Abstract
Background:
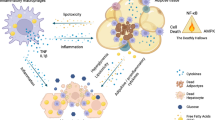
LIGHT (lymphotoxin-like inducible protein that competes with glycoprotein D for herpesvirus entry on T cells) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family, primarily expressed in lymphocytes, which was associated with the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and alterations of lipid homeostasis in animal models. We aimed to analyze whether LIGHT has a role in the human obesity-associated inflammatory status.
Methods:
The association between circulating LIGHT concentrations and clinical variables was studied in 190 subjects with different degrees of obesity and glucose tolerance. The expression and release of 21 different cytokines, and the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism were also evaluated after stimulation with LIGHT in cultured human differentiated adipocytes.
Results:
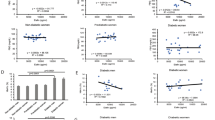
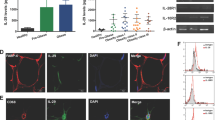
Serum LIGHT concentrations positively associated with body mass index (BMI), fat mass, glycated hemoglobin and fasting triglycerides, and negatively with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Circulating LIGHT concentrations were significantly increased in morbidly obese subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes. LIGHT induced the secretion of several cytokines and upregulated the expression and secretion of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, Growth Regulated Oncogene (GRO) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1). These observations were concomitant with the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB signalling in human differentiated adipocytes. LIGHT also upregulated the expression and synthesis of its own receptor (herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM)) and decreased the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) and fatty acid synthase.
Conclusion:
These data suggest that LIGHT may have a role in mediating chronic inflammation and alterations of lipid metabolism in obese subjects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma AM . Adipose tissue: a mediator of cardiovascular risk. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26 (Suppl 4): S5–S7.
Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ . The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 2001; 104: 487–501.
Mauri DN, Ebner R, Montgomery RI, Kochel KD, Cheung TC, Yu GL et al. LIGHT, a new member of the TNF superfamily, and lymphotoxin alpha are ligands for herpesvirus entry mediator. Immunity 1998; 8: 21–30.
Zhai Y, Guo R, Hsu TL, Yu GL, Ni J, Kwon BS et al. LIGHT, a novel ligand for lymphotoxin beta receptor and TR2/HVEM induces apoptosis and suppresses in vivo tumor formation via gene transfer. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1142–1151.
Schneider K, Potter KG, Ware CF . Lymphotoxin and LIGHT signaling pathways and target genes. Immunol Rev 2004; 202: 49–66.
Crowe PD, VanArsdale TL, Walter BN, Ware CF, Hession C, Ehrenfels B et al. A lymphotoxin-beta-specific receptor. Science 1994; 264: 707–710.
Oppenheim JJ, Zachariae CO, Mukaida N, Matsushima K . Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene ‘intercrine’ cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol 1991; 9: 617–648.
Montgomery RI, Warner MS, Lum BJ, Spear PG . Herpes simplex virus-1 entry into cells mediated by a novel member of the TNF/NGF receptor family. Cell 1996; 87: 427–436.
Yu KY, Kwon B, Ni J, Zhai Y, Ebner R, Kwon BS . A newly identified member of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TR6) suppresses LIGHT-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 13733–13736.
Shaikh RB, Santee S, Granger SW, Butrovich K, Cheung T, Kronenberg M et al. Constitutive expression of LIGHT on T cells leads to lymphocyte activation, inflammation, and tissue destruction. J Immunol 2001; 167: 6330–6337.
Rooney IA, Butrovich KD, Glass AA, Borboroglu S, Benedict CA, Whitbeck JC et al. The lymphotoxin-beta receptor is necessary and sufficient for LIGHT-mediated apoptosis of tumor cells. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 14307–14315.
Hehlgans T, Mannel DN . Recombinant, soluble LIGHT (HVEM ligand) induces increased IL-8 secretion and growth arrest in A375 melanoma cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2001; 21: 333–338.
Degli-Esposti MA, Davis-Smith T, Din WS, Smolak PJ, Goodwin RG, Smith CA . Activation of the lymphotoxin beta receptor by cross-linking induces chemokine production and growth arrest in A375 melanoma cells. J Immunol 1997; 158: 1756–1762.
Chang YH, Hsieh SL, Chao Y, Chou YC, Lin WW . Proinflammatory effects of LIGHT through HVEM and LTbetaR interactions in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biomed Sci 2005; 12: 363–375.
Rothe M, Wong SC, Henzel WJ, Goeddel DV . A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 1994; 78: 681–692.
Marsters SA, Ayres TM, Skubatch M, Gray CL, Rothe M, Ashkenazi A . Herpesvirus entry mediator, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family, interacts with members of the TNFR-associated factor family and activates the transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 14029–14032.
