Abstract
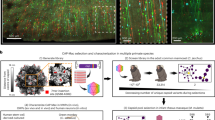
Characterization of adeno-associated viral vector (AAV) mediated gene delivery to the enteric nervous system (ENS) was recently described in mice and rats. In these proof-of-concept experiments, we show that intravenous injections of clinically relevant AAVs can transduce the ENS in guinea pigs and non-human primates. Neonatal guinea pigs were given intravenous injections of either AAV8 or AAV9 vectors that contained a green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression cassette or phosphate-buffered saline. Piglets were euthanized three weeks post injection and tissues were harvested for immunofluorescent analysis. GFP expression was detected in myenteric and submucosal neurons along the length of the gastrointestinal tract in AAV8 injected guinea pigs. GFP-positive neurons were found in dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and dorsal root ganglia. Less transduction occurred in AAV9-treated tissues. Gastrointestinal tissues were analyzed from young cynomolgus macaques that received systemic injection of AAV9 GFP. GFP expression was detected in myenteric neurons of the stomach, small and large intestine. These data demonstrate that ENS gene delivery translates to larger species. This work develops tools for the field of neurogastroenterology to explore gut physiology and anatomy using emerging technologies such as optogenetics and gene editing. It also provides a basis to develop novel therapies for chronic gut disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gombash SE, Cowley CJ, Fitzgerald JA, Hall JC, Mueller C, Christofi FL et al. Intravenous AAV9 efficiently transduces myenteric neurons in neonate and juvenile mice. Front Mol Neurosci 2014; 7: 81.
Benskey MJ, Kuhn NC, Galligan JJ, Garcia J, Boye SE, Hauswirth WW et al. Targeted Gene Delivery to the Enteric Nervous System Using AAV: A Comparison Across Serotypes and Capsid Mutants. Mol Ther 2015; 23: 488–500.
Buckinx R, Van Remoortel S, Gijsbers R, Waddington SN, Timmermans JP . Proof-of-concept: neonatal intravenous injection of adeno-associated virus vectors results in successful transduction of myenteric and submucosal neurons in the mouse small and large intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2016; 28: 299–305.
Ojala DS, Amara DP, Schaffer DV . Adeno-associated virus vectors and neurological gene therapy. Neuroscientist 2015; 21: 84–98.
Weinberg MS, Samulski RJ, McCown TJ . Adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy for neurological disease. Neuropharmacology 2013; 69: 82–88.
Mingozzi F . High KA. Therapeutic in vivo gene transfer for genetic disease using AAV: progress and challenges. Nat Rev Genet 2011; 12: 341–355.
Lomax AE, Furness JB . Neurochemical classification of enteric neurons in the guinea-pig distal colon. Cell Tissue Res 2000; 302: 59–72.
Furness JB . The Enteric Nervous System. Blackwell Publishing, 2006.
Lomax AE, Sharkey KA, Bertrand PP, Low AM, Bornstein JC, Furness JB . Correlation of morphology, electrophysiology and chemistry of neurons in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig distal colon. J Auton Nerv Syst 1999; 76: 45–61.
Lin Z, Gao N, Hu HZ, Liu S, Gao C, Kim G et al. Immunoreactivity of Hu proteins facilitates identification of myenteric neurones in guinea-pig small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2002; 14: 197–204.
Orandle MS, Veazey RS, Lackner AA . Enteric ganglionitis in rhesus macaques infected with simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 2007; 81: 6265–6275.
Neddens J, Buonanno A . Expression of the neuregulin receptor ErbB4 in the brain of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e27337.
Wang GD, Wang XY, Hu HZ, Fang XC, Liu S, Gao N et al. Angiotensin receptors and actions in guinea pig enteric nervous system. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2005; 289: G614–G626.
Harrington AM, Hutson JM, Southwell BR . Cholinergic neurotransmission and muscarinic receptors in the enteric nervous system. Prog Histochem Cytochem 2010; 44: 173–202.
Furness JB . Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst 2000; 81: 87–96.
Bergner AJ, Stamp LA, Gonsalvez DG, Allison MB, Olson DP, Myers MG Jr. et al. Birthdating of myenteric neuron subtypes in the small intestine of the mouse. J Compar Neurol 2014; 522: 514–527.
Costa M, Furness JB, Gibbins IL . Chemical coding of enteric neurons. Prog Brain Res 1986; 68: 217–239.
Steele PA, Brookes SJ, Costa M . Immunohistochemical identification of cholinergic neurons in the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 1991; 45: 227–239.
