Abstract
Objective:
We prospectively evaluated the rate of postnatal cytomegalovirus (CMV) transmission through breast milk in extremely premature infants to address the impact of CMV infection on preterm infants during lactation.
Study Design:
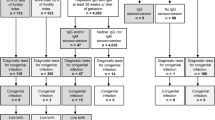
A total of 25 mothers and 27 infants (two sets of twins) with birth weights <1000 g and/or gestational ages <28 weeks were enrolled in the study. They were mostly fed frozen–thawed breast milk. Breast milk, serum and urine samples were collected every 2 weeks and screened for CMV infection using the real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Result:
All of the 21 CMV-seropositive mothers had detectable CMV DNA in their breast milk, with a peak at 4 to 6 weeks postpartum. CMV infection was confirmed in only one infant (4.3%) who displayed almost no clinical symptoms.
Conclusion:
At our institutes, we mainly use frozen–thawed breast milk. We found low CMV transmission rates even in extremely premature infants, and the CMV-positive infant did not develop serious symptoms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mocarski ES, Shenk T, Pass RF . Cytomegalovirus. In: Knipe DM, Howlley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, et al. (eds). Fields Virology, 5 edn, vol. 2. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2006, pp 2701–2772.
Pass RF, Stagno S, Myers GJ, Alford CA . Outcome of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: results of long-term longitudinal follow-up. Pediatrics 1980; 66 (5): 758–762.
Demmler GJ . Infectious Diseases Society of America and Centers for Disease Control. Summary of a workshop on surveillance for congenital cytomegalovirus disease. Rev Infect Dis 1991; 13 (2): 315–329.
Gehrz RC, Linner KM, Christianson WR, Ohm AE, Balfour Jr HH . Cytomegalovirus infection in infancy: virological and immunological studies. Clin Exp Immunol 1982; 47 (1): 27–33.
Hamprecht K, Maschmann J, Jahn G, Poets CF, Goelz R . Cytomegalovirus transmission to preterm infants during lactation. J Clin Virol 2008; 41 (3): 198–205.
Luck S, Sharland M . Postnatal cytomegalovirus: innocent bystander or hidden problem? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2009; 94 (1): F58–F64.
Kurath S, Halwachs-Baumann G, Muller W, Resch B . Transmission of cytomegalovirus via breast milk to the prematurely born infant: a systematic review. Clin Microbiol Infect 2010; 16 (8): 1172–1178.
Hirota K, Muraguchi K, Watabe N, Okumura M, Kozu M, Takahashi K et al. Prospective study on maternal, intrauterine, and perinatal infections with cytomegalovirus in Japan during 1976–1990. J Med Virol 1992; 37 (4): 303–306.
Yasuda A, Kimura H, Hayakawa M, Ohshiro M, Kato Y, Matsuura O et al. Evaluation of cytomegalovirus infections transmitted via breast milk in preterm infants with a real-time polymerase chain reaction assay. Pediatrics 2003; 111 (6 Part 1): 1333–1336.
Vochem M, Hamprecht K, Jahn G, Speer CP . Transmission of cytomegalovirus to preterm infants through breast milk. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1998; 17 (1): 53–58.
Hamprecht K, Maschmann J, Vochem M, Dietz K, Speer CP, Jahn G . Epidemiology of transmission of cytomegalovirus from mother to preterm infant by breastfeeding. Lancet 2001; 357 (9255): 513–518.
Maschmann J, Hamprecht K, Dietz K, Jahn G, Speer CP . Cytomegalovirus infection of extremely low-birth weight infants via breast milk. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 33 (12): 1998–2003.
Akrigg A, Wilkinson GW, Oram JD . The structure of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res 1985; 2 (2): 107–121.
Tanaka N, Kimura H, Iida K, Saito Y, Tsuge I, Yoshimi A et al. Quantitative analysis of cytomegalovirus load using a real-time PCR assay. J Med Virol 2000; 60 (4): 455–462.
Tanaka N, Kimura H, Hoshino Y, Kato K, Yoshikawa T, Asano Y et al. Monitoring four herpesviruses in unrelated cord blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26 (11): 1193–1197.
Picone O, Costa JM, Chaix ML, Ville Y, Rouzioux C, Leruez-Ville M . Human cytomegalovirus UL144 gene polymorphisms in congenital infections. J Clin Microbiol 2005; 43 (1): 25–29.
Diosi P, Babusceac L, Nevinglovschi O, Kun-Stoicu G . Cytomegalovirus infection associated with pregnancy. Lancet 1967; 2 (7525): 1063–1066.
Hayes K, Danks DM, Gibas H, Jack I . Cytomegalovirus in human milk. N Engl J Med 1972; 287 (4): 177–178.
