Abstract
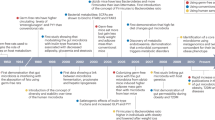
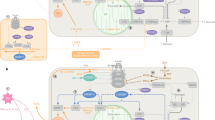
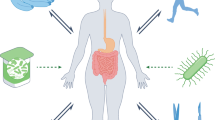
Human obesity can be viewed as a set of phenotypes that evolve over time in a sequence of stages that need to be precisely measured. Environmental, behavioral, genetic and biological factors interact to cause obesity. This presentation provides a clinical viewpoint on some biological processes that may explain some of the stages in the development of human obesity, its chronic maintenance and occurrence of complications, with a focus on brain structures, genetics, the profound alterations in adipose tissue biology and gut microbiota components. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery is an increasingly effective model to study in this context because it leads to major improvements in glucose and lipid homeostasis and to the amelioration of some systemic inflammatory markers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keith SW, Redden DT, Katzmarzyk PT, Boggiano MM, Hanlon EC, Benca RM et al. Putative contributors to the secular increase in obesity: exploring the roads less traveled. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30: 1585–1594.
Hawley JA, Holloszy JO . Exercise: it's the real thing! Nutr Rev 2009; 67: 172–178.
Patel SR, Hu FB . Short sleep duration and weight gain: a systematic review. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16: 643–653.
Hill JO, Wyatt HR, Reed GW, Peters JC . Obesity and the environment: where do we go from here? Science 2003; 299: 853–855.
Kuo LE, Kitlinska JB, Tilan JU, Li L, Baker SB, Johnson MD et al. Neuropeptide Y acts directly in the periphery on fat tissue and mediates stress-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nat Med 2007; 13: 803–811.
Casals-Casas C, Feige JN, Desvergne B . Interference of pollutants with PPARs: endocrine disruption meets metabolism. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32 (Suppl 6): S53–S61.
Kim MJ, Marchand P, Henegar C, Antignac JP, Alili R, Poitou C et al. Fate and complex pathogenic effects of dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls in obese subjects before and after drastic weight loss. Environ Health Perspect 2011; 119: 377–383.
Round JL, Mazmanian SK . The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 313–323.
van Ginneken V, Sitnyakowsky L, Jeffery JE . Infectobesity: viral infections (especially with human adenovirus-36: Ad-36) may be a cause of obesity. Med Hypotheses 2009; 72: 383–388.
Clément K, Sørensen TIA (eds). Obesity: Genomics and Postgenomics. Informa Healthcare, 2007, pp 1–600 (ISBN 978-0-8493-8089-1).
Prentice AM, Hennig BJ, Fulford AJ . Evolutionary origins of the obesity epidemic: natural selection of thrifty genes or genetic drift following predation release? Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32: 1607–1610.
Sorensen TI . Conference on ‘multidisciplinary approaches to nutritional problems’. Symposium on ‘diabetes and health’. Challenges in the study of causation of obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 2009; 68: 43–54.
Savage DB, Petersen KF, Shulman GI . Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 507–520.
Coll AP, Yeo GS, Farooqi IS, O’Rahilly S . SnapShot: the hormonal control of food intake. Cell 2008; 135: 572; e1–2.
Morton GJ, Cummings DE, Baskin DG, Barsh GS, Schwartz MW . Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 2006; 443: 289–295.
Nahon JL . The melanocortins and melanin-concentrating hormone in the central regulation of feeding behavior and energy homeostasis. C R Biol 2006; 329: 623–638; discussion 653–655.
Coppari R, Ramadori G, Elmquist JK . The role of transcriptional regulators in central control of appetite and body weight. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2009; 5: 160–166.
Scarpace PJ, Zhang Y . Leptin resistance: a prediposing factor for diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2009; 296: R493–R500.
Migrenne S, Marsollier N, Cruciani-Guglielmacci C, Magnan C . Importance of the gut-brain axis in the control of glucose homeostasis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2006; 6: 592–597.
Guyon A, Massa F, Rovere C, Nahon JL . How cytokines can influence the brain: a role for chemokines? J Neuroimmunol 2008; 198: 46–55.
Parton LE, Ye CP, Coppari R, Enriori PJ, Choi B, Zhang CY et al. Glucose sensing by POMC neurons regulates glucose homeostasis and is impaired in obesity. Nature 2007; 449: 228–232.
Bouchard C . Gene-environment interactions in the etiology of obesity: defining the fundamentals. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16 (Suppl 3): S5–S10.
Mutch DM, Clement K . Unraveling the genetics of human obesity. PLoS Genet 2006; 2: e188.
Junien C, Nathanielsz P . Report on the IASO Stock Conference 2006: early and lifelong environmental epigenomic programming of metabolic syndrome, obesity and type II diabetes. Obes Rev 2007; 8: 487–502.
