Abstract
Background:
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as epigenetic regulators of metabolism and energy homeostasis. There is a growing body of evidence pointing to miRNAs that have important regulatory roles in insulin sensitivity.
Objective:
The aim of this work was to explore the expression and mechanism of action of miR-26b in obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) in adipocytes.
Methods:
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to determine miR-26b expression in obese rodent models, human obesity subjects and insulin-resistant adipocytes. We analysed the roles of miR-26b overexpression and inhibition on glucose uptake in adipocytes. Western blotting was used to detect the levels of protein molecules involved in the phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway. Bioinformatics and the Dual Luciferase Assay were used to identify the target gene of miR-26b. We assessed the regulatory roles of miR-26b on the phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN)/PI3K/AKT pathway and the relationship between miR-26b and the metabolism of human obese subjects.
Results:
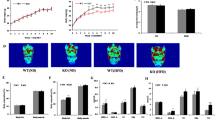
Levels of miR-26b are reduced in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) in obese rodent models, human obesity and insulin-resistant adipocytes. MiR-26b promotes insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and increases insulin-stimulated glucose transporter type 4 translocation to the plasma membrane in human mature adipocytes. MiR-26b modulates insulin-stimulated AKT activation via inhibition of its target gene, PTEN, and significantly increases insulin sensitivity via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. The expression level of miR-26b negatively correlates with increasing body mass index and homeostasis model assessment for IR in human obese subjects.
Conclusion:
Decreased miR-26b expression in VAT may be involved in obesity-related IR by interrupting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Office of Helath Communications and Public Relations. Obesity and Overweight. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J . Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32: 1431–1437.
Gupta N, Goel K, Shah P, Misra A . Childhood obesity in developing countries: epidemiology, determinants, and prevention. Endocr Rev 2012; 33: 48–70.
Wu N, Tang X, Wu Y, Qin X, He L, Wang J et al. Cohort profile: the Fangshan Cohort Study of cardiovascular epidemiology in Beijing, China. J Epidemiol 2014; 24: 84–93.
Kasper NM, Herran OF, Villamor E . Obesity prevalence in Colombian adults is increasing fastest in lower socio-economic status groups and urban residents: results from two nationally representative surveys. Public Health Nutr 2014; 17: 2398–2406.
Rottiers V, Naar AM . MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012; 13: 239–250.
Hilton C, Neville MJ, Karpe F . MicroRNAs in adipose tissue: their role in adipogenesis and obesity. Int J Obes (Lond) 2013; 37: 325–332.
Poy MN, Eliasson L, Krutzfeldt J, Kuwajima S, Ma X, Macdonald PE et al. A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 2004; 432: 226–230.
Jordan SD, Kruger M, Willmes DM, Redemann N, Wunderlich FT, Bronneke HS et al. Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 434–446.
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP . Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 367–377.
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Kerin MJ . Role of microRNAs in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev 2010; 11: 354–361.
Alexander R, Lodish H, Sun L . MicroRNAs in adipogenesis and as therapeutic targets for obesity. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2011; 15: 623–636.
Kang M, Yan LM, Zhang WY, Li YM, Tang AZ, Ou HS . Role of microRNA-21 in regulating 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation and adiponectin expression. Mol Biol Rep 2013; 40: 5027–5034.
Zaragosi LE, Wdziekonski B, Brigand KL, Villageois P, Mari B, Waldmann R et al. Small RNA sequencing reveals miR-642a-3p as a novel adipocyte-specific microRNA and miR-30 as a key regulator of human adipogenesis. Genome Biol 2011; 12: R64.
Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, Hanson E, Marcusson EG, Ravichandran LV et al. MicroRNA-143 regulates adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 52361–52365.
Ahn J, Lee H, Jung CH, Jeon TI, Ha TY . MicroRNA-146b promotes adipogenesis by suppressing the SIRT1-FOXO1 cascade. EMBO Mol Med 2013; 5: 1602–1612.
Kim SY, Kim AY, Lee HW, Son YH, Lee GY, Lee JW et al. MiR-27a is a negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation via suppressing PPARgamma expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 392: 323–328.
Chen H, Wang S, Chen L, Chen Y, Wu M, Zhang Y et al. MicroRNA-344 inhibits 3T3-L1 cell differentiation via targeting GSK3beta of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. FEBS Lett 2014; 588: 429–435.
Chen L, Cui J, Hou J, Long J, Li C, Liu L . A novel negative regulator of adipogenesis: microRNA-363. Stem Cells 2014; 32: 510–520.
Keller P, Gburcik V, Petrovic N, Gallagher IJ, Nedergaard J, Cannon B et al. Gene-chip studies of adipogenesis-regulated microRNAs in mouse primary adipocytes and human obesity. BMC Endocr Disord 2011; 11: 7.
Heneghan HM, Miller N, McAnena OJ, O'Brien T, Kerin MJ . Differential miRNA expression in omental adipose tissue and in the circulation of obese patients identifies novel metabolic biomarkers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 96: E846–E850.
Balasubramanyam M, Aravind S, Gokulakrishnan K, Prabu P, Sathishkumar C, Ranjani H et al. Impaired miR-146a expression links subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem 2011; 351: 197–205.
Song G, Xu G, Ji C, Shi C, Shen Y, Chen L et al. The role of microRNA-26b in human adipocyte differentiation and proliferation. Gene 2014; 533: 481–487.
