Abstract
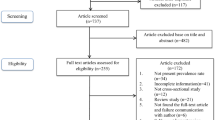
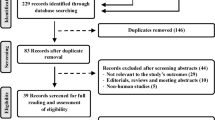
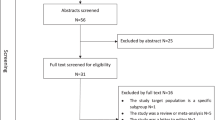
Hypertension is considered to be the leading risk factor for cardiovascular mortality and accounts for a large proportion of premature deaths in China. An empirical understanding of the pattern of disease burden, such as reliable information about the trend and prevalence of hypertension, is essential in developing effective prevention and control strategies and is also important in the decision-making and planning processes of health. However, there are limited comprehensive reviews or nationwide studies that reveal the current burden of hypertension in China. This review is to systematically evaluate hypertension prevalence and determinants as well as its awareness, treatment and control over decades in China. A systematic search was performed for epidemiological studies on hypertension, published between 1982 and January 2013. MeSH major topic terms ‘hypertension’ and ‘prevalence’ and ‘China’ were used in the search. Data on hypertension prevalence, determinants and awareness, as well as its treatment and control, were extracted and compared. Sixty articles were included for data extraction. The prevalence reported in the studies varied from 7.17 to 51.2%. Awareness, treatment and control rates also varied regionally. Except in the central region of China, where a declining trend in hypertension prevalence was witnessed, a rising trend in hypertension prevalence over time could still be observed in other parts of China. Higher hypertension prevalence was found among men and in the urban population, whereas lower prevalence was found in the southern region. Hypertension awareness and treatment rate varied extensively, with a low control rate, nationwide.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ezzati M, Lopez A, Rodgers A, Hoorn S, Murray C . Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 2002; 360 (9343): 1347–1360.
He J, Gu D, Chen J, Wu X, Kelly T, Huang J et al. Premature deaths attributable to blood pressure in China: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 2009; 374 (9703): 1765–1772.
Bai J, Tang Z, Li L, Gu L, Xue D . A systematic review: prevalence rate of hypertension in China. Shanghai J Prev Med 2012; 24 (11): 604–616.
Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP . STROBE Initiative. Lancet 2007; 370 (9596): 1453–1457.
Xu X, Tang X, Jing H . Analysis of epidemiological trends and influence factors of hypertension in Zhejiang Province. Prev Treat Cardio Dis 2004; 4 (5): 5–10.
Xu X, Tang X, Jing H . Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension patients in Zhejiang Province. Chin J Cardio Med 2005; 10 (1): 36–45.
Fu S, Cao Y, Li Y, Li F, Peng Y, Dong L et al. Hypertensive epidemiology in Heilongjiang Province in China. Chin Med J (Engl) 2002; 115 (4): 498–501.
Zhao Y, Lu F, Sun H, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Sun S et al. Trends in hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rates in Shandong Province of China. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2012; 14 (9): 637–643.
Hou Y . Epidemiological study of hypertension among adults aged 35 years and over in Chongqing of China. Master Dissertation. Chongqing Medical University, 2007.
Wu X, Duan X, Gu D, Hao J, Tao S, Fan D . Prevalence of hypertension and its trends in Chinese populations. Int J Cardiol 1995; 52 (1): 39–44.
Gu D, Reynolds K, Wu X, Chen J, Duan X, Muntner P et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in china. Hypertension 2002; 40 (6): 920–927.
Wu Y, Huxley R, Li L, Anna V, Xie G, Yao C et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertefnsion in China: data from the China National Nutrition and Health Survey 2002. Circulation 2008; 118 (25): 2679–2686.
Zheng X, Yao D, Zhuo-Ma C, Tang J, Wang T, Zhang H et al. Prevalence, self-awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in Lhasa, Tibet. Clin Exp Hypertens 2012; 34 (5): 328–333.
Liu H, Ma P, Xu Q, Chen L, Wu Y . Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension survey in Wuzhong City, Ningxia. Practical Med 2012; 28 (2): 313–316.
Liu H, Jia S, Xu Q, Ma X, Yang R, Guo Z et al. Hypertension prevalence and risk factors in Ningxia. J Ningxia Med Univ 2010; 32 (3): 388–392.
Li G, Liu W, Jiang X, Yang W, Tang D, Ye J et al. Investigation on awareness behavior of the hypertensive and epidemiological characteristic of hypertension among community population in Hunan Province. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Non-commun Dis 2002; 10 (5): 195–207.
