Abstract
Objective:
Alcohol consumption promotes insulin sensitivity. In obesity, a decrease in body fat levels decreases the risk of developing insulin resistance; therefore, it is possible that alcohol improves insulin sensitivity by negatively affecting body fat. The aim of this study was to determine whether alcohol consumption promotes insulin sensitivity by reducing body fat levels in C57BL/6 male mice.
Methods:
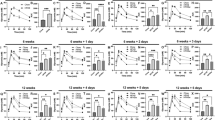
We examined the effects of alcohol consumption on insulin sensitivity in male mice with three different body weight (BW) phenotypes. The BWs were induced by feeding the mice a 30% calorie-restricted (CR) regimen, a low-fat (LF) diet and a high-fat (HF) diet. The mice had free access to water or 20% ethanol in the drinking water. To determine the effects of the three different BW phenotypes and of alcohol on glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity, we performed the insulin tolerance test (ITT) and glucose tolerance test (GTT) on the mice. The effects of the diets and alcohol on body composition, percent body fat (% BF), percent lean mass and bone mineral density (BMD) were determined by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA).
Results:
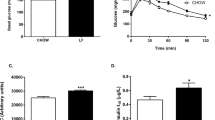
Data show that mice with the highest body fat levels (HF) were insulin resistant and glucose intolerant. In contrast, mice with the lowest body fat levels (CR) were the most insulin sensitive and cleared the injected endogenous glucose the fastest. Results show that alcohol did not affect GTT in any of the BW phenotypes. However, alcohol consumption promoted insulin sensitivity in mice consuming both the LF and HF diets. Alcohol consumption increased insulin sensitivity without affecting body fat levels, as body fat levels were similar in mice consuming the LF or HF diets and drinking either water or alcohol.
Conclusions:
Alcohol consumption promotes insulin sensitivity without affecting body fat levels in mice consuming LF and HF diets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, Beydoun MA . The obesity epidemic in the United States—gender, age, socioeconomic, racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev 2007; 29: 6–28.
Strumpf E . The obesity epidemic in the United States: causes and extent, risks and solutions. Commonw Fund 2004; 713: 1–6.
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM . Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006; 444: 840–846.
Kahn BB, Flier JS . Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2000; 106: 473–481.
Gigleux I, Gagnon J, St-Pierre A, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, Meyer F et al. Moderate alcohol consumption is more cardioprotective in men with the metabolic syndrome. J Nutr 2006; 136: 3027–3032.
Ajani UA, Hennekens CH, Spelsberg A, Manson JE . Alcohol consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus among US male physicians. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160: 1025–1030.
Flanagan DE, Moore VM, Godsland IF, Cockington RA, Robinson JS, Phillips DI . Alcohol consumption and insulin resistance in young adults. Eur J Clin Invest 2000; 30: 297–301.
Mayer EJ, Newman B, Quesenberry Jr CP, Friedman GD, Selby JV . Alcohol consumption and insulin concentrations: role of insulin in associations of alcohol intake with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides. Circulation 1993; 88: 2190–2197.
Koppes LL, Dekker JM, Hendriks HF, Bouter LM, Heine RJ . Moderate alcohol consumption lowers the risk of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 719–725.
Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Whincup PH . Alcohol and adiposity: effects of quantity and type of drink and time relation with meals. Int J Obes 2005; 29: 1436–1444.
Tsumura K, Hayashi T, Suematsu C, Endo G, Fujii S, Okada K . Daily alcohol consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes in Japanese men. Diabetes Care 1999; 22: 1432–1437.
Chan JM, Rimm EB, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC . Obesity, fat distribution, and weight gain as risk factors for clinical diabetes in men. Diabetes Care 1994; 17: 961–969.
Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003; 289: 76–79.
Wilding JP . The importance of free fatty acids in the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 2007; 24: 934–945.
Field AE, Coakley EH, Must A, Spadano JL, Laird N, Dietz WH et al. Impact of overweight on the risk of developing common chronic diseases during a 10-year period. Arch Intern Med 2001; 161: 1581–1586.
Núñez NP, Carpenter CL, Perkins SN, Berrigan D, Jaque SV, Ingles SA et al. Extreme obesity reduces bone mineral density: complementary evidence from mice and women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007; 15: 1980–1987.
Yakar S, Núñez NP, Pennisi P, Brodt P, Sun H, Fallavollita L et al. Increased tumor growth in mice with diet-induced obesity: impact of ovarian hormones. Endocrinology 2006; 147: 826–834.
Cañete R, Gil-Campos M, Aguilera CM, Gil A . Development of insulin resistance and its relation to diet in the obese child. Eur J Nutr 2007; 46: 181–187.
Nishikawa S, Yasoshima A, Doi K, Nakayama H, Uetsuka K . Involvement of sex, strain and age factors in high fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6J and BALB/cA mice. Exp Anim 2007; 56: 263–272.
