Abstract
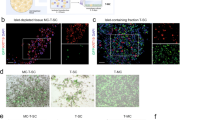
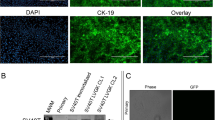
Gene therapy offers the possibility to treat pancreatic disease in cystic fibrosis (CF), caused by mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene; however, gene transfer to the pancreas is untested in humans. The pancreatic disease phenotype is very similar between humans and pigs with CF; thus, CF pigs create an excellent opportunity to study gene transfer to the pancreas. There are no studies showing efficient transduction of pig pancreas with gene-transfer vectors. Our objective is to develop a safe and efficient method to transduce wild-type (WT) porcine pancreatic ducts that express CFTR. We catheterized the umbilical artery of WT newborn pigs and delivered an adeno-associated virus serotype 9 vector expressing green-fluorescent protein (AAV9CMV.sceGFP) or vehicle to the celiac artery, the vessel that supplies major branches to the pancreas. This technique resulted in stable and dose-dependent transduction of pancreatic duct epithelial cells that expressed CFTR. Intravenous (IV) injection of AAV9CMV.sceGFP did not transduce the pancreas. Our technique offers an opportunity to deliver the CFTR gene to the pancreas of CF pigs. The celiac artery can be accessed via the umbilical artery in newborns and via the femoral artery at older ages—delivery approaches that can be translated to humans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riordan JR, Rommens JM, Kerem B, Alon N, Rozmahel R, Grzelczak Z et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science 1989; 245: 1066–1073.
Rommens JM, Iannuzzi MC, Kerem B, Drumm ML, Melmer G, Dean M et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science 1989; 245: 1059–1065.
Welsh MJ, Ramsey BW, Accurso FJ, Cutting GR . Cystic fibrosis. In: Scriver CR, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill: New York, 2001, pp 5121.
Borowitz D, Durie PR, Clarke LL, Werlin SL, Taylor CJ, Semler J et al. Gastrointestinal outcomes and confounders in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2005; 41: 273–285.
Ahmed N, Corey M, Forstner G, Zielenski J, Tsui LC, Ellis L et al. Molecular consequences of cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) gene mutations in the exocrine pancreas. Gut 2003; 52: 1159–1164.
Kristidis P, Bozon D, Corey M, Markiewicz D, Rommens J, Tsui LC et al. Genetic determination of exocrine pancreatic function in cystic fibrosis. Am J Hum Genet 1992; 50: 1178–1184.
Imrie JR, Fagan DG, Sturgess JM . Quantitative evaluation of the development of the exocrine pancreas in cystic fibrosis and control infants. Am J Pathol 1979; 95: 697–707.
Couper RT, Corey M, Durie PR, Forstner GG, Moore DJ . Longitudinal evaluation of serum trypsinogen measurement in pancreatic-insufficient and pancreatic-sufficient patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 1995; 127: 408–413.
Ooi CY, Dorfman R, Cipolli M, Gonska T, Castellani C, Keenan K et al. Type of CFTR mutation determines risk of pancreatitis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2011; 140: 153–161.
Augarten A, Ben TA, Madgar I, Barak A, Akons H, Laufer J et al. The changing face of the exocrine pancreas in cystic fibrosis: the correlation between pancreatic status, pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis genotype. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 20: 164–168.
Andersen DH . Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and its relation to celiac disease: clinical and pathological study. Am J Dis Child 1938; 56: 344–399.
Oppenheimer EH, Esterly JR . Pathology of cystic fibrosis review of the literature and comparison with 146 autopsied cases. Perspect Pediatr Pathol 1975; 2: 241–278.
Corey M, Edwards L, Levison H, Knowles M . Longitudinal analysis of pulmonary function decline in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 1997; 131: 809–814.
Gaskin K, Gurwitz D, Durie P, Corey M, Levison H, Forstner G . Improved respiratory prognosis in patients with cystic fibrosis with normal fat absorption. J Pediatr 1982; 100: 857–862.
Kraemer R, Rudeberg A, Hadorn B, Rossi E . Relative underweight in cystic fibrosis and its prognostic value. Acta Paediatr Scand 1978; 67: 33–37.
Moran A, Dunitz J, Nathan B, Saeed A, Holme B, Thomas W . Cystic fibrosis-related diabetes: current trends in prevalence, incidence, and mortality. Diabetes Care 2009; 32: 1626–1631.
Stecenko AA, Moran A . Update on cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2010; 16: 611–615.
Milla CE, Warwick WJ, Moran A . Trends in pulmonary function in patients with cystic fibrosis correlate with the degree of glucose intolerance at baseline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162 (3 Pt 1): 891–895.
Chamnan P, Shine BS, Haworth CS, Bilton D, Adler AI . Diabetes as a determinant of mortality in cystic fibrosis. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 311–316.