Kwon BS, Tan KB, Ni J, Oh KO, Lee ZH, Kim KK et al. A newly identified member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily with a wide tissue distribution and involvement in lymphocyte activation. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 14272–14276.
Fradette J, Wolfe D, Goins WF, Huang S, Flanigan RM, Glorioso JC . HSV vector-mediated transduction and GDNF secretion from adipose cells. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 48–58.
Granger SW, Rickert S . LIGHT-HVEM signaling and the regulation of T cell-mediated immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2003; 14: 289–296.
An MM, Fan KX, Zhang JD, Li HJ, Song SC, Liu BG et al. Lymphtoxin beta receptor-Ig ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis via blocking LIGHT/HVEM signaling. Pharmacol Res 2005; 52: 234–244.
Scholz H, Sandberg W, Damas JK, Smith C, Andreassen AK, Gullestad L et al. Enhanced plasma levels of LIGHT in unstable angina: possible pathogenic role in foam cell formation and thrombosis. Circulation 2005; 112: 2121–2129.
Lee WH, Kim SH, Lee Y, Lee BB, Kwon B, Song H et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 14 is involved in atherogenesis by inducing proinflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001; 21: 2004–2010.
Dahl CP, Gullestad L, Fevang B, Holm AM, Landro L, Vinge LE et al. Increased expression of LIGHT/TNFSF14 and its receptors in experimental and clinical heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 2008; 10: 352–359.
Beutler B, Cerami A . Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature 1986; 320: 584–588.
Lo JC, Wang Y, Tumanov AV, Bamji M, Yao Z, Reardon CA et al. Lymphotoxin beta receptor-dependent control of lipid homeostasis. Science 2007; 316: 285–288.
Santamarina-Fojo S, Gonzalez-Navarro H, Freeman L, Wagner E, Nong Z . Hepatic lipase, lipoprotein metabolism, and atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 1750–1754.
Poggi M, Jager J, Paulmyer-Lacroix O, Peiretti F, Gremeaux T, Verdier M et al. The inflammatory receptor CD40 is expressed on human adipocytes: contribution to crosstalk between lymphocytes and adipocytes. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 1152–1163.
Nieman DC, Henson DA, Nehlsen-Cannarella SL, Ekkens M, Utter AC, Butterworth DE et al. Influence of obesity on immune function. J Am Diet Assoc 1999; 99: 294–299.
Wang Y, Wang J, Sun Y, Wu Q, Fu YX . Complementary effects of TNF and lymphotoxin on the formation of germinal center and follicular dendritic cells. J Immunol 2001; 166: 330–337.
Morel Y, Schiano de Colella JM, Harrop J, Deen KC, Holmes SD, Wattam TA et al. Reciprocal expression of the TNF family receptor herpes virus entry mediator and its ligand LIGHT on activated T cells: LIGHT down-regulates its own receptor. J Immunol 2000; 165: 4397–4404.
Heo SK, Ju SA, Lee SC, Park SM, Choe SY, Kwon B et al. LIGHT enhances the bactericidal activity of human monocytes and neutrophils via HVEM. J Leukoc Biol 2006; 79: 330–338.
Edwards JR, Sun SG, Locklin R, Shipman CM, Adamopoulos IE, Athanasou NA et al. LIGHT (TNFSF14), a novel mediator of bone resorption, is elevated in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 1451–1462.
Fernandez-Real JM, Pickup JC . Innate immunity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2008; 19: 10–16.
Hansson GK . Medicine. LIGHT hits the liver. Science 2007; 316: 206–207.
Fernandez-Real JM, Ferri MJ, Vendrell J, Ricart W . Burden of infection and fat mass in healthy middle-aged men. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007; 15: 245–252.
Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL . The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 1–7.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Institut d'Investigació Biomèdica de Girona (Hospital de Girona, Dr Josep Trueta) and CIBER Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición CB06/03/010. We thank Oscar Rovira for clinical assistance and Gerard Pardo for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website (http://www.nature.com/ijo)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bassols, J., Moreno-Navarrete, J., Ortega, F. et al. LIGHT is associated with hypertriglyceridemia in obese subjects and increased cytokine secretion from cultured human adipocytes. Int J Obes 34, 146–156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.199
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.199
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Characterization of different fat depots in NAFLD using inflammation-associated proteome, lipidome and metabolome
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Increased Serum Levels of LIGHT/TNFSF14 in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Possible Role in Hepatic Inflammation
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology (2015)
-
LIGHT (TNFSF14) inhibits adipose differentiation without affecting adipocyte metabolism
International Journal of Obesity (2011)
-
DNA damage in normal-weight obese syndrome measured by Comet assay
Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism (2011)