Abstract
Objective:
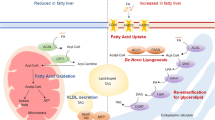
The aim of this study was to evaluate whether dysregulation of molecules involved in FOXO1-dependent insulin signaling in the liver is associated with de novo lipogenesis (DNL) and altered lipid metabolism in severely obese subjects.
Design:
Observational retrospective study.
Subjects:
We considered 71 obese subjects (age 20–68 years; body mass index (BMI)>40 kg m−2 or BMI>35 kg m−2 in the presence of metabolic complications) classified into three groups according to liver histology: normal liver (n=12), simple steatosis (n=27) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH; n=32). Key nodes in insulin signaling and gene expression of molecules implicated in insulin-dependent glucoregulatory pathway and DNL were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR and western blotting.
Results:
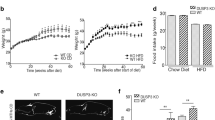
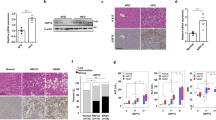
Patients with steatosis had decreased phosphorylation of the insulin kinase AKT1, mediating insulin receptor signaling, and the transcription factor FOXO1, which was therefore more active mediating insulin resistance at transcriptional level. Despite no changes in insulin receptor substrate (IRS)1 mRNA levels, the mRNA and protein levels of the FOXO1 target IRS2 increased progressively with the severity of steatosis from normal liver to NASH. IRS2 expression was correlated with the severity of steatosis, dyslipidemia and liver damage. In patients with NASH, upregulation of IRS2 was associated with preserved activation of AKT2, mediating the stimulating effect of insulin on DNL, and overexpression of its target sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c), inducing DNL at transcriptional level. Both FOXO1 and SREBP1c overexpression converged on upregulation of glucokinase, providing substrates for DNL, in NASH patients.
Conclusion:
Differential regulation of IRS1 and IRS2 and of their downstream effectors AKT1 and AKT2 is consistent with upregulation of FOXO1 and may justify the paradoxical state of insulin resistance relative to the glucoregulatory pathway and augmented insulin sensitivity of the liporegulatory pathway typical of steatosis and the metabolic syndrome in obese patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angulo P . Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 1221–1231.
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J . Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes 2008; 32: 1431–1437.
Eckel RH . Obesity and heart disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Nutrition Committee, American Heart Association. Circulation 1997; 96: 3248–3250.
Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, Marchesini G, Brunello F, Carucci P et al. Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2002; 123: 134–140.
Kotronen A, Westerbacka J, Bergholm R, Pietilainen KH, Yki-Jarvinen H . Liver fat in the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 3490–3497.
Matsumoto M, Pocai A, Rossetti L, Depinho RA, Accili D . Impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production in mice lacking the forkhead transcription factor foxo1 in liver. Cell Metab 2007; 6: 208–216.
Postic C, Girard J . The role of the lipogenic pathway in the development of hepatic steatosis. Diabetes Metab 2008; 34: 643–648.
Taniguchi CM, Ueki K, Kahn R . Complementary roles of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in the hepatic regulation of metabolism. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 718–727.
He L, Hou X, Kanel G, Zeng N, Galicia V, Wang Y et al. The critical role of AKT2 in hepatic steatosis induced by PTEN loss. Am J Pathol 2010; 176: 2302–2308.
Leavens KF, Easton RM, Shulman GI, Previs SF, Birnbaum MJ . Akt2 is required for hepatic lipid accumulation in models of insulin resistance. Cell Metab 2009; 10: 405–418.
Matsumoto M, Han S, Kitamura T, Accili D . Dual role of transcription factor FoxO1 in controlling hepatic insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2464–2472.
Ide T, Shimano H, Yahagi N, Matsuzaka T, Nakakuki M, Yamamoto T et al. SREBPs suppress IRS-2-mediated insulin signalling in the liver. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 351–357.
Zhang J, Ou J, Bashmakov Y, Horton JD, Brown MS, Goldstein JL . Insulin inhibits transcription of IRS-2 gene in rat liver through an insulin response element (IRE) that resembles IREs of other insulin-repressed genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 3756–3761.
Frescas D, Valenti L, Accili D . Nuclear trapping of the forkhead transcription factor FoxO1 via Sirt-dependent deacetylation promotes expression of glucogenetic genes. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 20589–20595.
Valenti L, Rametta R, Dongiovanni P, Maggioni M, Fracanzani AL, Zappa M et al. Increased expression and activity of the transcription factor FOXO1 in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Diabetes 2008; 57: 1355–1362.
Mathurin P, Hollebecque A, Arnalsteen L, Buob D, Leteurtre E, Caiazzo R et al. Prospective study of the long-term effects of bariatric surgery on liver injury in patients without advanced disease. Gastroenterology 2009; 137: 532–540.
Valenti L, Nobili V, Al-Serri A, Rametta R, Leathart JB, Zappa MA et al. The APOC3 T-455C and C-482 T promoter region polymorphisms are not associated with the severity of liver damage independently of PNPLA3 I148M genotype in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. J Hepatol 2011; 55: 1409–1414.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005; 41: 1313–1321.
Ono H, Shimano H, Katagiri H, Yahagi N, Sakoda H, Onishi Y et al. Hepatic Akt activation induces marked hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, and hypertriglyceridemia with sterol regulatory element binding protein involvement. Diabetes 2003; 52: 2905–2913.
