Abstract
Background:
There is growing evidence that interleukin-6 (IL-6) is linked to the regulation of fat mass (FM). Our previous data define the common −174G>C IL-6 polymorphism as a marker for ‘vulnerable’ individuals at risk of age- and obesity-related diseases. An association between −174G>C IL-6 polymorphism and weight loss after bariatric surgery has been demonstrated.
Objective:
We investigated the impact of −174G>C IL-6 polymorphism on weight loss, body composition, fluid distribution and cardiometabolic changes in obese subjects, after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) surgery.
Design and Outcome measures:
A total of 40 obese subjects were studied at baseline and at 6 months follow-up after LAGB surgery. Cardiometabolic and genetic assessment of −174G>C IL-6 polymorphism, anthropometric, body composition and fluid distribution analysis were performed.
Results:
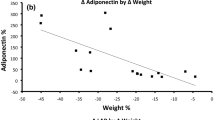
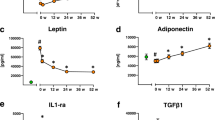
After LAGB surgery, significant reductions in weight (Δ%=−11.66±7.78, P<0.001), body mass index (P<0.001), total and trunk FM (kg, %) (Δ% of total FM=−22.22±12.15, P<0.01), bone mineral density (T-score) (P<0.001), resting metabolic rate (RMR) (P<0.01), and total body water and intracellular water (TBW, ICW) (P<0.05) were observed. At baseline, C(−) carriers of IL-6 polymorphism had a significantly higher RMR (P<0.05), free FM (kg), but less total and trunk FM (%), higher body cell mass (BCM), content of TBW (L) and ECW (extracellular water)/ICW ratio compared with C(+) carriers (P<0.001). After LAGB, C(+) carriers had a significantly stronger reduction of total FM (kg), but lower bone density, compared with C(−) carriers (P<0.05).
Conclusions:
Beyond the relationship between −174G>C IL-6 polymorphism and body composition, this study provides first evidence about the association of IL-6 variant with fluid distribution, at baseline, and FM and bone density loss in obese subjects at 6 months follow-up after LAGB surgery. LAGB was less effective if the subjects were carrying risk genotypes, C(−) carriers, for obesity, suggesting a role of genetic variations on bariatric surgery outcomes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohamed-Ali V, Goodrick S, Rawesh A, Katz DR, Miles JM, Yudkin JS et al. Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin- 6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 4196–4200.
Bastard JP, Jardel C, Bruckert E, Blondy P, Capeau J, Laville M et al. Elevated levels of interleukin 6 are reduced in serum and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 3338–3342.
Sopasakis VR, Sandqvist M, Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Schmelz M, Yang X et al. High local concentrations and effects on differentiation implicate interleukin-6 as a paracrine regulator. Obes Res 2004; 12: 454–460.
Fain JN, Madan AK, Hiler ML, Cheema P, Bahouth SW . Comparison of the release of adipokines by adipose tissue, adipose tissue matrix, and adipocytes from visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissues of obese humans. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 2273–2282.
Fried SK, Bunkin DA, Greenberg AS . Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 847–850.
Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Ahrén B, Rudling M, Carlsten H, Dickson SL et al. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat Med 2002; 8: 75–79.
Wallenius K, Wallenius VW, Sunter D, Dickson SL, Jansson J-O . Intracerebroventricular interleukin-6 treatment decreases body fat in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 2002; 293: 560–565.
Li G, Klein RL, Matheny M, King MA, Meyer EM, Scarpace PJ . Induction of uncoupling protein 1 by central interleukin-6 gene delivery is dependent on sympathetic innervation of brown adipose tissue, underlies one mechanism of body weight reduction in rats. Neuroscience 2002; 115: 879–889.
Hirano T . Interleukin 6, its receptor: ten years later. Int Rev Immunol 1998; 16: 249–284.