Nelson BA, Robinson KA, Buse MG . High glucose and glucosamine induce insulin resistance via different mechanisms in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetes 2000; 49: 981–991.
Ceddia RB, Somwar R, Maida A, Fang X, Bikopoulos G, Sweeney G . Globular adiponectin increases GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 132–139.
Palumbo T, Faucz FR, Azevedo M, Xekouki P, Iliopoulos D, Stratakis CA . Functional screen analysis reveals miR-26b and miR-128 as central regulators of pituitary somatomammotrophic tumor growth through activation of the PTEN-AKT pathway. Oncogene 2013; 32: 1651–1659.
Xie H, Lim B, Lodish HF . MicroRNAs induced during adipogenesis that accelerate fat cell development are downregulated in obesity. Diabetes 2009; 58: 1050–1057.
Xu G, Ji C, Shi C, Fu H, Zhu L, Xu L et al. Modulation of hsa-miR-26b levels following adipokine stimulation. Mol Biol Rep 2013; 40: 3577–3582.
Xu G, Shi C, Ji C, Song G, Chen L, Yang L et al. Expression of microRNA-26b, an obesity-related microRNA, is regulated by free fatty acids, glucose, dexamethasone and growth hormone in human adipocytes. Mol Med Rep 2014; 10: 223–228.
Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Akin A, Zavolan M et al. MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature 2011; 474: 649–653.
Kornfeld JW, Baitzel C, Konner AC, Nicholls HT, Vogt MC, Herrmanns K et al. Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs glucose metabolism through silencing of Hnf1b. Nature 2013; 494: 111–115.
Lebovitz HE, Banerji MA . Point: visceral adiposity is causally related to insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 2322–2325.
Fox CS, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Pou KM, Maurovich-Horvat P, Liu CY et al. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007; 116: 39–48.
Verghese ET, Drury R, Green CA, Holliday DL, Lu X, Nash C et al. Mir-26b is down-regulated in carcinoma-associated fibroblasts from ER-positive breast cancers leading to enhanced cell migration and invasion. J Pathol 2013; 231: 388–399.
Wu N, Zhao X, Liu M, Liu H, Yao W, Zhang Y et al. Role of microRNA-26b in glioma development and its mediated regulation on Epha2. PloS one 2011; 6: e16264.
Rahbari R, Holloway AK, He M, Khanafshar E, Clark OH, Kebebew E . Identification of differentially expressed microRNA in parathyroid tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 2011; 18: 1158–1165.
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ . Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1625–1638.
Wolin KY, Carson K, Colditz GA . Obesity and cancer. Oncologist 2010; 15: 556–565.
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR . Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 85–96.
Tang X, Powelka AM, Soriano NA, Czech MP, Guilherme A . PTEN, but not SHIP2, suppresses insulin signaling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 22523–22529.
Kurlawalla-Martinez C, Stiles B, Wang Y, Devaskar SU, Kahn BB, Wu H . Insulin hypersensitivity and resistance to streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice lacking Pten in adipose tissue. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 2498–2510.
Stiles B, Wang Y, Stahl A, Bassilian S, Lee WP, Kim YJ et al. Liver-specific deletion of negative regulator Pten results in fatty liver and insulin hypersensitivity [corrected]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 2082–2087.
Stiles BL, Kuralwalla-Martinez C, Guo W, Gregorian C, Wang Y, Tian J et al. Selective deletion of Pten in pancreatic beta cells leads to increased islet mass and resistance to STZ-induced diabetes. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 2772–2781.
Wijesekara N, Konrad D, Eweida M, Jefferies C, Liadis N, Giacca A et al. Muscle-specific Pten deletion protects against insulin resistance and diabetes. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 1135–1145.
Pal A, Barber TM, Van de Bunt M, Rudge SA, Zhang Q, Lachlan KL et al. Pten mutations as a cause of constitutive insulin sensitivity and obesity. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1002–1011.
Ishihara H, Sasaoka T, Kagawa S, Murakami S, Fukui K, Kawagishi Y et al. Association of the polymorphisms in the 5'-untranslated region of Pten gene with type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. FEBS Lett 2003; 554: 450–454.
Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K et al. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 1685–1694.
Kasinski AL, Kelnar K, Stahlhut C, Orellana E, Zhao J, Shimer E et al. A combinatorial microRNA therapeutics approach to suppressing non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2014. e-pub ahead of print 1 September 2014; doi:10.1038/onc.2014.282.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by grants from the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB530604), the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81330067), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81170797), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK2011107), the Program for Innovative Research Teams of Jiangsu Province (LJ201108) and Nanjing Technological Development Program (201104013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Ji, C., Song, G. et al. MiR-26b modulates insulin sensitivity in adipocytes by interrupting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Int J Obes 39, 1523–1530 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.95
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.95
This article is cited by
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of miR-181a and Its Role in Adipogenesis, Obesity, and Lipid Metabolism Through Review of Literature
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
Up-regulation of miR-133a-3p promotes ovary insulin resistance on granulosa cells of obese PCOS patients via inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling
BMC Women's Health (2022)
-
Physical Activity Modulates miRNAs Levels and Enhances MYOD Expression in Myoblasts
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2022)
-
Obesity, leptin, and deregulation of microRNA in lipid metabolisms: their contribution to breast cancer prognosis
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2021)
-
MiR-26b-5p regulates the preadipocyte differentiation by targeting FGF21 in goats
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2021)