Dib M, Chang T, Tsuchida TN, Clancy RR . Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography in neonates. Pediatr Neurol 2009; 41 (5): 315–326.
Murray DM, Boylan GB, Ali I, Ryan CA, Murphy BP, Connolly S . Defining the gap between electrographic seizure burden, clinical expression and staff recognition of neonatal seizures. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008; 93 (3): F187–191.
Rosén I . The physiological basis for continuous electroencephalogram monitoring in the neonate. Clin Perinatol 2006; 33 (3): 593–611 v.
Watanabe K, Hara K, Iwase K . The evolution of neurophysiological features in holoprosencephaly. Neuropadiatrie 1976; 7 (1): 19–41.
Demyer W, White PT . EEG in holoprosencephaly (Arhinencephaly). Arch Neurol 1964; 11: 507–520.
Shah KN, Rajadhyaksha S, Shah VS, Wakde M . EEG recognition of holoprosencephaly and Aicardi syndrome. Indian J Pediatr 1992; 59 (1): 103–108.
Dubourg C, Bendavid C, Pasquier L, Henry C, Odent S, David V . Holoprosencephaly. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2007; 2: 8.
Yang MT, Lee WT, Peng SS, Lin HC, Tseng CL, Liang JS et al. The roles of electroencephalography and neuroimaging in children with holoprosencephaly. Epileptic Disord 2004; 6 (3): 173–180.
Plawner LL, Delgado MR, Miller VS, Levey EB, Kinsman SL, Barkovich AJ et al. Neuroanatomy of holoprosencephaly as predictor of function: beyond the face predicting the brain. Neurology 2002; 59 (7): 1058–1066.
Hellström-Westas L, Vries LSD, Rosen I . An Atlas of Amplitude-Integrated EEGs in the Newborn. The Parthenon Publishing Group: New York, 2003 pp. 51–57.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs T Negoro and H Yamamoto for critical comments on the interpretation of EEG results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, M., Kidokoro, H., Sugiyama, Y. et al. Paradoxical downward seizure pattern on amplitude-integrated electroencephalogram. J Perinatol 34, 642–644 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.84
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.84