Quinson N, Robbins HL, Clark MJ, Furness JB . Calbindin immunoreactivity of enteric neurons in the guinea-pig ileum. Cell Tissue Res 2001; 305: 3–9.
Furness JB, Callaghan BP, Rivera LR, Cho HJ . The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: integrated local and central control. Adv Exp Med Biol 2014; 817: 39–71.
Levy Bde F, Cunha Jdo C, Chadi G . Cellular analysis of S100Beta and fibroblast growth factor-2 in the dorsal root ganglia and sciatic nerve of rodents. focus on paracrine actions of activated satellite cells after axotomy. Int J Neurosci 2007; 117: 1481–1503.
Bevan AK, Duque S, Foust KD, Morales PR, Braun L, Schmelzer L et al. Systemic gene delivery in large species for targeting spinal cord, brain, and peripheral tissues for pediatric disorders. Mol Ther 2011; 19: 1971–1980.
Zincarelli C, Soltys S, Rengo G, Rabinowitz JE . Analysis of AAV serotypes 1-9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1073–1080.
Wang DB, Dayton RD, Henning PP, Cain CD, Zhao LR, Schrott LM et al. Expansive gene transfer in the rat CNS rapidly produces amyotrophic lateral sclerosis relevant sequelae when TDP-43 is overexpressed. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 2064–2074.
Wang D, Zhong L, Nahid MA, Gao G . The potential of adeno-associated viral vectors for gene delivery to muscle tissue. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2014; 11: 345–364.
Curthoys IS, Vulovic V . Vestibular primary afferent responses to sound and vibration in the guinea pig. Exp Brain Res 2011; 210: 347–352.
Woolf NK . Guinea pig model of congenital CMV-induced hearing loss: a review. Transplant Proc 1991; 23 (3 Suppl 3): 32–34; discussion 4.
Bundoc VG, Keane-Myers A . Animal models of ocular allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 3: 375–379.
Deng HW, Tian Y, Zhou XJ, Zhang XM, Meng J . Effect of bilberry extract on development of form-deprivation myopia in the guinea pig. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 2016; 32: 196–202.
Budenz CL, Wong HT, Swiderski DL, Shibata SB, Pfingst BE, Raphael Y . Differential effects of AAV.BDNF and AAV.Ntf3 in the deafened adult guinea pig ear. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 8619.
Wang GP, Guo JY, Peng Z, Liu YY, Xie J, Gong SS . Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer targeting normal and traumatized mouse utricle. Gene Therapy 2014; 21: 958–966.
Byrne LC, Lin YJ, Lee T, Schaffer DV, Flannery JG . The expression pattern of systemically injected AAV9 in the developing mouse retina is determined by age. Mol Ther 2015; 23: 290–296.
Mattar CN, Waddington SN, Biswas A, Johana N, Ng XW, Fisk AS et al. Systemic delivery of scAAV9 in fetal macaques facilitates neuronal transduction of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Gene Therapy 2013; 20: 69–83.
Sharkey KA . Emerging roles for enteric glia in gastrointestinal disorders. J Clin Invest 2015; 125: 918–925.
Di Giovangiulio M, Verheijden S, Bosmans G, Stakenborg N, Boeckxstaens GE, Matteoli G . The Neuromodulation of the Intestinal Immune System and Its Relevance in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Immunol 2015; 6: 590.
Buckley MM, O'Halloran KD, Rae MG, Dinan TG, O'Malley D . Modulation of enteric neurons by interleukin-6 and corticotropin-releasing factor contributes to visceral hypersensitivity and altered colonic motility in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome. J Physiol 2014; 592: 5235–5250.
Portales-Casamar E, Swanson DJ, Liu L, de Leeuw CN, Banks KG, Ho Sui SJ et al. A regulatory toolbox of MiniPromoters to drive selective expression in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 16589–16594.
deLeeuw CN, Korecki AJ, Berry GE, Hickmott JW, Lam SL, Lengyell TC et al. rAAV-compatible MiniPromoters for restricted expression in the brain and eye. Mol Brain 2016; 9: 52.
Akache B, Grimm D, Pandey K, Yant SR, Xu H, Kay MA . The 37/67-kilodalton laminin receptor is a receptor for adeno-associated virus serotypes 8, 2, 3, and 9. J Virol 2006; 80: 9831–9836.
Shen S, Bryant KD, Brown SM, Randell SH, Asokan A . Terminal N-linked galactose is the primary receptor for adeno-associated virus 9. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 13532–13540.