Chung WK, Leibel RL . Molecular physiology of syndromic obesities in humans. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2005; 16: 267–272.
Farooqi IS, O’Rahilly S . Mutations in ligands and receptors of the leptin-melanocortin pathway that lead to obesity. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2008; 4: 569–577.
Hardy J, Singleton A . Genomewide association studies and human disease. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 1759–1768.
Leibel RL . Energy in, energy out, and the effects of obesity-related genes. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 2603–2604.
Hofker M, Wijmenga C . A supersized list of obesity genes. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 139–140.
Qi L, Cho YA . Gene-environment interaction and obesity. Nutr Rev 2008; 66: 684–694.
Cinti S . The adipose organ. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2005; 73: 9–15.
Arner P, Langin D . The role of neutral lipases in human adipose tissue lipolysis. Curr Opin Lipidol 2007; 18: 246–250.
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y et al. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1752–1761.
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 2004; 306: 457–461.
Boden G, Duan X, Homko C, Molina EJ, Song W, Perez O et al. Increase in endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins and genes in adipose tissue of obese, insulin-resistant individuals. Diabetes 2008; 57: 2438–2444.
Hosogai N, Fukuhara A, Oshima K, Miyata Y, Tanaka S, Segawa K et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 2007; 56: 901–911.
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante Jr AW . Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1796–1808.
Sethi JK, Vidal-Puig AJ . Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue function and plasticity orchestrate nutritional adaptation. J Lipid Res 2007; 48: 1253–1262.
Ailhaud G . Adipose tissue as a secretory organ: from adipogenesis to the metabolic syndrome. C R Biol 2006; 329: 570–577; discussion 653–655.
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA . Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 885–896.
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM . Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 2006; 444: 847–853.
Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO, Bernard S, Buchholz BA, Bergmann O et al. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature 2008; 453: 783–787.
Fruhbeck G, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Muruzabal FJ, Burrell MA . The adipocyte: a model for integration of endocrine and metabolic signaling in energy metabolism regulation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001; 280: E827–E847.
Guerre-Millo M . Adipose tissue and adipokines: for better or worse. Diabetes Metab 2004; 30: 13–19.
Skurk T, Alberti-Huber C, Herder C, Hauner H . Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 1023–1033.
Nijhuis J, Rensen SS, Slaats Y, van Dielen FM, Buurman WA, Greve JW . Neutrophil activation in morbid obesity, chronic activation of acute inflammation. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009; 17: 2014–2018.
Nishimura S, Manabe I, Nagasaki M, Eto K, Yamashita H, Ohsugi M et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med 2009; 15: 914–920.
Henegar C, Tordjman J, Achard V, Lacasa D, Cremer I, Guerre-Millo M et al. Adipose tissue transcriptomic signature highlights the pathological relevance of extracellular matrix in human obesity. Genome Biol 2008; 9: R14.
Curat CA, Miranville A, Sengenes C, Diehl M, Tonus C, Busse R et al. From blood monocytes to adipose tissue-resident macrophages: induction of diapedesis by human mature adipocytes. Diabetes 2004; 53: 1285–1292.
Cancello R, Tordjman J, Poitou C, Guilhem G, Bouillot JL, Hugol D et al. Increased infiltration of macrophages in omental adipose tissue is associated with marked hepatic lesions in morbid human obesity. Diabetes 2006; 55: 1554–1561.
Caspar-Bauguil S, Cousin B, Andre M, Nibbelink M, Galinier A, Periquet B et al. Weight-dependent changes of immune system in adipose tissue: importance of leptin. Exp Cell Res 2006; 312: 2195–2202.
Kintscher U, Hartge M, Hess K, Foryst-Ludwig A, Clemenz M, Wabitsch M et al. T-lymphocyte infiltration in visceral adipose tissue: a primary event in adipose tissue inflammation and the development of obesity-mediated insulin resistance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008; 28: 1304–1310.
Liu J, Divoux A, Sun J, Zhang J, Clement K, Glickman JN et al. Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat Med 2009; 15: 940–945.
Villaret A, Galitzky J, Decaunes P, Esteve D, Marques MA, Sengenes C et al. Adipose tissue endothelial cells from obese human subjects: differences among depots in angiogenic, metabolic, and inflammatory gene expression and cellular senescence. Diabetes 2010; 59: 2755–2763.
Lacasa D, Taleb S, Keophiphath M, Miranville A, Clement K . Macrophage-secreted factors impair human adipogenesis: involvement of proinflammatory state in preadipocytes. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 868–877.
Keophiphath M, Achard V, Henegar C, Rouault C, Clement K, Lacasa D . Macrophage-secreted factors promote a profibrotic phenotype in human preadipocytes. Mol Endocrinol 2009; 23: 11–24.