Trayhurn P, Wood IS . Adipokines: inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr 2004; 92: 347–355.
Di Renzo L, Galvano F, Orlandi C, Bianchi A, Di Giacomo C, La Fauci L et al. Oxidative Stress in normal-weight obese syndrome. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2010; 18: 2401.
De Lorenzo A, Deurenberg P, Pietrantuono M, Di Daniele N, Cervelli V, Andreoli A . How fat is obese? Acta Diabetol 2003; 40: S254–S257.
De Lorenzo A, Martinoli R, Vaia F, Di Renzo L . Normal weight obese (NWO) women: an evaluation of a candidate new syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2006; 16: 513–523.
De Lorenzo A, Del Gobbo V, Premrov MG, Bigioni M, Galvano F, Di Renzo L . Normal-weight obese syndrome: early inflammation? Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 85: 40–45.
Fishman D, Faulds G, Jeffery R, Mohamed-Ali V, Yudkin JS, Humphries S et al. The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1369–1376.
Wernstedt I, Eriksson AL, Berndtsson A, Hoffstedt J, Skrtic S, Hedner T et al. A common polymorphism in the interleukin-6 gene promoter is associated with overweight. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28: 1272–1279.
Berthier MT, Paradis AM, Tchernof A, Bergeron J, Prud'homme D, Després JP et al. The interleukin 6-174G/C polymorphism is associated with indices of obesity in men. J Hum Genet 2003; 48: 14–19.
Strandberg L, Mellström D, Ljunggren O, Grundberg E, Karlsson MK, Holmberg AH et al. IL6 and IL1B polymorphisms are associated with fat mass in older men: the MrOS Study Sweden. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16: 710–713.
Poitou C, Lacorte JM, Coupaye M, Bertrais S, Bedel JF, Lafon N et al. Relationship between single nucleotide polymorphisms in leptin, IL6 and adiponectin genes and their circulating product in morbidly obese subjects before and after gastric banding surgery. Obes Surg 2005; 15: 11–23.
Lubrano C, Mariani S, Badiali M, Cuzzolaro M, Barbaro G, Migliaccio S et al. Metabolic or bariatric surgery? Long-term effects of malabsorptive vs restrictive bariatric techniques on body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010; 34: 1404–1414.
Sesti G, Perego L, Cardellini M, Andreozzi F, Ricasoli C, Vedani P et al. Impact of common polymorphisms in candidate genes for insulin resistance and obesity on weight loss of morbidly obese subjects after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and hypocaloric diet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 5064–5069. Erratum in: J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90(10): 5810.
Anonymous. 1995 Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry: report of a WHO expert committee. WHO Tech Rep Ser 854: 1–452.
Consensus Development Conference Panel. NIH conference. Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Intern Ann Med 1991; 115: 956–961.
Marcus MD, Kalarchian MA . Courcoulas AP psychiatric evaluation follow-up of bariatric surgery patients. Am J Psychiatry 2009; 166: 285–291.
Lo Coco G, Gullo S, Salerno L, Iacoponelli R . The association among interpersonal problems, binge behaviors, and self-esteem, in the assessment of obese individuals. Compr Psychiatry 2011; 52: 164–170.
Wilson MM, Thomas DR, Rubenstein LZ, Chibnall JT, Anderson S, Baxi A et al. Appetite assessment: simple appetite questionnaire predicts weight loss in community-dwelling adults and nursing home residents. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82: 1074–1081.
Gortmaker SL, Peterson K, Wiecha J, Sobol AM, Dixit S, Fox MK et al. Reducing obesity via a school-based interdisciplinary intervention among youth: planet health. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153: 409–418.
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R . Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual 1998. Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL.
Di Renzo L, Del Gobbo V, Bigioni M, Premrov MG, Cianci R, De Lorenzo A . Body composition analyses in normal weight obese women. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2006; 10: 191–196.
