Abstract
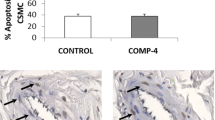
Diabetes mellitus (DM)-associated ED is predominantly due to neurovascular dysfunction mediated by nitric oxide (NO) suppression. Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) are widely used for treating cardiovascular disease in China. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of PNS on penile erection and corpus cavernosum tissues in rats with diabetes-associated ED. Four weeks after PNS treatment, erectile function was assessed by intracavernous pressure (ICP) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) measurements. The level of NO, cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in cavernous tissue were assessed. Immunohistochemical staining and TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling) were performed for detecting endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) and apoptosis, respectively. The results show that ICP/MAP ratio was significantly increased in high-dose (150 mg kg−1 per day) PNS-treated group compared with the diabetic ED untreated group (DM group). Compared with the untreated group, the expression of eNOS and the levels of NO and cGMP were increased in the PNS-treated groups. Moreover, apoptosis was markedly decreased in the group that received 150 mg kg−1 per day of PNS. These results suggest that PNS may be used for improving the ED in diabetic rats via the NO/cGMP pathway and restores the function of endothelium in corpus cavernosum.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costabile RA . Optimizing treatment for diabetes mellitus induced erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2003; 170: S35–S38, discussion S39.
Burnett AL, Lowenstein CJ, Bredt DS, Chang TS, Snyder SH . Nitric oxide: a physiologic mediator of penile erection. Science 1992; 257: 401–403.
Akingba AG, Burnett AL . Endothelial nitric oxide synthase protein expression, localization, and activity in the penis of the alloxan-induced diabetic rat. Mol Urol 2001; 5: 189–197.
Cartledge JJ, Eardley I, Morrison JF . Advanced glycation end-products are responsible for the impairment of corpus cavernosal smooth muscle relaxation seen in diabetes. BJU Int 2001; 87: 402–407.
Chaiban JT, Azar ST . Erectile dysfunction in diabetic patients. J Med Liban 2004; 52: 217–219.
Corbin JD, Francis SH, Webb DJ . Phosphodiesterase type 5 as a pharmacologic target in erectile dysfunction. Urology 2002; 60: 4–11.
Angulo J, Cuevas P, Gabancho S, Gonzalez-Corrochano R, Videla S, Saenz de Tejada I . Enhancement of both EDHF and NO/cGMP pathways is necessary to reverse erectile dysfunction in diabetic rats. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 341–346.
Moore CR, Wang R . Pathophysiology and treatment of diabetic erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl 2006; 8: 675–684.
Wang CZ, McEntee E, Wicks S, Wu JA, Yuan CS . Phytochemical and analytical studies of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) FH Chen. J Nat Med 2006; 60: 97–106.
Chen SW, Li XH, Ye KH, Jiang ZF, Ren XD . Total saponins of Panax notoginseng protected rabbit iliac artery against balloon endothelial denudation injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2004; 25: 1151–1156.
Hong SJ, Wan JB, Zhang Y, Hu G, Lin HC, Seto SW et al. Angiogenic effect of saponin extract from Panax notoginseng on HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. Phytother Res 2009; 23: 677–686.
Wu L, Zhang W, Tang YH, Li H, Chen BY, Zhang GM et al. Effect of total saponins of "panax notoginseng root" on aortic intimal hyperplasia and the expressions of cell cycle protein and extracellular matrix in rats. Phytomedicine 2010; 17: 233–240.
Sun K, Wang CS, Guo J, Horie Y, Fang SP, Wang F et al. Protective effects of ginsenoside Rb1, ginsenoside Rg1, and notoginsenoside R1 on lipopolysaccharide-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat mesentery. Life Sci 2007; 81: 509–518.
Guan YY, Zhou JG, Zhang Z, Wang GL, Cai BX, Hong L et al. Ginsenoside-Rd from panax notoginseng blocks Ca2+ influx through receptor- and store-operated Ca2+ channels in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2006; 548: 129–136.
Kwan CY, Kwan TK . Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2000; 21: 1101–1105.
Yang CY, Wang J, Zhao Y, Shen L, Jiang X, Xie ZG et al. Anti-diabetic effects of Panax notoginseng saponins and its major anti-hyperglycemic components. J Ethnopharmacol 2010; 130: 231–236.
Shirai M, Yamanaka M, Shiina H, Igawa M, Kawakami T, Ishii N et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor restores erectile function through modulation of the insulin-like growth factor system and sex hormone receptors in diabetic rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 341: 755–762.
Yamanaka M, Shirai M, Shiina H, Tanaka Y, Enokida H, Tsujimura A et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor restores erectile function through inhibition of apoptosis in diabetic rat penile crura. J Urol 2005; 173: 318–323.
LacKamp A, Zhang GC, Mao LM, Fibuch EE, Wang JQ . Loss of surface N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor proteins in mouse cortical neurones during anaesthesia induced by chloral hydrate in vivo. Br J Anaesth 2009; 102: 515–522.
Cheng F, Yu WM, Xia Y, Zhang XB, Yang SX, Ge MH . Effects of buried penis on the structure and function of corpus cavernosum in a rat model. Chin Med J (Engl) 2010; 123: 1736–1740.
