Abstract
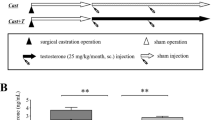
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) is a well-known mechanism for the effective treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Androgen supplementation has also been prescribed for treating ED. However, it has been widely accepted that androgen can upregulate PDE5 expression, and thus creating a paradox in which a positive regulator of erectile function (androgen) could possibly increase the level of a negative regulator (PDE5). To solve this paradox, we conducted a systematic search of the PubMed and a non-systematic search of the Internet using PDE5, erectile, penis, testosterone and androgen as keywords. The retrieved papers were analyzed for data concerning the expression and regulation of PDE5 by androgens. Human and rat PDE5A gene sequences were retrieved from GenBank and computer-analyzed. The results showed that a putative androgen-response element (ARE) was reported in a study of human PDE5A gene promoter, and this prompted a separate study on whether androgen regulates PDE5 expression. The positive outcome in the latter study has since been cited in 17 review and editorial articles as the underlying mechanism for androgen’s therapeutic effects on ED. In addition, five other research studies also reached the same conclusion. On the other hand, two independent studies on the genome-wide searches for androgen-regulated genes did not find PDE5A as a candidate. Sequence analysis conducted in this study also failed to find ARE in rat PDE5A gene. Two independent studies on Leydig cells also failed to find positive regulation of PDE5 expression by androgen. Two other studies found concomitant reduction of cavernous smooth muscle and PDE5 expression in castrated rats. One of these studies also found no effect of androgen on PDE5 expression in cultured cavernous smooth muscle cells. Thus, it appears that reduced PDE5 expression in castrated animals is due to reduced smooth muscle content and that PDE5A gene is not directly regulated by androgens.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Litwin MS, Nied RJ, Dhanani N . Health-related quality of life in men with erectile dysfunction. J Gen Intern Med 1998; 13: 159–166.
Dorsey P, Keel C, Klavens M, Hellstrom WJ . Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2010; 11: 1109–1122.
Thomas MK, Francis SH, Corbin JD . Characterization of a purified bovine lung cGMP-binding cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 1990; 265: 14964–14970.
Lin CS . Phosphodiesterase type 5 regulation in the penile corpora cavernosa. J Sex Med 2009; 6 (Suppl 3): 203–209.
Lin CS, Lin G, Lue TF . Cyclic nucleotide signaling in cavernous smooth muscle. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 478–491.
Lin CS, Xin ZC, Wang Z, Lin G, Lue TF . Molecular Yin and Yang of erectile function and dysfunction. Asian J Androl 2008; 10: 433–440.
Shabsigh R . Testosterone therapy in erectile dysfunction and hypogonadism. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 785–792.
Vignozzi L, Corona G, Petrone L, Filippi S, Morelli AM, Forti G et al. Testosterone and sexual activity. J Endocrinol Invest 2005; 28: 39–44.
Morelli A, Filippi S, Zhang XH, Luconi M, Vignozzi L, Mancina R . Peripheral regulatory mechanisms in erection. Int J Androl 2005; 28 (Suppl 2): 23–27.
Seftel AD . Testosterone regulates PDE5 expression and in vivo responsiveness to tadalafil in rat corpus cavernosum. J Urol 2005; 174: 657–658.
Morelli A, Vignozzi L, Filippi S, Mancina R, Maggi M . Erectile dysfunction: molecular biology, pathophysiology and pharmacological treatment. Miner Urol Nefrol 2005; 57: 85–90.
Gooren LJ, Saad F . Recent insights into androgen action on the anatomical and physiological substrate of penile erection. Asian J Androl 2006; 8: 3–9.
Buvat J, Bou Jaoude G . Significance of hypogonadism in erectile dysfunction. World J Urol 2006; 24: 657–667.
Shabsigh R, Rajfer J, Aversa A, Traish AM, Yassin A, Kalinchenko SY et al. The evolving role of testosterone in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Int J Clin Pract 2006; 60: 1087–1092.
Greco EA, Spera G, Aversa A . Combining testosterone and PDE5 inhibitors in erectile dysfunction: basic rationale and clinical evidences. Eur J Urol 2006; 50: 940–947.
Burnett AL . Molecular pharmacotherapeutic targeting of PDE5 for preservation of penile health. J Androl 2008; 29: 3–14.
Gurbuz N, Mammadov E, Usta MF . Hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction: an overview. Asian J Androl 2008; 10: 36–43.
Hwang TI, Lin YC . The relationship between hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2008; 20: 231–235.
Traish AM . Androgens play a pivotal role in maintaining penile tissue architecture and erection: a review. J Androl 2009; 30: 363–369.
Yassin AA, Saad F . Testosterone and erectile dysfunction. J Androl 2008; 29: 593–604.
Yassin AA, Akhras F, El-Sakka AI, Saad F . Cardiovascular diseases and erectile dysfunction: the two faces of the coin of androgen deficiency. Andrologia 2011; 43: 1–8.