De Lorenzo A, Candeloro N, Andreoli A, Durenberg P . Determination of intracellular water by multifrequency bioelectrical impedance. Ann Nutr Metab 1995; 39: 177–184.
Weir JB . New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol 1949; 109: 1–9.
International Diabetes Federation (IDF). The IDF Consensus Worldwide Definition of the Metabolic Syndrome 2006. International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium.
World Health Organization (WHO). Definition and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus and Intermediate Hyperglycemia. Report of a WHO/IDF Consultation. WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data, 2006.
Di Renzo L, Bertoli A, Bigioni M, Del Gobbo V, Premrov MG, Calabrese V et al. Body composition and −174G/C interleukin-6 promoter gene polymorphism: association with progression of insulin resistance in normal weight obese syndrome. Curr Pharm Des 2008; 14: 2699–2706.
Coupaye M, Bouillot JL, Coussieu C, Guy-Grand B, Basdevant A, Oppert JM . One-year changes in energy expenditure and serum leptin following adjustable silicone gastric banding in obese women. Obes Surg 2005; 15: 827–833.
Sergi G, Lupoli L, Busetto L . Changes in fluid compartments and body composition in obese women after weight loss induced by gastric banding. Ann Nutr Metab 2003; 47: 152–157.
Coupaye M, Bouillot JL, Poitou C, Schutz Y, Basdevant A, Oppert JM . Is lean body mass decreased after obesity treatment by adjustable gastric banding? Obes Surg 2007; 17: 427–433.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2004; 292: 1724–1737 (review). Erratum in JAMA 2005; 293(14): 1728.
Giusti V, Suter M, Héraïef E, Gaillard RC, Burckhardt P . Effects of laparoscopic gastric banding on body composition, metabolic profile and nutritional status of obese women: 12-months follow-up. Obes Surg 2004; 14: 239–245.
Gasteyger C, Suter M, Calmes JM, Gaillard RC, Giusti V . Changes in body composition, metabolic profile and nutritional status 24 months after gastric banding. Obes Surg 2006; 16: 243–250.
Andreoli A, Melchiorri G, De Lorenzo A, Caruso I, Sinibaldi Salimei P, Guerrisi M . Bioelectrical impedance measures in different position and vs dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2002; 42: 186–189.
Benedetti G, Mingrone G, Marcoccia S, Benedetti M, Giancaterini A, Greco AV et al. Body composition and energy expenditure after weight loss,following bariatric surgery. J Am Coll Nutr 2000; 19: 270–274.
Infanger D, Baldinger R, Branson R, Barbier T, Steffen R, Horber FF . Effect of significant intermediate-term weight loss on serum leptin levels and body composition in severely obese subjects. Obes Surg 2003; 13: 879–888.
Matthie J, Zarowitz B, De Lorenzo A, Andreoli A, Katzarski K, Pan G et al. Analytic assessment of the various bioimpedance methods used to estimate body water. J Appl Physiol 1998; 84: 1801–1816.
Savastano S, Belfiore A, Di Somma C, Mauriello C, Rossi A, Pizza G et al. Validity of bioelectrical impedance analysis to estimate body composition changes after bariatric surgery in premenopausal morbidly women. Obes Surg 2010; 20: 332–339.
Stephens JW, Hurel SJ, Cooper JA, Acharya J, Miller GJ, Humphries SE . A common functional variant in the interleukin-6 gene is associated with increased body mass index in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol Genet Metab 2004; 82: 180–186.
Klipstein-Grobusch K, Möhlig M, Spranger J, HoLMann K, Rodrigues FU, Sharma AM et al. Interleukin-6 g.-174G_C promoter polymorphism is associated with obesity in the EPIC-Potsdam Study. Obes Res 2006; 14: 14–18.
Grallert H, Huth C, Kolz M, Meisinger C, Herder C, Strassburger K et al. IL-6 promoter polymorphisms and quantitative traits related to the metabolic syndrome in KORA S4. Exp Gerontol 2006; 41: 737–745.