Feng XT, Qin CB, Leng J, Tang QL, Shi H, Zhai LN et al. Yidiyin, a Chinese herbal decoction, improves erectile dysfunction in diabetic patients and rats through the NO-cGMP pathway. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2012; 76: 257–263.
De Vriese AS, Verbeuren TJ, Van de Voorde J, Lameire NH, Vanhoutte PM . Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 2000; 130: 963–974.
Musicki B, Burnett AL . Endothelial dysfunction in diabetic erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2007; 19: 129–138.
Hsueh WA, Anderson PW . Hypertension, the endothelial cell, and the vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 1992; 20: 253–263.
Bernabe J, Rampin O, Sachs BD, Giuliano F . Intracavernous pressure during erection in rats: an integrative approach based on telemetric recording. Am J Physiol 1999; 276: R441–R449.
Lin YM, Lin JS . The rabbit as an intracavernous injection study model. Urol Res 1996; 24: 27–32.
Albersen M, Fandel TM, Zhang H, Banie L, Lin G, De Ridder D et al. Pentoxifylline promotes recovery of erectile function in a rat model of postprostatectomy erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol 2011; 59: 286–296.
Yang R, Wang J, Chen Y, Sun Z, Wang R, Dai Y . Effect of caffeine on erectile function via up-regulating cavernous cyclic guanosine monophosphate in diabetic rats. J Androl 2008; 29: 586–591.
Huang YC, Ning H, Shindel AW, Fandel TM, Lin G, Harraz AM et al. The effect of intracavernous injection of adipose tissue-derived stem cells on hyperlipidemia-associated erectile dysfunction in a rat model. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 1391–1400.
Zhao W, Sato Y, Melman A, Andersson KE, Christ G . Metrics for evaluation of age-related changes in erectile capacity in a rodent model. J Sex Med 2009; 6: 1885–1892.
Angulo J, Gonzalez-Corrochano R, Cuevas P, Fernandez A, La Fuente JM, Rolo F et al. Diabetes exacerbates the functional deficiency of NO/cGMP pathway associated with erectile dysfunction in human corpus cavernosum and penile arteries. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 758–768.
Cartledge JJ, Eardley I, Morrison JF . Nitric oxide-mediated corpus cavernosal smooth muscle relaxation is impaired in ageing and diabetes. BJU Int 2001; 87: 394–401.
Leung KW, Cheng YK, Mak NK, Chan KK, Fan TP, Wong RN . Signaling pathway of ginsenoside-Rg1 leading to nitric oxide production in endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 3211–3216.
Chan LS, Yue PY, Mak NK, Wong RN . Role of microRNA-214 in ginsenoside-Rg1-induced angiogenesis. Eur J Pharm Sci 2009; 38: 370–377.
Lu JP, Ma ZC, Yang J, Huang J, Wang SR, Wang SQ . Ginsenoside Rg1-induced alterations in gene expression in TNF-alpha stimulated endothelial cells. Chin Med J (Engl) 2004; 117: 871–876.
Seftel AD, Vaziri ND, Ni Z, Razmjouei K, Fogarty J, Hampel N et al. Advanced glycation end products in human penis: elevation in diabetic tissue, site of deposition, and possible effect through iNOS or eNOS. Urology 1997; 50: 1016–1026.
Singh R, Barden A, Mori T, Beilin L . Advanced glycation end-products: a review. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 129–146.
Kim JJ, Xiao H, Tan Y, Wang ZZ, Paul Seale J, Qu X . The effects and mechanism of saponins of Panax notoginseng on glucose metabolism in 3T3-L1 cells. Am J Chin Med 2009; 37: 1179–1189.
Alici B, Gumustas MK, Ozkara H, Akkus E, Demirel G, Yencilek F et al. Apoptosis in the erectile tissues of diabetic and healthy rats. BJU Int 2000; 85: 326–329.
Yamanaka M, Shirai M, Shiina H, Tanaka Y, Tsujimura A, Matsumiya K et al. Diabetes induced erectile dysfunction and apoptosis in penile crura are recovered by insulin treatment in rats. J Urol 2003; 170: 291–297.
Zhang Y, Ye QF, Lu L, Xu XL, Ming YZ, Xiao JS . Panax notoginseng saponins preconditioning protects rat liver grafts from ischemia/reperfusion injury via an antiapoptotic pathway. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2005; 4: 207–212.
Qiang H, Zhang C, Shi ZB, Yang HQ, Wang KZ . Protective effects and mechanism of Panax Notoginseng saponins on oxidative stress-induced damage and apoptosis of rabbit bone marrow stromal cells. Chin J Integr Med 2010; 16: 525–530.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, F., Gou, X. Panax notoginseng saponins improve the erectile dysfunction in diabetic rats by protecting the endothelial function of the penile corpus cavernosum. Int J Impot Res 25, 206–211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2013.19
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2013.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The therapeutic effect of ALT-711 on erectile function in rats treated with high-level AGEs (advanced glycation end products) containing diet
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Resveratrol treatment may preserve the erectile function after radiotherapy by restoring antioxidant defence mechanisms, SIRT1 and NOS protein expressions
International Journal of Impotence Research (2018)