Fueki Y, Miida T, Wardaningsih E, Ito M, Nakamura A, Takahashi A et al. Regular alcohol consumption improves insulin resistance in healthy Japanese men independent of obesity. Clin Chim Acta 2007; 382: 71–76.
Hu FB, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Colditz G, Liu S, Solomon CG et al. Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 790–797.
Nunez NP, Perkins SN, Smith NC, Berrigan D, Berendes DM, Varticovski L et al. Obesity accelerates mouse mammary tumor growth in the absence of ovarian hormones. Nutr Cancer 2008; 60: 534–541.
Steinberger J, Daniels SR . Obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in children. Circulation 2003; 107: 1448–1453.
Beulens JW, de Zoete EC, Kok FJ, Schaafsma G, Hendriks HF . Effect of moderate alcohol consumption on adipokines and insulin sensitivity in lean and overweight men: a diet intervention study. Eur J Clin Nutr 2007; 10: 1–8.
Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG . Alcohol, body weight, and weight gain in middle-aged men. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77: 1312–1317.
Muller M, Grobbee DE, den Tonkelaar I, Lamberts SW, van der Schouw YT . Association between alcohol consumption and insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular disease risk factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 2618–2623.
Liu S, Serdula MK, Williamson DF, Mokdad AH, Byers T . A prospective study of alcohol intake and change in body weight among U.S. adults. Am J Epidemiol 1994; 140: 912–920.
Shah M, Jeffrey RW, Hannan PJ, Onstad L . Relationship between socio-demographic and behavior variables, and body mass index in a population with high-normal blood pressure: hypertension prevention trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 1989; 43: 583–596.
Dixon JB, Dixon ME, O’Brien PE . Alcohol consumption in the severely obese: relationship with the metabolic syndrome. Obes Res 2002; 10: 245–252.
Hendriks HF . Moderate alcohol consumption and insulin sensitivity: observations and possible mechanisms. Ann Epidemiol 2007; 17: S40–S42.
Zilkens RR, Burke V, Watts G, Beilin LJ, Puddey IB . The effect of alcohol intake on insulin sensitivity in men: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 608–612.
Wei M, Gibbons LW, Mitchell TL, Kampert JB, Blair SN . Alcohol intake and incidence of type 2 diabetes in men. Diabetes Care 2000; 23: 18–22.
Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Perry IJ, Alberti KG . Alcohol consumption and the incidence of type 2 diabetes. J Epidemiol Community Health 2002; 56: 542–548.
Kang L, Sebastian BM, Pritchard MT, Pratt BT, Previs SF, Nagy LE . Chronic ethanol-induced insulin resistance is associated with macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue and altered expression of adipocytokines. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2007; 31: 1–8.
Kim JY, Nolte LA, Hansenn PA, Han DH, Ferguson K, Thompson PA et al. High-fat diet-induced muscle insulin resistance: relationship to visceral fat mass. Am J Physiol Regul Integrat Comp Physiol 2000; 279: 2057–2065.
van de Wiel A . Diabetes mellitus and alcohol. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2004; 20: 263–267.
Jonsson IM, Verdrengh M, Brisslert M, Lindblad S, Bokarewa M, Islander U et al. Ethanol prevents development of destructive arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 258–263.
Joosten MM, Beulens JW, Kersten S, Hendriks HF . Moderate alcohol consumption increases insulin sensitivity and ADIPOQ expression in postmenopausal women: a randomized, crossover trial. Diabetologia 2008; 51: 1375–1381.
Lu JY, Huang KC, Chang LC, Huang YS, Chi YC, Su TC et al. Adiponectin: a biomarker of obesity-induced insulin resistance in adipose tissue and beyond. J Biomed Sci 2008; 15: 565–576.
Huang Z, Sjöholm A . Ethanol acutely stimulates islet blood flow, amplifies insulin secretion, and induces hypoglycemia via nitric oxide and vagally mediated mechanisms. Endocrinology 2008; 149: 232–236.
Acknowledgements
Animal care was provided in accordance with the procedures outlined in the ‘Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals’ (NIH Publication No. 86-23, 1985). This work was supported by grants ACS RSG CNE-113703 (NPN), NCI 1K22CA127519-01A1 (NPN); and by NIEHS National Institutes of Health Grant ES09145 & National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Center grants ES007784.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J., Smith, R., Harvey, A. et al. Alcohol consumption promotes insulin sensitivity without affecting body fat levels. Int J Obes 33, 197–203 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.266
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.266
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Wine consumption throughout life is inversely associated with type 2 diabetes risk, but only in overweight individuals: results from a large female French cohort study
European Journal of Epidemiology (2014)
-
Effects of body weight and alcohol consumption on insulin sensitivity
Nutrition Journal (2010)