Abstract
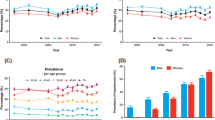
This study aims to investigate the trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension among rural residents aged 35–74 years in northern China during the country’s rapid economic development from 1991 to 2011. Two surveys, conducted in 1991and 2011, included 2196 and 1939 participants aged 35–74 years from same villages in Ji County, Tianjin of China, respectively. The prevalence of hypertension, adjusted by age and gender using the world standard population in 2000, increased 30% (39.9% vs 51.7%) between 1991 and 2011. The increase was greatest (68%) in women aged 35–44 years. Meanwhile, the prevalence of stage II hypertension increased by 75% overall, with a 4-fold increase in men aged 45–54 years. Although the awareness, treatment and control of hypertension increased significantly during the same period, they remained unacceptably poor. In conclusion, the community-based surveys showed that the prevalence of hypertension in rural residents of northern China aged 35–74 years increased rapidly over the past 20 years, and most dramatically in young women. Efforts in the primary prevention of hypertension, particularly for young women, and promoting education for hypertension awareness, treatment and control are of paramount importance in rural China.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang L, Kong L, Wu F, Bai Y, Burton R . Preventing chronic diseases in China. Lancet 2005; 366: 1821–1824.
Kannel WB . Framingham study insights into hypertensive risk of cardiovascular disease. Hypertens Res 1995; 18: 181–196.
Himmelmann A, Hedner T, Hansson L, O'Donnell CJ, Levy D . Isolated systolic hypertension: an important cardiovascular risk factor. Blood Press 1998; 7: 197–207.
Li L (eds). Chinese Residents Nutrition and Health Condition Investigation Report of the Four: Hypertension. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House: Beijing, 2002.
The Health Ministry Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Research Center. (eds). China Cardiovascular Disease Report. China Encyclopedia Press: Beijing, 2006.
Hajjar I, Kotchen TA . Trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the United States, 1988–2000. JAMA 2003; 290: 199–206.
Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, Lau CP, Lam KS . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension 2007; 49: 69–75.
Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN . US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA 2010; 303: 2043–2050.
McAlister FA, Wilkins K, Joffres M, Leenen FH, Fodor G, Gee M et al. Changes in the rates of awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Canada over the past two decades. CMAJ 2011; 183: 1007–1013.
Ministries of Health and Science and Technology and the National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. (eds). The Nutrition and Health Status of the Chinese People. Beijing: State Information Office: Beijing, 2004.
Meng XJ, Dong GH, Wang D, Liu MM, Lin Q, Tian S et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, control, and risk factors associated with hypertension in urban adults from 33 communities of China: The CHPSNE study. J Hypertens 2011; 29: 1303–1310.
Gu D, Reynolds K, Wu X, Chen J, Duan X, Muntner P et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in China. Hypertension 2002; 40: 920–927.
Dong GH, Sun ZQ, Zhang XZ, Li JJ, Zheng LQ, Li J et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment & control of hypertension in rural Liaoning province, China. Indian J Med Res 2008; 128: 122–127.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL et al. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of high blood pressure: The JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003; 289: 2560–2572.
Li H, Meng Q, Sun X, Salter A, Briggs NE, Hiller JE . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural China: results from Shandong province. J Hypertens 2010; 28: 432–438.
Cai L, Liu A, Zhang L, Li S, Wang P . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among adults in Beijing, China. Clin Exp Hypertens 2012; 34: 45–52.
Wang Z, Wu Y, Zhao L, Li Y, Yang J, Zhou B . Trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in the middle-aged population of China, 1992-1998. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 703–709.
Reynolds K, Gu D, Muntner P, Wu X, Chen J, Huang G et al. Geographic variations in the prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in China. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 1273–1281.
Redondo A, Benach J, Subirana I, Martinez JM, Munoz MA, Masia R et al. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of cardiovascular risk factors across educational level in the 1995-2005 period. Ann Epidemiol 2011; 21: 555–563.
Burt VL, Cutler JA, Higgins M, Horan MJ, Labarthe D, Whelton P et al. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population. Data from the health examination surveys, 1960 to 1991. Hypertension 1995; 26: 60–69.
Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Law MR, Elliott P, MacMahon S, Rodgers A . Blood pressure and the global burden of disease 2000. Part ii: estimates of attributable burden. J Hypertens 2006; 24: 423–430.
Tu K, Chen Z, Lipscombe LL . Prevalence and incidence of hypertension from 1995 to 2005: A population-based study. CMAJ 2008; 178: 1429–1435.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ 1998; 317: 703–713.
Curb JD, Pressel SL, Cutler JA, Savage PJ, Applegate WB, Black H et al. Effect of diuretic-based antihypertensive treatment on cardiovascular disease risk in older diabetic patients with isolated systolic hypertension. Systolic hypertension in the Elderly Program Cooperative Research Group. JAMA 1996; 276: 1886–1892.
Staessen JA, Gasowski J, Wang JG, Thijs L, Den Hond E, Boissel JP et al. Risks of untreated and treated isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly: meta-analysis of outcome trials. Lancet 2000; 355: 865–872.
Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R . Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002; 360: 1903–1913.
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J . Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005; 365: 217–223.
Estoppey D, Paccaud F, Vollenweider P, Marques-Vidal P . Trends in self-reported prevalence and management of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes in Swiss adults, 1997-2007. BMC Public Health 2011; 11: 114.
World Health Organization. Noncommunicable diseases country profiles 2011. Available at http://www.Who.Int/nmh/publications/ncd_profiles2011/en/.
Gupta R, Pandey RM, Misra A, Agrawal A, Misra P, Dey S et al. High prevalence and low awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Asian Indian women. J Hum Hypertens 2011; 26: 585–593.
Salt intake of residents from Tianjin. Berhai Morning Post 2011. Available at http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/dfpd/tianjin/2011-08-15/content_3498295.html.
Acknowledgements
We thank the residents of Ji County who have participated this study, and all local medical care professionals, for their enthusiasm, tireless work and sustained support. We also thank P. Minick and N. Su for their assistance. This study was supported in part by the National People’s Republic of China Ministry of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Health through the 7th, 8th and 10th National Five-Year Key Research Plan (contracts 85-915-01-01, 85-915-01-02 and 2001BA703B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Ning, X., Yang, L. et al. Trends of hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control in rural areas of northern China during 1991–2011. J Hum Hypertens 28, 25–31 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.44
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.44
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence and income-related equity in hypertension in rural China from 1991 to 2011: differences between self-reported and tested measures
BMC Health Services Research (2019)
-
Association between socioeconomic status and post-stroke functional outcome in deprived rural southern China: a population-based study
BMC Neurology (2018)
-
Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Control of hypertension in the Malaysian population: findings from the National Health and Morbidity Survey 2006–2015
Journal of Human Hypertension (2018)
-
Correlation between hypertension and common carotid artery intima-media thickness in rural China: a population-based study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2018)
-
Carotid Intima-media Thickness and its Association with Conventional Risk Factors in Low-income Adults: A Population-based Cross-Sectional Study in China
Scientific Reports (2017)