Pan J, Wang C, Yang L, Shen M, Chen X, Liang S et al. Prevalence of hypertension and influencing factors among rural adults in Henan Province. J Zhengzhou Univ(Medical Science) 2010; 45 (3): 429–431.
Yang M . Investigation of hypertension prevalence and its risk factors among country folks of Wujiang municipal. Modern Hospital 2010; 10 (9): 147–148.
Zhou Q, Pan B, Lin G, Wu X, Liang B, Du L . Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in 15-69 years old residents in Guangzhou. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Non-commun Dis 2010; 18 (6): 587–590.
Wei W, Zhou M, Sha Q, Zhou S, Xu Z, Zhang C et al. Analysis on prevalence and risk factors of hypertension among inhabitants in Qinghai Province. Modern Prev Med 2012; 39 (23): 6222–6225.
Wang Y, Xu F, Gu N, Zhan X, Wang F . Investigation on prevalence and epidemiological characteristics of hypertension in urban and rural areas of Dalian in 2006. Prev Med Trib 2008; 14 (10): 869–871.
Yao S, Zeng W, Wei Y, Wang Q, Lu R, Xia J . Epidemic situation and analysis of risk factors of hypertension in urban and rural residents on Chengdu City. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Non-commun Dis 2012; 20 (3): 265–267.
Jiao S, Wang Y, Pang X, Yin X, Xie J, Shi Y et al. Analysis on prevalence and epidemic trend of hypertension in Beijing. Chin J Public Health 2005; 21 (12): 1491–1492.
Zhao X, Zhou Z, Sun G, Xu M, Lu Y, Zou Z et al. Investigation on hypertension among community population aged 35 and over in Changshu. Acta Univ Med Nangjing (Natural Science) 2006; 26 (8): 721–724.
Zhang J, Jia H, Wang L, Sun J, Zhu J . Analysis on prevalence and distribution characteristics of hypertension among adults in Hebei Province. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Non-commun Dis 2007; 15 (4): 347–350.
Wu G, Du D, Geng G, Zhao S, Wang X, Yang L et al. Hypertension survey study in Tianjing. Tianjing Med 1994, 89–92.
Yuan B, Pan X, Shi Z, Dai Y . Epidemiological survey of hypertension prevalence and risk factors in Jiangsu Province. Jiangsu Prev Med 2004; 15 (3): 5–7.
Wu Q, Dai Z, Jin S, Li J, Wang S, Jia S et al. An investigation of epidemic features of hypertension in the population in Anhui Province. Disease Surveillance 2006; 21 (10): 541–543.
Guan X, Wang L, Zhang X, Hou Y, Ding D, Zhang J . Survey on prevalence rate and prevention and treatment situation of hypertension in the adults in Jilin Province, 2002. Chin Prev Med 2008; 9 (3): 197–201.
Huang X, Hu R, Le Q, Hou Y, Luo K, Hu D et al. Epidemiological study of hypertension in Chongqing area of China. Chin J Public Health 2009; 25 (1): 25–27.
Li J, Xu J, Yao H, Lu W . Epidemiological status of hypertension in residents aged 15 and 69 in Shanghai. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Non-commun Dis 2010; 18 (3): 233–235.
Xi B, Liang Y, Reilly KH, Wang Q, Hu Y, Tang W . Trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among Chinese adults 1991–2009. Int J Cardiol 2012; 158 (2): 326–329.
Lao XQ, Xu YJ, Wong MC, Zhang YH, Ma WJ, Xu XJ et al. Hypertension Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, Control and Associated Factors in a Developing Southern Chinese Population: Analysis of Serial Cross-Sectional Health Survey Data 2002-2010. Am J Hypertens 2013; 26 (11): 1335–1345.
Center for Health Statistics and Information. An Analysis Report of National Health Services Survey in China 2008; p132–33.
Ministry of Health, China. China Health Statistical Yearbook 2012, p 18.
Yang G, Kong L, Zhao W, Wang X, Zhai Y, Chen L et al. Emergence of chronic non-communicable diseases in China. Lancet 2008; 372 (9650): 1697–1705.
