Abstract
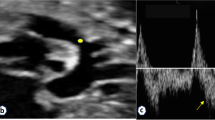
A 22-week fetus presented with a large left ventricular aneurysm, 24 × 21 × 18 mm in size, detected by abnormal four-chamber view, and severe fetal hydrops with pericardial effusion, ascites and skin edema. The aneurysm was thin-walled, hypokinetic, and had enlarged with gestational age, causing compression of the lung. Although the left ventricular function had progressively impaired as expressed by increase in Tei index, hydrops had resolved by 32 weeks of gestation, probably because of maternal digoxin therapy and successful compensation by the right ventricle, as represented by retrograde blood flow in the distal aortic arch via the patent arterial duct. Because of the significant risk of severe cardiorespiratory failure, we transported the mother to a neonatal cardiac surgical center at 38 weeks of gestation. Indeed, the baby showed severe cardiopulmonary failure after birth, showing 100% of cardiothoracic ratio on the chest X-ray film, but was saved by the successful Dor procedure, including surgical resection of the aneurysm at 10 h of life. In this case, serial echocardiographic evaluation can allow us to monitor the hemodynamics and lead to successful postnatal management.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hornberger LK, Allan LD, Sharland G (eds) Text of Fetal Cardiology. Greenwich Medical Media: London, 2000.
Ohlow MA . Congenital left ventricular aneurysms and diverticula: definition, pathophysiology, clinical relevance and treatment. Cardiology 2006; 106: 63–72.
Weichert J, Chiriac A, Axt-Fliedner R . Fetal diagnosis of left ventricular aneurysm of the free wall and the interventricular septum: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2010; 23: 1510–1515.
Cavalle-Garrido T, Cloutier A, Harder J, Boutin C, Smallhorn JF . Evolution of fetal ventricular aneurysms and diverticula of the heart: an echocardiographic study. Am J Perinatol 1997; 14: 393–400.
McElhinney DB, Silverman NH . Left ventricular aneurysm in the fetus: a diagnosis with a mixed prognosis. Cardiol Young 1999; 9: 123–126.
Chaubal N, Dighe M, Shah M, Chaubal J, Raghavan J . Congenital left ventricular aneurysm: prenatal sonographic diagnosis. J Ultrasound Med 2004; 23: 125–128.
El Kady D, Gerscovich EO, Moon-Grady A, Towner D, McGahan JP, Rhee-Morris L et al. Congenital cardiac left ventricular aneurysm with pericardial effusion: early prenatal diagnosis and intervention. J Ultrasound Med 2005; 24: 1011–1015.
Matias A, Fredouille C, Nesmann C, Azancot A . Prenatal diagnosis of left ventricular aneurysm: a report of three cases and a review. Cardiol Young 1999; 9: 175–184.
Sepulveda W, Drysdale K, Kyle PM, McNeal AD, Moore IE . Congenital left ventricular aneurysm causing hydrops fetalis: prenatal diagnosis with color Doppler ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 1996; 15: 327–331.
Bernasconi A, Delezoide AL, Menez F, Vuillard E, Oury JF, Azancot A . Prenatal rupture of a left ventricular diverticulum: a case report and review of the literature. Prenat Diagn 2004; 24: 504–507.
Gembruch U, Steil E, Redel DA, Hansmann M . Prenatal diagnosis of a left ventricular aneurysm. Prenat Diagn 1990; 10: 203–209.
Hornberger LK, Dalvi B, Benacerraf BR . Prenatal sonographic detection of cardiac aneurysms and diverticula. J Ultrasound Med 1994; 13: 967–970.
Aoki M, Harada K, Ogawa M, Tanaka T . Quantitative assessment of right ventricular function using doppler tissue imaging in fetuses with and without heart failure. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2004; 17: 28–35.
Dor V . The endoventricular circular patch plasty (‘Dor procedure’) in ischemic akinetic dilated ventricles. Heart Fail Rev 2001; 6: 187–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirose, A., Maeno, Y., Suda, K. et al. Serial hemodynamic assessment using Doppler echocardiography in a fetus with left ventricular aneurysm presented as fetal hydrops. J Perinatol 33, 486–489 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2012.93
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2012.93