Abstract
Objective:
The T allele of the single-nucleotide polymorphism rs7903146 in TCF7L2 (transcription factor 7 like 2 gene) is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The aim of this study was to analyze whether there is an allele-dosage effect on changes of insulin resistance and sensitivity indices in overweight children participating in a lifestyle intervention.
Methods:
We genotyped rs7903146 in 236 overweight children (mean age 10.7 years, mean body mass index (BMI) 28.1 kg/m2) completing a 1-year lifestyle intervention. Degree of overweight as BMI-SDS, homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and the insulin sensitivity index QUICKI were measured before and after intervention.
Results:
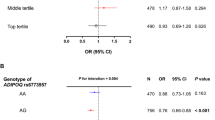
Lifestyle intervention resulted in an overweight reduction of −0.29±0.02 BMI-SDS. HOMA-IR (−0.63±0.22) and QUICKI (+0.008±0.003) indices improved significantly (P<0.05) in the course of the intervention in the 155 children with a decrease of BMI-SDS. There was an additive negative effect of T allele on changes of HOMA-IR (P=0.041) and QUICKI (P=0.001) in linear regression analyses adjusted to changes of weight status, age, gender and pubertal stage.
Conclusion:
Overweight children showed a negative dosage-allele effect per T allele at single-nucleotide polymorphism rs7903146 in TCF7L2 concerning an improvement of insulin resistance and sensitivity after overweight reduction in a lifestyle intervention. This finding further suggests that this polymorphism might be involved in glucose metabolism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reinehr T, Kiess W, Kapellen T, Andler W . Insulin sensitivity among obese children and adolescents, according to degree of weight loss. Pediatrics 2004; 114: 1569–1573.
Reinehr T, de Sousa G, Andler W . Longitudinal analyses between overweight, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular risk factors in children. Obes Res 2005; 13: 1824–1833.
Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 320–323.
Chandak GR, Janipalli CS, Bhaskar S, Kulkarni SR, Mohankrishna P, Hattersley AT et al. Common variants in the TCF7L2 gene are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Indian population. Diabetologia 2007; 50: 63–67.
Humphries SE, Gable D, Cooper JA, Ireland H, Stephens JW, Hurel SJ et al. Common variants in the TCF7L2 gene and predisposition to type 2 diabetes in UK European Whites, Indian Asians and Afro-Caribbean men and women. J Mol Med 2006; 84: 1–10.
Lehman DM, Hunt KJ, Leach RJ, Hamlington J, Arya R, Abboud HE et al. Haplotypes of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene and its upstream region are associated with type 2 diabetes and age of onset in Mexican Americans. Diabetes 2007; 56: 389–393.
Florez JC, Jablonski KA, Bayley N, Pollin TI, de Bakker PI, Shuldiner AR et al. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. TCF7L2 polymorphisms and progression to diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 241–250.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH . Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity world-wide: international survey. BMJ 2000; 320: 1240–1243.
Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Wabitsch M, Geller F, Ziegler A, Geiß HC, Hesse V et al. Percentiles of body mass index in children and adolescents evaluated from different regional German studies. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 2001; 149: 807–818.
Cole TJ . The LMS method for constructing normalized growth standards. Eur J Clin Nutr 1990; 44: 45–60.
Reinehr T, de Sousa G, Toschke M, Andler W . Long-term follow-up of cardiovascular risk factors in obese children after intervention. Am J Clin Nutr 2006; 84: 490–496.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Katz A, Nambi SS, Mather K, Baron AD, Follmann DA, Sullivan G et al. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index: a simple, accurate method for assessing insulin sensitivity in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 2402–2410.
Ye S, Dhillon S, Ke X, Collins AR, Day IN . An efficient procedure for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: E88.
Roth CL, Hinney A, Reinehr T, Schreiner F, Nguyen TT, Müller T et al. TCF7L2 polymorphism rs7903146 and predisposition for type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese children. Horm Metab Res 2008 [e-pub ahead of print].
Knip M, Nuutinien O . Long-term effects of weight reduction on serum lipids and plasma insulin in obese children. Am J Clin Nutr 1993; 57: 490–493.
Körner A, Berndt J, Sturmvoll M, Kiess W, Kovacs P . TCF7L2-gene polymorphisms confer an increased risk for early impairment of glucose metabolism and increased height in obese children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 1956–1960.
Lyssenko V, Lupi R, Marchetti P, Del Guerra S, Orho-Melander M, Almgren P et al. Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2155–2163.
Cauchi S, Choquet H, Gutiérrez-Aguilar R, Capel F, Grau K, Proença C et al. Effects of TCF7L2 polymorphisms on obesity in European populations. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16: 476–482.
Wallace TM, Matthews DR . The assessment of insulin resistance in man. Diabet Med 2002; 19: 527–533.
Acknowledgements
We thank all probands and their families for their participation. This work was supported by grants from the German Ministry of Education and Research (Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung; National Genome Research Network, NGFN1 and 2 and NGFNplus, obesity network LARGE), the European Union (FP6 LSHMCT-2003-503041) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG; HE 1446/4-1). The skilful technical assistance of S Düerkop and Essen was highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study is registered at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00435734).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinehr, T., Friedel, S., Mueller, T. et al. Evidence for an influence of TCF7L2 polymorphism rs7903146 on insulin resistance and sensitivity indices in overweight children and adolescents during a lifestyle intervention. Int J Obes 32, 1521–1524 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.146
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.146
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effect of TCF7L2 on the relationship between lifestyle factors and glycemic parameters: a systematic review
Nutrition Journal (2022)
-
Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: inter-relation of risk factors and treatment
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2020)
-
Reversing the tide — diagnosis and prevention of T2DM in populations of African descent
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2018)
-
Susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus—from genes to prevention
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2014)
-
Long-term effects of an inpatient weight-loss program in obese children and the role of genetic predisposition-rationale and design of the LOGIC-trial
BMC Pediatrics (2012)