Abstract
Objective:
Piperonal is an important flavor additive with antibacterial and anxiolytic properties. We investigated the effects and possible mechanisms of piperonal protection against high-fat diet (HFD)-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance.
Methods:
C57BL/6 J mice were fed with a normal diet (ND; based on the AIN-76 rodent diet), HFD (20% fat and 1% cholesterol), or piperonal-supplemented diet (POD; HFD supplemented with 0.05% piperonal) for 10 weeks.
Results:
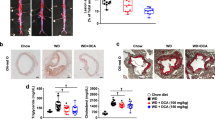
Piperonal supplementation reduced hepatic lipid concentrations, liver dysfunction and plasma levels of insulin and glucose in HFD-fed mice. Piperonal significantly enhanced mRNA expression and secretion of adiponectin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Dietary piperonal significantly increased circulating adiponectin levels and hepatic AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation in HFD-fed mice; these were associated with the suppression of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c and activation of glucose transporter-2 translocation in the livers. Piperonal also significantly reduced the expression of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress markers in the livers of HFD-fed mice.
Conclusions:
Piperonal may activate the adiponectin/AMPK pathway in the livers of mice. The activated adiponectin/AMPK axis may inhibit p70S6 kinase signaling and the ER stress response, with protective effects on hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nasrallah SM, Wills CE Jr, Galambos JT . Hepatic morphology in obesity. Dig Dis Sci 1981; 26: 325–327.
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Morselli-Labate AM, Bianchi G, Bugianesi E, McCullough AJ et al. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. Am J Med 1999; 107: 450–455.
Bacon BR, Farahvash MJ, Janney CG, Neuschwander-Tetri BA . Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: an expanded clinical entity. Gastroenterology 1994; 107: 1103–1109.
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2001; 50: 1844–1850.
Ferre P, Foufelle F . Hepatic steatosis: a role for de novo lipogenesis and the transcription factor SREBP-1c. Diabetes Obes Metab 2010; 12 (Suppl 2): 83–92.
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 1167–1174.
Ajmo JM, Liang XM, Rogers CQ, Pennock B, You M . Resveratrol alleviates alcoholic fatty liver in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2008; 295: G833–G842.
Um SH, Frigerio F, Watanabe M, Picard F, Joaquin M, Sticker M et al. Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin sensitivity. Nature 2004; 431: 200–205.
Li S, Ogawa W, Emi A, Hayashi K, Senga Y, Nomura K et al. Role of S6K1 in regulation of SREBP1c expression in the liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011; 412: 197–202.
Krebs M, Brunmair B, Brehm A, Artwohl M, Szendroedi J, Nowotny P et al. The Mammalian target of rapamycin pathway regulates nutrient-sensitive glucose uptake in man. Diabetes 2007; 56: 1600–1607.
Sabio G, Das M, Mora A, Zhang Z, Jun JY, Ko HJ et al. A stress signaling pathway in adipose tissue regulates hepatic insulin resistance. Science 2008; 322: 1539–1543.
Krimi RB, Letteron P, Chedid P, Nazaret C, Ducroc R, Marie JC . Resistin-like molecule-beta inhibits SGLT-1 activity and enhances GLUT2-dependent jejunal glucose transport. Diabetes 2009; 58: 2032–2038.
Malhi H, Kaufman RJ . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 795–809.
Hampton RY . ER stress response: getting the UPR hand on misfolded proteins. Curr Biol 2000; 10: R518–R521.
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 2004; 306: 457–461.
Yamagishi R, Yokomaku A, Omoto F, Misao K, Takada K, Yoshimatsu S et al. Sleep-improving effects of the aromatic compound heliotropin. Sleep Biol Rhythms 2010; 8: 254–260.
Frosch PJ, Johansen JD, Menne T, Pirker C, Rastogi SC, Andersen KE et al. Further important sensitizers in patients sensitive to fragrances - II. Reactivity to essential oils. Contact Dermatitis 2002; 47: 279–287.
Japon-Lujan R, Luque-Rodriguez JM, de Castro MDL . Dynamic ultrasound-assisted extraction of oleuropein and related biophenols from olive leaves. J Chromatogr A 2006; 1108: 76–82.
Bowles BL, Juneja VK . Inhibition of foodborne bacterial pathogens by naturally occurring food additives. J Food Saf 1998; 18: 101–112.
Redd WH, Manne SL, Peters B, Jacobsen PB, Schmidt H . Fragrance administration to reduce anxiety during Mr-imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 1994; 4: 623–626.