Foust KD, Nurre E, Montgomery CL, Hernandez A, Chan CM, Kaspar BK . Intravascular AAV9 preferentially targets neonatal neurons and adult astrocytes. Nat Biotechnol 2009; 27: 59–65.
Duque S, Joussemet B, Riviere C, Marais T, Dubreil L, Douar AM et al. Intravenous administration of self-complementary AAV9 enables transgene delivery to adult motor neurons. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 1187–1196.
Samaranch L, Salegio EA, San Sebastian W, Kells AP, Foust KD, Bringas JR et al. Adeno-associated virus serotype 9 transduction in the central nervous system of nonhuman primates. Hum Gene Ther 2012; 23: 382–389.
Lisowski L, Dane AP, Chu K, Zhang Y, Cunningham SC, Wilson EM et al. Selection and evaluation of clinically relevant AAV variants in a xenograft liver model. Nature 2014; 506: 382–386.
Watakabe A, Ohtsuka M, Kinoshita M, Takaji M, Isa K, Mizukami H et al. Comparative analyses of adeno-associated viral vector serotypes 1, 2, 5, 8 and 9 in marmoset, mouse and macaque cerebral cortex. Neurosci Res 2015; 93: 144–157.
Mendell JR, Al-Zaidy S, Shell R, Arnold WD, Rodino-Klapac L, Kissel JT et al. Gene Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1 Shows Potential to Improve Survival and Motor Functional Outcomes. Mol Ther 2016; 24: S190.
Chamberlin NL, Du B, de Lacalle S, Saper CB . Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector: use for transgene expression and anterograde tract tracing in the CNS. Brain Res 1998; 793: 169–175.
Shimano T, Fyk-Kolodziej B, Mirza N, Asako M, Tomoda K, Bledsoe S et al. Assessment of the AAV-mediated expression of channelrhodopsin-2 and halorhodopsin in brainstem neurons mediating auditory signaling. Brain Res 2013; 1511: 138–152.
Gaj T, Epstein BE, Schaffer DV . Genome engineering using adeno-associated virus: basic and clinical research applications. Mol Ther 2016; 24: 458–464.
Podsakoff G, Wong KK Jr., Chatterjee S . Efficient gene transfer into nondividing cells by adeno-associated virus-based vectors. J Virol 1994; 68: 5656–5666.
Penaud-Budloo M, Le Guiner C, Nowrouzi A, Toromanoff A, Cherel Y, Chenuaud P et al. Adeno-associated virus vector genomes persist as episomal chromatin in primate muscle. J Virol 2008; 82: 7875–7885.
Davidson BL, Stein CS, Heth JA, Martins I, Kotin RM, Derksen TA et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2, 4, and 5 vectors: transduction of variant cell types and regions in the mammalian central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3428–3432.
von Jonquieres G, Frohlich D, Klugmann CB, Wen X, Harasta AE, Ramkumar R et al. Recombinant human myelin-associated glycoprotein promoter drives selective AAV-mediated transgene expression in oligodendrocytes. Front Mol Neurosci 2016; 9: 13.
Gulbransen BD, Sharkey KA . Novel functional roles for enteric glia in the gastrointestinal tract. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 9: 625–632.
Gao G, Vandenberghe LH, Alvira MR, Lu Y, Calcedo R, Zhou X et al. Clades of Adeno-associated viruses are widely disseminated in human tissues. J Virol 2004; 78: 6381–6388.
Deverman BE, Pravdo PL, Simpson BP, Kumar SR, Chan KY, Banerjee A et al. Cre-dependent selection yields AAV variants for widespread gene transfer to the adult brain. Nat Biotechnol 2016; 34: 204–209.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by NIH T32# 5T32NS077984-02 (SEG) and NIH RC2 #NS69476-01 (BKK). We thank Emily Armstrong (Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA) for assistance with tissue processing. Also, We thank Christian Mueller (UMASS Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA) for providing vector and Brian K Kaspar (Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, OH, USA) for donation of the cynomologus macaque tissues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
BKK is a shareholder, scientific founder and Chief Scientific Officer of Avexis. KDF is currently an employee of Avexis. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gombash, S., Cowley, C., Fitzgerald, J. et al. Systemic gene delivery transduces the enteric nervous system of guinea pigs and cynomolgus macaques. Gene Ther 24, 640–648 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2017.72
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2017.72
This article is cited by
-
HRD1-induced TMEM2 ubiquitination promotes ER stress-mediated apoptosis through a non-canonical pathway in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
Optimization of AAV vectors to target persistent viral reservoirs
Virology Journal (2021)