Zhang XH, Melman A, Disanto ME . Update on corpus cavernosum smooth muscle contractile pathways in erectile function: a role for testosterone? J Sex Med 2011; 8: 1865–1879.
Mazzola CR, Mulhall JP . Impact of androgen deprivation therapy on sexual function. Asian J Androl 2012; 14: 198–203.
Faisst S, Meyer S . Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 1992; 20: 3–26.
Lin CS, Chow S, Lau A, Tu R, Lue TF . Human PDE5A gene encodes three PDE5 isoforms from two alternate promoters. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 15–24.
Lin CS, Lin G, Xin ZC, Lue TF . Expression, distribution and regulation of phosphodiesterase 5. Curr Pharm Des 2006; 12: 3439–3457.
Lin CS, Chow S, Lau A, Tu R, Lue TF . Identification and regulation of human PDE5A gene promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 280: 684–692.
Kasper S, Rennie PS, Bruchovsky N, Sheppard PC, Cheng H, Lin L et al. Cooperative binding of androgen receptors to two DNA sequences is required for androgen induction of the probasin gene. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 31763–31769.
Scheller A, Hughes E, Golden KL, Robins DM . Multiple receptor domains interact to permit, or restrict, androgen-specific gene activation. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 24216–24222.
Lin CS, Lau A, Yeh CC, Chang CH, Lue TF . Upregulation of L-plastin gene by testosterone in breast and prostate cancer cells: identification of three cooperative androgen receptor-binding sequences. DNA Cell Biol 2000; 19: 1–7.
Bolton EC, So AY, Chaivorapol C, Haqq CM, Li H, Yamamoto KR . Cell- and gene-specific regulation of primary target genes by the androgen receptor. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 2005–2017.
Massie CE, Adryan B, Barbosa-Morais NL, Lynch AG, Tran MG, Neal DE et al. New androgen receptor genomic targets show an interaction with the ETS1 transcription factor. EMBO Rep 2007; 8: 871–878.
Morelli A, Filippi S, Mancina R, Luconi M, Vignozzi L, Marini M et al. Androgens regulate phosphodiesterase type 5 expression and functional activity in corpora cavernosa. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 2253–2263.
Zhang XH, Morelli A, Luconi M, Vignozzi L, Filippi S, Marini M et al. Testosterone regulates PDE5 expression and in vivo responsiveness to Tadalafil in rat corpus cavernosum. Eur Urol 2005; 47: 409–416.
Zhang XH, Filippi S, Morelli A, Vignozzi L, Luconi M, Donati S et al. Testosterone restores diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction and sildenafil responsiveness in two distinct animal models of chemical diabetes. J Sex Med 2006; 3: 253–264.
Filippi S, Morelli A, Sandner P, Fibbi B, Mancina R, Marini M et al. Characterization and functional role of androgen-dependent PDE5 activity in the bladder. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 1019–1029.
Harris DE, Warshaw DM, Periasamy M . Nucleotide sequences of the rabbit alpha-smooth-muscle and beta-non-muscle actin mRNAs. Gene 1992; 112: 265–266.
Traish AM, Toselli P, Jeong SJ, Kim NN . Adipocyte accumulation in penile corpus cavernosum of the orchiectomized rabbit: a potential mechanism for veno-occlusive dysfunction in androgen deficiency. J Androl 2005; 26: 242–248.
Hayward SW, Baskin LS, Haughney PC, Foster BA, Cunha AR, Dahiya R et al. Stromal development in the ventral prostate, anterior prostate and seminal vesicle of the rat. Acta Anat (Basel) 1996; 155: 94–103.
Niu YJ, Ma TX, Zhang J, Xu Y, Han RF, Sun G . Androgen and prostatic stroma. Asian J Androl 2003; 5: 19–26.
Stacey P, Rulten S, Dapling A, Phillips SC . Molecular cloning and expression of human cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 247: 249–254.
Lin CS, Lau A, Tu R, Lue TF . Expression of three isoforms of cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5) in human penile cavernosum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 268: 628–635.
Agha AM, Taha RA . Sildenafil inhibits agonist-evoked rat uterine contractility: influence of guanylyl cyclase inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol 2001; 428: 343–348.
Rybalkin SD, Rybalkina IG, Feil R, Hofmann F, Beavo JA . Regulation of cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5) phosphorylation in smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 3310–3317.
Lin CS, Lin G, Lue TF . Isolation of two isoforms of phosphodiesterase 5 from rat penis. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 129–136.
Buhimschi CS, Garfield RE, Weiner CP, Buhimschi IA . The presence and function of phosphodiesterase type 5 in the rat myometrium. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 190: 268–274.
Khan RN, Hamoud H, Warren A, Wong LF, Arulkumaran S . Relaxant action of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on human myometrium of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 191: 315–321.