Qi L, Zhang C, van Dam RM, Hu FB . Interleukin-6 genetic variability and adiposity: associations in two prospective cohorts and systematic review in 26 944 individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 3618–3625.
Huth C, Illig T, Herder C, Gieger C, Grallert H, Vollmert C et al. Joint analysis of individual participants′ data from 17 studies on the association of the IL6 variant −174G>C with circulating glucose levels, interleukin-6 levels, and body mass index. Ann Med 2009; 41: 128–138.
Vozarova B, Fernandez-Real JM, Knowler WC, Gallart L, Hanson RL, Gruber JD et al. The interleukin-6 (-174) G/C promoter polymorphism is associated with type-2 diabetes mellitus in Native Americans and Caucasians. Hum Genet 2003; 112: 409–413.
Mohlig M, Boeing H, Spranger J, Osterhoff M, Kroke A, Fisher E et al. Body mass index and C–174G interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism interact in predicting type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1885–1890.
Fernandez-Real JM, Broch M, Vendrell J, Gutierrez C, Casamitjana R, Pugeat M et al. Interleukin-6 gene polymorphism and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2000; 49: 517–520.
Hamid YH, Rose CS, Urhammer SA, Glumer C, Nolsoe R, Kristiansen OP et al. Variations of the interleukin-6 promoter are associated with features of the metabolic syndrome in Caucasian Danes. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 251–260.
Bonaf M, Olivieri F, Cavallone L, Giovagnetti S, Mayegiani F, Cardelli M et al. A gender--dependent genetic predisposition to produce high levels of IL-6 is detrimental for longevity. Eur J Immunol 2001; 31: 2357–2361.
Riikola A, Sipilä K, Kähönen M, Jula A, Nieminen MS, Moilanen L et al. Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism and cardiovascular risk factors: the Health 2000 Survey. Atherosclerosis 2009; 207: 466–470.
Moleres A, Rendo-Urteaga T, Azcona C, Martínez JA, Gómez-Martínez S, Ruiz JR et al. Il6 gene promoter polymorphism (-174G/C) influences the association between fat mass and cardiovascular risk factors. J Physiol Biochem 2009; 65: 405–413.
Eder K, Baffy N, Falus A, Fulop AK . The major inflammatory mediator interleukin-6 and obesity. Inflamm Res 2009; 58: 727–736 (review).
Yang X, Jansson PA, Pellmé F, Laakso M, Smith U . Effect of the interleukin-6 (-174) g/c promoter polymorphism on adiponectin and insulin sensitivity. Obes Res 2005; 13: 813–817.
Kubaszek A, Pihlajamaki J, Punnonen K, Karhapaa P, Vauhkonen I, Laakso M . The C-174G promoter polymorphism of the IL-6 gene affects energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2003; 52: 558–561.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from Ministero Politiche Agricole e Forestali, Italy (PACB, D.M. 91567 Dic 29, 2004/2008). We thank Federica Fabiocchi, Annamaria Di Dionisio and Gaia Giugno for their contribution to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Renzo, L., Carbonelli, M., Bianchi, A. et al. Body composition changes after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: what is the role of −174G>C interleukin-6 promoter gene polymorphism in the therapeutic strategy?. Int J Obes 36, 369–378 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.132
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.132
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Genetic Correlates of Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery
Obesity Surgery (2021)
-
Why primary obesity is a disease?
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)
-
Changes in Resting Energy Expenditure in Relation to Body Weight and Composition Following Gastric Restriction: A Systematic Review
Obesity Surgery (2016)
-
C677T gene polymorphism of MTHFR and metabolic syndrome: response to dietary intervention
Journal of Translational Medicine (2014)
-
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Compared to a Multidisciplinary Weight Loss Program for Obesity—Effects on Body Composition and Protein Status
Obesity Surgery (2013)