Stagno S, Reynolds DW, Pass RF, Alford CA . Breast milk and the risk of cytomegalovirus infection. N Engl J Med 1980; 302 (19): 1073–1076.
Dworsky M, Yow M, Stagno S, Pass RF, Alford C . Cytomegalovirus infection of breast milk and transmission in infancy. Pediatrics 1983; 72 (3): 295–299.
Meier J, Lienicke U, Tschirch E, Kruger DH, Wauer RR, Prosch S . Human cytomegalovirus reactivation during lactation and mother-to-child transmission in preterm infants. J Clin Microbiol 2005; 43 (3): 1318–1324.
Jim WT, Shu CH, Chiu NC, Kao HA, Hung HY, Chang JH et al. Transmission of cytomegalovirus from mothers to preterm infants by breast milk. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2004; 23 (9): 848–851.
Kerrey BT, Morrow A, Geraghty S, Huey N, Sapsford A, Schleiss MR . Breast milk as a source for acquisition of cytomegalovirus (HCMV) in a premature infant with sepsis syndrome: detection by real-time PCR. J Clin Virol 2006; 35 (3): 313–316.
Chou SW, Dennison KM . Analysis of interstrain variation in cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B sequences encoding neutralization-related epitopes. J Infect Dis 1991; 163 (6): 1229–1234.
Benedict CA, Butrovich KD, Lurain NS, Corbeil J, Rooney I, Schneider P et al. Cutting edge: a novel viral TNF receptor superfamily member in virulent strains of human cytomegalovirus. J Immunol 1999; 162 (12): 6967–6970.
Lurain NS, Kapell KS, Huang DD, Short JA, Paintsil J, Winkfield E et al. Human cytomegalovirus UL144 open reading frame: sequence hypervariability in low-passage clinical isolates. J Virol 1999; 73 (12): 10040–10050.
Schleiss MR . Acquisition of human cytomegalovirus infection in infants via breast milk: natural immunization or cause for concern? Rev Med Virol 2006; 16 (2): 73–82.
Hamele M, Flanagan R, Loomis CA, Stevens T, Fairchok MP . Severe morbidity and mortality with breast milk associated cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2010; 29 (1): 84–86.
Doctor S, Friedman S, Dunn MS, Asztalos EV, Wylie L, Mazzulli T et al. Cytomegalovirus transmission to extremely low-birthweight infants through breast milk. Acta Paediatr 2005; 94 (1): 53–58.
Friis H, Andersen HK . Rate of inactivation of cytomegalovirus in raw banked milk during storage at −20 degrees C and pasteurisation. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 1982; 285 (6355): 1604–1605.
Dworsky M, Stagno S, Pass RF, Cassady G, Alford C . Persistence of cytomegalovirus in human milk after storage. J Pediatr 1982; 101 (3): 440–443.
Sharland M, Khare M, Bedford-Russell A . Prevention of postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2002; 86 (2): F140.
Lee HC, Enright A, Benitz WE, Madan A . Postnatal cytomegalovirus infection from frozen breast milk in preterm, low birth weight infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2007; 26 (3): 276.
Hamprecht K, Maschmann J, Muller D, Dietz K, Besenthal I, Goelz R et al. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) inactivation in breast milk: reassessment of pasteurization and freeze-thawing. Pediatr Res 2004; 56 (4): 529–535.
Goelz R, Hihn E, Hamprecht K, Dietz K, Jahn G, Poets C et al. Effects of different CMV-heat-inactivation-methods on growth factors in human breast milk. Pediatr Res 2009; 65 (4): 458–461.
Kurath S, Resch B . Cytomegalovirus and transmission via breast milk: how to support breast milk to premature infants and prevent severe infection? Pediatr Infect Dis J 2010; 29 (7): 680–681.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan (16591022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, S., Kimura, H., Oshiro, M. et al. Transmission of cytomegalovirus via breast milk in extremely premature infants. J Perinatol 31, 440–445 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.150
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.150
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevention of human milk-acquired cytomegalovirus infection in very-low-birth-weight infants
BMC Pediatrics (2023)
-
Perinatal Cytomegalovirus Infection
Current Treatment Options in Pediatrics (2022)
-
Transmission of cytomegalovirus via breast milk in low birth weight and premature infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis
BMC Pediatrics (2021)
-
Transmission of cytomegalovirus in fresh and freeze–thawed mother’s own milk to very preterm infants: a cohort study
Journal of Perinatology (2021)
-
Severe late-onset multisystem cytomegalovirus infection in a premature neonate previously treated for congenital infection
BMC Pediatrics (2013)