Fleischmann M, Iynedjian PB . Regulation of sterol regulatory-element binding protein 1 gene expression in liver: role of insulin and protein kinase B/cAkt. Biochem J 2000; 349: 13–17.
Foretz M, Guichard C, Ferre P, Foufelle F . Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on the hepatic expression of glucokinase and lipogenesis-related genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 12737–12742.
Foufelle F, Ferre P . New perspectives in the regulation of hepatic glycolytic and lipogenic genes by insulin and glucose: a role for the transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c. Biochem J 2002; 366: 377–391.
Diraison F, Dusserre E, Vidal H, Sothier M, Beylot M . Increased hepatic lipogenesis but decreased expression of lipogenic gene in adipose tissue in human obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2002; 282: E46–E51.
Pettinelli P, Del Pozo T, Araya J, Rodrigo R, Araya AV, Smok G et al. Enhancement in liver SREBP-1c/PPAR-alpha ratio and steatosis in obese patients: correlations with insulin resistance and n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid depletion. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1792: 1080–1086.
Kamagate A, Qu S, Perdomo G, Su D, Kim DH, Slusher S et al. FoxO1 mediates insulin-dependent regulation of hepatic VLDL production in mice. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 2347–2364.
Altomonte J, Cong L, Harbaran S, Richter A, Xu J, Meseck M et al. Foxo1 mediates insulin action on apoC-III and triglyceride metabolism. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1493–1503.
Dongiovanni P, Valenti L, Rametta R, Daly AK, Nobili V, Mozzi E et al. Genetic variants regulating insulin receptor signaling are associated with the severity of liver damage in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2010; 59: 267–273.
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2001; 50: 1844–1850.
Nakae J, Biggs WH, Kitamura T, Cavenee WK, Wright CV, Arden KC et al. Regulation of insulin action and pancreatic beta-cell function by mutated alleles of the gene encoding forkhead transcription factor Foxo1. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 245–253.
Kamagate A, Kim DH, Zhang T, Slusher S, Gramignoli R, Strom SC et al. FoxO1 links hepatic insulin action to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology 2010; 151: 3521–3535.
Michael MD, Kulkarni RN, Postic C, Previs SF, Shulman GI, Magnuson MA et al. Loss of insulin signaling in hepatocytes leads to severe insulin resistance and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Mol Cell 2000; 6: 87–97.
Kubota N, Kubota T, Itoh S, Kumagai H, Kozono H, Takamoto I et al. Dynamic functional relay between insulin receptor substrate 1 and 2 in hepatic insulin signaling during fasting and feeding. Cell Metab 2008; 8: 49–64.
Donnelly KL, Smith CI, Schwarzenberg SJ, Jessurun J, Boldt MD, Parks EJ . Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1343–1351.
Tamura S, Shimomura I . Contribution of adipose tissue and de novo lipogenesis to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1139–1142.
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr Biol 1997; 7: 261–269.
Wu X, Williams KJ . NOX4 pathway as a source of selective insulin resistance and responsiveness. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2012; 32: 1236–1245.
Girard J, Ferre P, Foufelle F . Mechanisms by which carbohydrates regulate expression of genes for glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes. Annu Rev Nutr 1997; 17: 325–352.
Prip-Buus C, Perdereau D, Foufelle F, Maury J, Ferre P, Girard J . Induction of fatty-acid-synthase gene expression by glucose in primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Dependency upon glucokinase activity. Eur J Biochem 1995; 230: 309–315.
Foufelle F, Gouhot B, Pegorier JP, Perdereau D, Girard J, Ferre P . Glucose stimulation of lipogenic enzyme gene expression in cultured white adipose tissue. A role for glucose 6-phosphate. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 20543–20546.
Towle HC, Kaytor EN, Shih HM . Regulation of the expression of lipogenic enzyme genes by carbohydrate. Annu Rev Nutr 1997; 17: 405–433.
Vaulont S, Vasseur-Cognet M, Kahn A . Glucose regulation of gene transcription. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 31555–31558.
Speliotes EK, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Wu J, Hernaez R, Kim LJ, Palmer CD et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that have distinct effects on metabolic traits. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: e1001324.
Kim SY, Kim HI, Kim TH, Im SS, Park SK, Lee IK et al. SREBP-1c mediates the insulin-dependent hepatic glucokinase expression. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 30823–30829.
Acknowledgements
We thank Alessandra Dorigo and Paolo Maggioni for clinical assistance, Marco Antonio Zappa and Enzo Lattuada for help in the collection of biological samples. The work was supported by the Associazione Malattie Metaboliche del Fegato ONLUS (nonprofit organization for the study and treatment of metabolic liver diseases).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rametta, R., Mozzi, E., Dongiovanni, P. et al. Increased insulin receptor substrate 2 expression is associated with steatohepatitis and altered lipid metabolism in obese subjects. Int J Obes 37, 986–992 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.181
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.181
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Phytochemicals targeting NAFLD through modulating the dual function of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) transcription factor signaling pathways
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2022)
-
The protective effects of the β3 adrenergic receptor agonist BRL37344 against liver steatosis and inflammation in a rat model of high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Connectivity mapping of angiotensin-PPAR interactions involved in the amelioration of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by Telmisartan
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Selective insulin resistance with differential expressions of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in human NAFLD livers
International Journal of Obesity (2018)
-
Proteomic and phosphoproteomic analysis of renal cortex in a salt-load rat model of advanced kidney damage
Scientific Reports (2016)