Abstract
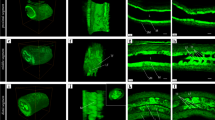
The objective of the present study was to identify kit-positive interstitial cells (ICs) in guinea pig corpus cavernosum and examine their relationships with adjacent smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and intramural nerves. In addition, we investigated the possible involvement of ICs in nitric oxide (NO)-mediated relaxation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle (CCSM). ICs were identified by their immunoreactivity to the kit receptor, a cell surface marker encoded by c-kit proto-oncogene and specific for interstitial cells of Cajal. ICs were abundantly distributed in guinea pig corporal tissues. Ultrastructural investigation by conventional transmission electron microscopy revealed the ultrastructural features of ICs and gap junctions located between ICs and adjacent SMCs, furthermore, a close contact between ICs and intramural nerves for the first time. Western blot analysis of purified ICs by fluorescence-activated cell sorting revealed coexpression of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC)α1, sGCβ1 and kit receptor tyrosine kinase protein in them. These observations imply that ICs express the NO-sensitive sGC molecule and may be involved in the NO-mediated relaxation of CCSM in the guinea pig corpus cavernosum.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saenz de Tejada I, Angulo J, Cellek S, Gonzalez-Cadavid N, Heaton J, Pickard R et al. Physiology of erectile function. J Sex Med 2004; 1: 254–265.
Hashitani H, Fukuta H, Dickens EJ, Suzuki H . Cellular mechanisms of nitric oxide-induced relaxation of corporeal smooth muscle in the guinea-pig. J Physiol 2002; 538 (part 2): 573–581.
Dean RC, Lue TF . Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am 2005; 32: 379–395, v.
Thuneberg L . One hundred years of interstitial cells of Cajal. Microsc Res Tech 1999; 47: 223–238.
Komuro T . Structure and organization of interstitial cells of Cajal in the gastrointestinal tract. J Physiol 2006; 576: 653–658.
Ward SM, Sanders KM . Involvement of intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal in neuroeffector transmission in the gastrointestinal tract. J Physiol 2006; 576: 675–682.
Lyons AD, Gardiner TA, McCloskey KD . Kit-positive interstitial cells in the rabbit urethra: structural relationships with nerves and smooth muscle. BJU Int 2007; 99: 687–694.
Rasmussen H, Rumessen JJ, Hansen A, Smedts F, Horn T . Ultrastructure of Cajal-like interstitial cells in the human detrusor. Cell Tissue Res 2009; 335: 517–527.
Negreanu LM, Assor P, Mateescu B, Cirstoiu C . Interstitial cells of Cajal in the gut--a gastroenterologist's point of view. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14: 6285–6288.
Iino S, Horiguchi K, Nojyo Y, Ward SM, Sanders KM . Interstitial cells of Cajal contain signalling molecules for transduction of nitrergic stimulation in guinea pig caecum. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2009; 21: 542–550, e512–543.
Huizinga JD, Lammers WJ . Gut peristalsis is governed by a multitude of cooperating mechanisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2009; 296: G1–G8.
Publicover NG, Hammond EM, Sanders KM . Amplification of nitric oxide signaling by interstitial cells isolated from canine colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993; 90: 2087–2091.
Iino S, Horiguchi K, Nojyo Y . Interstitial cells of Cajal are innervated by nitrergic nerves and express nitric oxide-sensitive guanylate cyclase in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Neuroscience 2008; 152: 437–448.
Garcia-Pascual A, Sancho M, Costa G, Triguero D . Interstitial cells of Cajal in the urethra are cGMP-mediated targets of nitrergic neurotransmission. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2008; 295: F971–F983.
Shafik A . Study of interstitial cells in the penis: human study. J Sex Med 2007; 4: 66–71.
Hashitani H, Suzuki H . Identification of interstitial cells of Cajal in corporal tissues of the guinea-pig penis. Br J Pharmacol 2004; 141: 199–204.
Hashitani H, Yanai Y, Shirasawa N, Soji T, Tomita A, Kohri K et al. Interaction between spontaneous and neurally mediated regulation of smooth muscle tone in the rabbit corpus cavernosum. J Physiol 2005; 569: 723–735.
Craven M, Sergeant GP, Hollywood MA, McHale NG, Thornbury KD . Modulation of spontaneous Ca2+-activated Cl− currents in the rabbit corpus cavernosum by the nitric oxide-cGMP pathway. J Physiol 2004; 556: 495–506.
Karkanis T, DeYoung L, Brock GB, Sims SM . Ca2+-activated Cl- channels in corpus cavernosum smooth muscle: a novel mechanism for control of penile erection. J Appl Physiol 2003; 94: 301–313.
Chen H, Redelman D, Ro S, Ward SM, Ordög T, Sanders KM . Selective labeling and isolation of functional classes of interstitial cells of Cajal of human and murine small intestine. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2007; 292: C497–C507.
Torihashi S, Horisawa M, Watanabe Y . c-Kit immunoreactive interstitial cells in the human gastrointestinal tract. J Auton Nerv Syst 1999; 75: 38–50.
Huizinga JD . Physiology and pathophysiology of the interstitial cell of Cajal: from bench to bedside. II. Gastric motility: lessons from mutant mice on slow waves and innervation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2001; 281: G1129–G1134.
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Kluppel M, Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB, Bernstein A . W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature 1995; 373: 347–349.
Hashitani H . Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis. J Physiol 2006; 576: 707–714.
Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Thuneberg L . Guide to the identification of interstitial cells of Cajal. Microsc Res Tech 1999; 47: 248–266.
Komuro T . Comparative morphology of interstitial cells of Cajal: ultrastructural characterization. Microsc Res Tech 1999; 47: 267–285.
Uckert S, Kedia GT, Satzger I, Geismar U, Sohn M, Kuczyk MA et al. C-kit-positive multipolar cells in human penile erectile tissue: expression of connexin 43 and relation to trabecular smooth muscle cells. Georgian Med News 2010; 180: 13–19.
Koesling D, Russwurm M, Mergia E, Mullershausen F, Friebe A . Nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase: structure and regulation. Neurochem Int 2004; 45: 813–819.
Friebe A, Mergia E, Dangel O, Lange A, Koesling D . Fatal gastrointestinal obstruction and hypertension in mice lacking nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2007; 104: 7699–7704.
Ordög T, Redelman D, Miller LJ, Horváth VJ, Zhong Q, Almeida-Porada G et al. Purification of interstitial cells of Cajal by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004; 286: C448–C456.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Xiao Nan and Zhang Xiaoping for technical support. This study was supported by the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Grant no. 30801146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, W., Song, B., Li, W. et al. Ultrastructural features and possible functional role of kit-positive interstitial cells in the guinea pig corpus cavernosum. Int J Impot Res 23, 173–179 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2011.27
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2011.27
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Calcium signalling in Cajal-like interstitial cells of the lower urinary tract
Nature Reviews Urology (2014)