Huang Z, Wu X, Stamler J, Rao X, Tao S, Friedewald W et al. A north-south comparison of blood pressure and factors related to blood pressure in the People’s Republic of China: a report from the PRC-USA Collaborative Study of Cardiovascular Epidemiology. J Hypertens 1994; 12 (9): 1103–1112.
Van de Poel E, O’Donnell O, Van Doorslaer E . Urbanization and the spread of diseases of affluence in China. Econ Hum Biol 2009; 7 (2): 200–216.
Ma Q, Mei W, Yin P, Yang X, Rastegar S, Yan J . Prevalence of hypertension in Chinese cities: a meta-analysis of published studies. PLoS One 2013; 8 (3): e58302.
Zhang X, Shao Y . Epidemiological survey on hypertension prevalence and its relevant factors among residents in Wenzhou City. Shanghai Prev Med 2012; 24 (5): 225–28+32.
Anderson C, Appel L, Okuda N, Brown I, Chan Q, Zhao L et al. Dietary sources of sodium in China, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States, women and men aged 40 to 59 years: the INTERMAP study. J Am Diet Assoc 2010; 110 (5): 736–745.
Liu Z . A comprehensive review on the relationships between salt intake and hypertension prevalence over time in China. Chin J Hypertens 2009; 17 (6): 482–485.
Zhao L, Stamler J, Yan LL, Zhou B, Wu Y, Liu K et al. Blood pressure differences between northern and southern Chinese: role of dietary factors: the International Study on Macronutrients and Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2004; 43 (6): 1332–1337.
Zhou YH, Yang QD, Xu HW, Liu YH, Xie YQ, Zhang L . Epidemiology of Hypertension in Middle and Old-aged Popualtion in Changsha Urban. Chin J Hypertens 2002; 10 (3): 278–280.
Liu L, Deng HH, Ceng RC . Analysis on prevalence and distribution characteristics of hypertension in Guangdong Province. Guangdong Medical Journal 2002; 23 (4): 417–419.
Qiang L, Zhang DF, Gao WZ, Xu XX, Xu DQ . Survey on prevalence rate and influence factors of hypertension in rural Qingdao. Lit & Inf Prev Med 2002; 8 (5): 523–524.
Sun R, Gu JJ, Sun F, Chen XY, Wang Y . Research on prevalence rate of hypertension and analysis of relevant factors among people in Jiangsu. J Jiangsu Clinic Med 2002; 6 (6): 534–536.
Cui J, Zhang T, Zhang LN . An Investigation of Hypertension Incidence in Urban Residents Aged 35∼74 in Ningbo. Disease Surveillance 2005; 20 (1): 40–43.
Ma WJ, Xu YJ, Xu HF, Nie SP, Li JS, Fu CX et al. Analysis on Epidemiological Characteristics and Control Effect of Hypertension in Guangdong. South China J Prev Med 2003; 29 (6): 20–24.
Zhao XL, Yang JG, Zhang DK, Shen HB . Survey on the Prevalence Status of Hypertension in Urban Population of Taizhou Jiangsu Province. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Nanjing (Social Science) 2005; 20 (3): 229–231.
Chen NY, Meng XY, Wei B, Xie YH, Zhuo JT, Zhang Y . Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control among city residents in Guangxi. Chin J Prev Contro Non-commun Dis 2004; 12 (5): 215–216.
Liu WJ, Chen WQ, Luo BF, Pan BY, Chen J, Wang JH et al. Analysis on Epidemiological Characteristics and Control Status of Hypertension in Residents Aged 15 and above in Guangzhou. Chin J Prev Contro Non-commun Dis 2007; 15 (2): 110–112.
Li L, Liu QM, Fang SY, Chen RH, Shi WY, Qiu Y et al. Survey on hypertension epidemiology in Hangzhou in 2005. Chin Prev Med 2007; 8 (3): 234–237.
Dong GH, Sun ZQ, Zheng LQ, Li J, Zhang XZ, Zheng XG et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural adults from Liaoning Province, northeast China. Hypertens Res 2007; 30 (19): 951–958.
Shi QP, Chen Y, Xu W, Yang YF, Duan J, Xiao YZ . Prevalence, Status of Awareness, Treatment and Control of Hypertension in Yunnan Province Residents. Prevention and Treatment of Cardio Cerebral Vascular Disease 2010; 10 (2): 103–106.