Srinivasan K . Black pepper and its pungent principle-piperine: a review of diverse physiological effects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2007; 47: 735–748.
Diwan V, Poudyal H, Brown L . Piperine Attenuates Cardiovascular, Liver and Metabolic Changes in High Carbohydrate, High Fat-Fed Rats. Cell Biochem Biophys 2011. e-pub ahead of print 30 October 2011; doi:10.1007/s12013-011-9306-1.
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH . A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 1957; 226: 497–509.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med 2001; 7: 941–946.
Park S, Choi Y, Um SJ, Yoon SK, Park T . Oleuropein attenuates hepatic steatosis induced by high-fat diet in mice. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 984–993.
Hagan EC, Hansen WH, Fitzhugh OG, Jenner PM, Jones WI, Taylor JM et al. Food flavourings and compounds of related structure. II. Subacute and chronic toxicity. Food Cosmet Toxicol 1967; 5: 141–157.
Adams TB, Cohen SM, Doull J, Feron VJ, Goodman JI, Marnett LJ et al. The FEMA GRAS assessment of hydroxy- and alkoxy-substituted benzyl derivatives used as flavor ingredients. Food Chem Toxicol 2005; 43: 1241–1271.
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N . Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J 2008; 22: 659–661.
Hagan EC, Jenner PM, Jones WI, Fitzhugh OG, Long EL, Brouwer JG et al. Toxic properties of compounds related to safrole. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1965; 7: 18–24.
Klungsoyr J, Scheline RR . Metabolism of piperonal and piperonyl alcohol in the rat with special reference to the scission of the methylenedioxy group. Acta Pharm Suec 1984; 21: 67–72.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature Medicine 2002; 8: 1288–1295.
Schaffler A, Scholmerich J, Buchler C . Mechanisms of disease: adipocytokines and visceral adipose tissue--emerging role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 2: 273–280.
Tilg H . The role of cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis 2010; 28: 179–185.
Laplante M, Sabatini DM . An emerging role of mTOR in lipid biosynthesis. Curr Biol 2009; 19: R1046–R1052.
Hwahng SH, Ki SH, Bae EJ, Kim HE, Kim SG . Role of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-p70 ribosomal S6 kinase-1 pathway in repression of liver X receptor-alpha-dependent lipogenic gene induction and hepatic steatosis by a novel class of dithiolethiones. Hepatology 2009; 49: 1913–1925.
Forbes JM . The physiological deadlock between AMPK and gluconeogenesis SOGA, a novel protein, may provide the key. Am J Pathol 2010; 177: 1600–1602.
Wang CH, Mao XM, Wang LX, Liu ML, Wetzel MD, Guan KL et al. Adiponectin sensitizes insulin signaling by reducing p70 S6 kinase-mediated serine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 7991–7996.
Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, Kajimura S, Bostrom P, Laznik D et al. Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARgamma by Cdk5. Nature 2010; 466: 451–456.
Wang Y, Wu Z, Li D, Wang D, Wang X, Feng X et al. Involvement of oxygen-regulated protein 150 in AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated alleviation of lipid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 11119–11131.
Zhang C, Chen X, Zhu RM, Zhang Y, Yu T, Wang H et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in hepatic SREBP-1c activation and lipid accumulation in fructose-fed mice. Toxicol Lett 2012; 212: 229–240.
Tilg H, Moschen AR . Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010; 52: 1836–1846.
Dara L, Ji C, Kaplowitz N . The contribution of endoplasmic reticulum stress to liver diseases. Hepatology 2011; 53: 1752–1763.
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O'Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W et al. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 13681–13686.
Tuncman G, Hirosumi J, Solinas G, Chang LF, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS . Functional in vivo interactions between JNK1 and JNK2 isoforms in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 10741–10746.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Industrialization Support Program for Biotechnology of Agriculture and Forestry (810002031SB110), Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Republic of Korea and by the SRC program (Center for Food and Nutritional Genomics: no. 2012-0000643) of the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Choi, Y., Yanakawa, Y. et al. Piperonal prevents high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice via activation of adiponectin/AMPK pathway. Int J Obes 38, 140–147 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.70
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.70
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Piperonal synthase from black pepper (Piper nigrum) synthesizes a phenolic aroma compound, piperonal, as a CoA-independent catalysis
Applied Biological Chemistry (2022)
-
Antiobesity potential of Piperonal: promising modulation of body composition, lipid profiles and obesogenic marker expression in HFD-induced obese rats
Nutrition & Metabolism (2017)
-
Biosynthesis of Heliotropin by a Novel Strain of Serratia liquefaciens
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2017)