Constant VA, Gagnon A, Landry A, Sorisky A . Macrophage-conditioned medium inhibits the differentiation of 3T3-L1 and human abdominal preadipocytes. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 1402–1411.
Cinti S, Mitchell G, Barbatelli G, Murano I, Ceresi E, Faloia E et al. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J Lipid Res 2005; 46: 2347–2355.
Suganami T, Nishida J, Ogawa Y . A paracrine loop between adipocytes and macrophages aggravates inflammatory changes: role of free fatty acids and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 2062–2068.
Permana PA, Menge C, Reaven PD . Macrophage-secreted factors induce adipocyte inflammation and insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 341: 507–514.
Chun TH, Hotary KB, Sabeh F, Saltiel AR, Allen ED, Weiss SJ . A pericellular collagenase directs the 3-dimensional development of white adipose tissue. Cell 2006; 125: 577–591.
Pasarica M, Gowronska-Kozak B, Burk D, Remedios I, Hymel D, Gimble J et al. Adipose tissue collagen VI in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94: 5155–5162.
Divoux A, Tordjman J, Lacasa D, Veyrie N, Hugol D, Aissat A et al. Fibrosis in human adipose tissue: composition, distribution, and link with lipid metabolism and fat mass loss. Diabetes 2010; 59: 2817–2825.
Tordjman J, Poitou C, Hugol D, Bouillot JL, Basdevant A, Bedossa P et al. Association between omental adipose tissue macrophages and liver histopathology in morbid obesity: influence of glycemic status. J Hepatol 2009; 51: 354–362.
van der Poorten D, Milner KL, Hui J, Hodge A, Trenell MI, Kench JG et al. Visceral fat: a key mediator of steatohepatitis in metabolic liver disease. Hepatology 2008; 48: 449–457.
Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 741–752.
Cancello R, Henegar C, Viguerie N, Taleb S, Poitou C, Rouault C et al. Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes 2005; 54: 2277–2286.
Aron-Wisnewsky J, Tordjman J, Poitou C, Darakhshan F, Hugol D, Basdevant A et al. Human adipose tissue macrophages: m1 and m2 cell surface markers in subcutaneous and omental depots and after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94: 4619–4623.
Capel F, Klimcakova E, Viguerie N, Roussel B, Vitkova M, Kovacikova M et al. Macrophages and adipocytes in human obesity: adipose tissue gene expression and insulin sensitivity during calorie restriction and weight stabilization. Diabetes 2009; 58: 1558–1567.
Zhang H, DiBaise JK, Zuccolo A, Kudrna D, Braidotti M, Yu Y et al. Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 2365–2370.
Furet JP, Kong LC, Tap J, Poitou C, Basdevant A, Bouillot JL et al. Differential adaptation of human gut microbiota to bariatric surgery-induced weight loss: links with metabolic and low-grade inflammation markers. Diabetes 2010; 59: 3049–3057.
Cani PD, Delzenne NM . Interplay between obesity and associated metabolic disorders: new insights into the gut microbiota. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2009; 9: 737–743.
Zeyda M, Farmer D, Todoric J, Aszmann O, Speiser M, Gyori G et al. Human adipose tissue macrophages are of an anti-inflammatory phenotype but capable of excessive pro-inflammatory mediator production. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007; 31: 1420–1428.
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR . Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 175–184.
Lumeng CN, Deyoung SM, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR . Increased inflammatory properties of adipose tissue macrophages recruited during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2007; 56: 16–23.
Shi H, Kokoeva MV, Inouye K, Tzameli I, Yin H, Flier JS . TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 3015–3025.
Acknowledgements
I thank Dr Joan Tordjman for her contribution to the iconography.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Nutriomic projects on inflammation are supported by the Region Ile de France, the Commission of the European Communities (Collaborative Project ADAPT, contract number HEALTH-F2-2008-201100), Hepadip (http://www.hepadip.org/, contract LSHM-CT-2005-018734 and FLIP (Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no. Health-F2-2009-241762).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clément, K. Bariatric surgery, adipose tissue and gut microbiota. Int J Obes 35 (Suppl 3), S7–S15 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.141
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.141
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Changes in adipokine levels and metabolic profiles following bariatric surgery
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2022)
-
De la dysfonction du tissu adipeux blanc aux phénotypes anatomocliniques de l’obésité
Obésité (2017)
-
The Effects of Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss on Adipose Tissue in Morbidly Obese Women Depends on the Initial Metabolic Status
Obesity Surgery (2016)
-
Weight Loss and the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Using Lifestyle Therapy, Pharmacotherapy, and Bariatric Surgery: Mechanisms of Action
Current Obesity Reports (2015)
-
Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes upregulates elongase 6 and downregulates genes affecting triacylglycerol synthesis
International Journal of Obesity (2014)