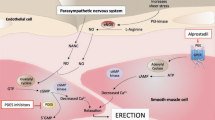
Abstract
Several studies have suggested combination therapy with testosterone supplementation in patients not responding to PDE5 inhibitors. Considering the pathophysiological basis for testosterone supplementation, the present study aims to identify whether combination therapy allows persistence of treatment effect after testosterone discontinuation. Furthermore, we evaluated whether the degree of testosterone depletion affects treatment outcome from combination therapy. Hypogonadal patients (<350 ng dl−1) with erectile dysfunction who previously did not respond to PDE5 inhibitors were treated with testosterone enanthate injections and daily tadalafil. Patients were stratified into two groups depending on the level of testosterone deficiency, with 250 ng dl−1 as a reference point. Following testosterone supplementation (12 weeks) and combination therapy (12 weeks), patients with severe testosterone deficiency showed higher IIEF (International Index of Erectile Function) erectile function (EF) domain score (16.47±4.019 vs 12.36±4.051, P=0.001) and more patients responding satisfactorily to treatment by general assessment (57.9 vs 16.0%, P=0.009), despite reaching similar levels of serum total testosterone (602±169 ng dl−1 vs 698±165 ng dl−1, P=0.057). Testosterone supplementation was then discontinued and patients were maintained only on daily tadalafil (12 weeks). The severe depletion group maintained higher EF domain scores than baseline (13.06±3.38 vs 7.20±2.24, P=0.0004), despite testosterone levels returning to baseline. The results suggest that combination therapy was more beneficial to patients with severe testosterone depletion, possibly by improving underlying pathophysiology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulton A, Selam JL, Sweeney M, Ziegler D . Sildenafil citrate for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 1296–1301.
Shabsigh R, Kaufman J, Steidle C, Padma-Nathan H . Randomized study of testosterone gel as adjunctive therapy to sildenafil in hypogonadal men with erectile dysfunction who do not respond to sildenafil alone. J Urol 2004; 172: 658–663.
Greenstein A, Mabjeesh NJ, Sofer M, Kaver I, Matzkin H, Chen J . Does sildenafil combined with testosterone gel improve erectile dysfunction in hypogonadal men in whom testosterone supplement therapy alone failed? J Urol 2005; 173: 530–532.
Kalinchenko S, Kozlov G, Gontcharov N, Katsiya G . Oral testosterone undecanoate reverses erectile dysfunction associated with diabetes mellitus in patients failing on sildenafil citrate therapy alone. Aging Male 2003; 6: 94–99.
Greco EA, Spera G, Aversa A . Combining testosterone and PDE5 inhibitors in erectile dysfunction: basic rationale and clinical evidences. Eur Urol 2006; 50: 940–947.
Lu YL, Kuang L, Zhu H, Wu H, Wang XF, Pang YP et al. Changes in aortic endothelium ultrastructure in male rats following castration, replacement with testosterone and administration of 5¥á-reductase inhibitor. Asian J Androl 2007; 9: 843–847.
Shabsigh R . The effects of testosterone on the cavernous tissue and erectile function. World J Urol 1997; 15: 21–26.
Salehian B, Wang C, Alexander G, Davidson T, McDonald V, Berman N et al. Pharmacokinetics, bioefficacy, and safety of sublingual testosterone cyclodextrin in hypogonadal men: comparison to testosterone enanthate--a clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995; 80: 3567–3575.
Aversa A, Bruzziches R, Greco E, Pili M, Spera G . Possible involvement of gonadic steroids in determining erectile response to pharmacoerection test in men with erectile dysfunction. It J Sex Reprod Med 2006; 13: 3–9.
Morales A, Heaton JPW . Hormonal erectile dysfunction: evaluation and management. Urol Clin North Am 2001; 28: 279–288.
Traish A, Saad F, Guay A . The dark side of testosterone deficiency: II. Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. J Androl 2009; 30: 23–32.
Zhang XH, Filippi S, Morelli A, Vignozzi L, Luconi M, Donati S et al. Testosterone restores diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction and sildenafil responsiveness in two distinct animal models of chemical diabetes. J Sex Med 2006; 3: 253–266.
Cummings M, Alexander W . Erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes. Hosp Med 1999; 60: 638–644.
Seftel AD, Sun P, Swindle R . The prevalence of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus and depression in men with erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2004; 171: 2341–2345.
Group UKPDS. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. Br Med J 1998; 317: 703–713.
Zitzmann M, Faber S, Nieschlag E . Association of specific symptoms and metabolic risks with serum testosterone in older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 4335–4343.
Zitzmann M, Nieschlag E . The CAG repeat polymorphism within the androgen receptor gene and maleness1. Int J Androl 2003; 26: 76–83.
Zitzmann M, Gromoll J, Von Eckardstein A, Nieschlag E . The CAG repeat polymorphism in the androgen receptor gene modulates body fat mass and serum concentrations of leptin and insulin in men. Diabetologia 2003; 46: 31–39.
Jockenhovel F, Minnemann T, Schubert M, Freude S, Hubler D, Schumann C et al. Comparison of long-acting testosterone undecanoate formulation versus testosterone enanthate on sexual function and mood in hypogonadal men. Eur J Endocrinol 2009; 160: 815–819.
Aversa A, Isidori AM, Spera G, Lenzi A, Fabbri A . Androgens improve cavernous vasodilation and response to sildenafil in patients with erectile dysfunction. Clin Endocrinol 2003; 58: 632–638.
Shamloul R, Ghanem H, Fahmy I, El-Meleigy A, Ashoor S, Elnashaar A et al. Testosterone therapy can enhance erectile function response to sildenafil in patients with PADAM: a pilot study. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 559–564.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Oh, M., Park, M. et al. Combination therapy of testosterone enanthate and tadalafil on PDE5 inhibitor non-reponders with severe and intermediate testosterone deficiency. Int J Impot Res 25, 29–33 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2012.32
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2012.32
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of testosterone in male sexual function
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders (2022)
-
Non-invasive Management Options for Erectile Dysfunction When a Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor Fails
Drugs & Aging (2018)
-
Daily Dosing of PDE5 Inhibitors: Where Does it Fit in?
Current Urology Reports (2013)