Belmonte A, Ticconi C, Dolci S, Giorgi M, Zicari A, Lenzi A et al. Regulation of phosphodiesterase 5 expression and activity in human pregnant and non-pregnant myometrial cells by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Soc Gynecol Invest 2005; 12: 570–577.
Dolci S, Belmonte A, Santone R, Giorgi M, Pellegrini M, Carosa E et al. Subcellular localization and regulation of type-1C and type-5 phosphodiesterases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 341: 837–846.
Ticconi C, Zicari A, Belmonte A, Realacci M, Rao ChV, Piccione E . Pregnancy-promoting actions of HCG in human myometrium and fetal membranes. Placenta 2007; 28 (Suppl A): S137–S143.
Chiossi G, Costantine MM, Betancourt A, Hankins GD, Longo M, Saade GR et al. Does sildenafil citrate affect myometrial contractile response to nifedipine in vitro? Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010; 203: 252. e1–e5.
Armagan A, Kim NN, Goldstein I, Traish AM . Dose–response relationship between testosterone and erectile function: evidence for the existence of a critical threshold. J Androl 2006; 27: 517–526.
Zhang X, Zang N, Wei Y, Yin J, Teng R, Seftel A et al. Testosterone regulates smooth muscle contractile pathways in the rat prostate: emphasis on PDE5 signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2012; 302: E243–E253.
Lin CS et al. PDE5 expression and function in the lower urinary tract: a critical review. Urology 2013 doi:10.1016/j.urology.2012.11.028 (in press).
Traish AM, Park K, Dhir V, Kim NN, Moreland RB, Goldstein I et al. Effects of castration and androgen replacement on erectile function in a rabbit model. Endocrinology 1999; 140: 1861–1868.
Palese MA, Crone JK, Burnett AL . A castrated mouse model of erectile dysfunction. J Androl 2003; 24: 699–703.
Rogers RS, Graziottin TM, Lin CS, Kan YW, Lue TF . Intracavernosal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injection and adeno-associated virus-mediated VEGF gene therapy prevent and reverse venogenic erectile dysfunction in rats. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 26–37.
Antonioli E, Cardoso AB, Carvalho HF . Effects of long-term castration on the smooth muscle cell phenotype of the rat ventral prostate. J Androl 2007; 28: 777–783.
Buttyan R, Ghafar MA, Shabsigh A . The effects of androgen deprivation on the prostate gland: cell death mediated by vascular regression. Curr Opin Urol 2000; 10: 415–420.
Tek M, Balli E, Cimen B, Efesoy O, Oğuz I, Cayan S . The effect of testosterone replacement therapy on bladder functions and histology in orchiectomized mature male rats. Urology 2010; 75: 886–890.
Albersen M, Lin G, Fandel TM, Zhang H, Qiu X, Lin CS et al. Functional, metabolic, and morphologic characteristics of a novel rat model of type 2 diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Urology 2011; 78: e471–e478.
Zhou F, Xin H, Liu T, Li GY, Gao ZZ, Liu J et al. Effects of icariside II on improving erectile function in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Androl 2012; 33: 832–844.
Liu WJ, Xin ZC, Xin H, Yuan YM, Tian L, Guo YL . Effects of icariin on erectile function and expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in castrated rats. Asian J Androl 2005; 7: 381–388.
Yang R, Huang YC, Lin G, Wang G, Hung S, Dai YT et al. Lack of direct androgen regulation of PDE5 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 380: 758–762.
Lin CS, Chow S, Lau A, Tu R, Lue TF . Regulation of human PDE5A2 intronic promoter by cAMP and cGMP: identification of a critical Sp1-binding site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 280: 693–699.
Kotera J, Fujishige K, Imai Y, Kawai E, Michibata H, Akatsuka H et al. Genomic origin and transcriptional regulation of two variants of cGMP-binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterases. Eur J Biochem 1999; 262: 866–873.
Andric SA, Janjic MM, Stojkov NJ, Kostic TS . Testosterone-induced modulation of nitric oxide-cGMP signaling pathway and androgenesis in the rat Leydig cells. Biol Reprod 2010; 83: 434–442.
Muller D, Mukhopadhyay AK, Davidoff MS, Middendorff R . Cyclic GMP signaling in rat urinary bladder, prostate, and epididymis: tissue-specific changes with aging and in response to Leydig cell depletion. Reproduction 2011; 142: 333–343.
Shigehara K, Sugimoto K, Konaka H, Iijima M, Fukushima M, Maeda Y et al. Androgen replacement therapy contributes to improving lower urinary tract symptoms in patients with hypogonadism and benign prostate hypertrophy: a randomised controlled study. Aging Male 2011; 14: 53–58.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (DK045370, DK64538 and DK069655).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CS., Xin, Z., Namiki, M. et al. Direct androgen regulation of PDE5 gene or the lack thereof. Int J Impot Res 25, 81–85 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2013.11
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2013.11
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Upregulation of Phosphodiesterase type 5 in the Hyperplastic Prostate
Scientific Reports (2015)