Cheng H, Pan RY, Luo YJ, Chen WQ, Jing CX . Status of Hypertension Prevalence and Its Risk FactorAnalysis in Communities of Guangzhou City. Occup and Health 2009; 25 (14): 1534–1536.
Chen B, Li DY, Liang XD, Li YR . Prevalence of hypertension and its influence factors among inhabitants aged 15-69 years in Zhuhai city. Chin J Public Health 2011; 27 (5): 619–621.
Li H, Meng QY, Sun XY, Salter A, Briggs NE, Hiller JE . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural China-results from Shandong Province. Journal of Hypertension 2010; 28 (3): 432–438.
Fu SY, Li WM, Zhao YJ, Dong LH, Zhao JB, Wang BQ et al. Prevalence of hypertension and risk factors in Heilongjiang province in 2007. Chin Med J 2010; 123 (6): 752–755.
Yi YJ, Huang XB, Liu Y, Zeng W, Ouyang LY, Zhang TJ et al. The Prevalence of Hypertension Among Middle-Aged and Elderly People in Chengdu. Chin J Hypertens 2010; 18 (5): 469–473.
Diao WL, Zheng LQ, Xing LY, Mu HJ, Liu YQ, Zhou HL et al. Hypertension prevalence and its awareness, medication and control among rural residents in Liaoning province. Chin J Public Health 2010; 26 (5): 602–603.
Yan YY . Study on the Hypertension Prevalence and Control Strategies in Shijiazhuang. Modern Preventive Medicine 2010; 37 (15): 2906–2910.
Cai L, Liu AP, Zhang L, Li SP, Wang PY . Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension among Adults in Beijing, China. Clin Exp Hypertens 2012; 34 (1): 45–52.
Xia RF, Hu YE, Cheng YH, Wu YJ, Zhang WP . Study on Prevalence and Risk Factors of Hypertension Among Adults in Yongzhou. Practical Preventive Medicine 2010; 17 (7): 1292–1295.
Yan F, Zhang MR, Yang Z, Shen L, Li ZK, Tian R . Analysis on prevalence and awareness rate of hypertension and diabetes among residents in Kunming. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Dis 2012; 20 (3): 331–332.
Cai L, Dong J, Lu YC, Shu ZK, Zhao KY . Multilevel Analysis of the Determinants of Pre-hypertension and Hypertension in Rural Southwest China. Public Health Rep 2011; 126 (3): 420–427.
Feng YY, Peng Y, Li YQ, Zhang LT, Liu Y, Chen W et al. Investgation Analysis of Hypertension Patients and Drugs Treatment in Rural Areas of Bazhou City. Medical Information 2010; 23 (9): 3110–3112.
Cheng MN, Xu JY, Yao HH, Yan QH, Li XJ, Zhong WJ . Prevalence of Hypertension in Residents Aged over 15 Years in Shanghai. J Environ Occup Med 2012; 29 (6): 339–342.
Zhang N, Zhou ZY, Xu XY, Zhou B . Awareness and Treatment of Hypertension in Rural Residents of Changshu City. Occup and Health 2011; 27 (23): 2679–2681.
Bu P, Yan J . The Investigation and Analysis of Hypertension Epidemiology in Changsha. J Hunan Normal Univ (Med Sci) 2011; 8 (3): 86–89.
Meng XJ, Dong GH, Wang D, Liu MM, Lin Q, Tian S et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, control, and risk factors associated with hypertension in urban adults from 33 communities of China: the CHPSNE study. Journal of Hypertension 2011; 29 (7): 1303–1310.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Yonghua Hu, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Peking University Health Science Center, for his kind and valuable suggestions in the review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Journal of Human Hypertension website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, L., Song, J., Ma, Z. et al. Prevalence and characteristics of hypertension in mainland Chinese adults over decades: a systematic review. J Hum Hypertens 28, 649–656 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2014.5
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A glimpse into the future: modelling global prevalence of hypertension
BMC Public Health (2023)
-
Trends in output of hypertension management and associated factors in primary care facilities: a latent trajectory analysis in China from 2009 to 2017
BMC Primary Care (2023)
-
Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension and their risk factors in Shaanxi Province in 2004–18
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Hypertension in China: burdens, guidelines and policy responses: a state-of-the-art review
Journal of Human Hypertension (2022)
-
Distribution of risk factors of hypertension patients in different age groups in Tianjin
BMC Public Health (2021)