Snouwaert JN, Brigman KK, Latour AM, Malouf NN, Boucher RC, Smithies O et al. An animal model for cystic fibrosis made by gene targeting. Science 1992; 257: 1083–1088.
Clarke LL, Grubb BR, Gabriel SE, Smithies O, Koller BH, Boucher RC . Defective epithelial chloride transport in a gene-targeted mouse model of cystic fibrosis. Science 1992; 257: 1125–1128.
Rogers CS, Stoltz DA, Meyerholz DK, Ostedgaard LS, Rokhlina T, Taft PJ et al. Disruption of the CFTR gene produces a model of cystic fibrosis in newborn pigs. Science 2008; 321: 1837–1841.
Stoltz DA, Meyerholz DK, Pezzulo AA, Ramachandran S, Rogan MP, Davis GJ et al. Cystic fibrosis pigs develop lung disease and exhibit defective bacterial eradication at birth. Sci Transl Med 2010; 2: 29ra31.
Ostedgaard LS, Meyerholz DK, Chen JH, Pezzulo AA, Karp PH, Rokhlina T et al. The DeltaF508 mutation causes CFTR misprocessing and cystic fibrosis-like disease in pigs. Sci Transl Med 2011; 3: 74ra24.
Abu-El-Haija M, Ramachandran S, Meyerholz DK, Griffin M, Giriyappa RL, Stoltz DA et al. Pancreatic damage in fetal and newborn cystic fibrosis pigs involves the activation of inflammatory and remodeling pathways. Am J Pathol 2012; 181: 499–507.
Meyerholz DK, Stoltz DA, Pezzulo AA, Welsh MJ . Pathology of gastrointestinal organs in a porcine model of cystic fibrosis. Am J Pathol 2010; 176: 1377–1389.
Uc A, Giriyappa R, Meyerholz DK, Griffin M, Ostedgaard LS, Tang XX et al. Pancreatic and biliary secretion are both altered in cystic fibrosis pigs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012; 303: G961–G968.
Raper SE, DeMatteo RP . Adenovirus-mediated in vivo gene transfer and expression in normal rat pancreas. Pancreas 1996; 12: 401–410.
McClane SJ, Hamilton TE, Burke CV, Raper SE . Functional consequences of adenovirus-mediated murine pancreatic gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther 1997; 8: 739–746.
Wang AY, Peng PD, Ehrhardt A, Storm TA, Kay MA . Comparison of adenoviral and adeno-associated viral vectors for pancreatic gene delivery in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 405–413.
Ayuso E, Chillon M, Agudo J, Haurigot V, Bosch A, Carretero A et al. In vivo gene transfer to pancreatic beta cells by systemic delivery of adenoviral vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 805–812.
Jimenez V, Ayuso E, Mallol C, Agudo J, Casellas A, Obach M et al. In vivo genetic engineering of murine pancreatic beta cells mediated by single-stranded adeno-associated viral vectors of serotypes 6, 8 and 9. Diabetologia 2011; 54: 1075–1086.
Loiler SA, Tang Q, Clarke T, Campbell-Thompson ML, Chiodo V, Hauswirth W et al. Localized gene expression following administration of adeno-associated viral vectors via pancreatic ducts. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 519–527.
Cheng H, Wolfe SH, Valencia V, Qian K, Shen L, Phillips MI et al. Efficient and persistent transduction of exocrine and endocrine pancreas by adeno-associated virus type 8. J Biomed Sci 2007; 14: 585–594.
Ye X, Jerebtsova M, Ray PE . Liver bypass significantly increases the transduction efficiency of recombinant adenoviral vectors in the lung, intestine, and kidney. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 621–627.
Aitken ML, Moss RB, Waltz DA, Dovey ME, Tonelli MR, McNamara SC et al. A phase I study of aerosolized administration of tgAAVCF to cystic fibrosis subjects with mild lung disease. Hum Gene Ther 2001; 12: 1907–1916.
Wagner JA, Nepomuceno IB, Messner AH, Moran ML, Batson EP, Dimiceli S et al. A phase II, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of tgAAVCF using maxillary sinus delivery in patients with cystic fibrosis with antrostomies. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 1349–1359.
Wagner JA, Messner AH, Moran ML, Daifuku R, Kouyama K, Desch JK et al. Safety and biological efficacy of an adeno-associated virus vector-cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (AAV-CFTR) in the cystic fibrosis maxillary sinus. Laryngoscope 1999; 109 (2 Pt 1): 266–274.
Flotte TR, Carter BJ . Adeno-associated virus vectors for gene therapy. Gene Ther 1995; 2: 357–362.
Inagaki K, Fuess S, Storm TA, Gibson GA, McTiernan CF, Kay MA et al. Robust systemic transduction with AAV9 vectors in mice: efficient global cardiac gene transfer superior to that of AAV8. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 45–53.
Wang Z, Zhu T, Rehman KK, Bertera S, Zhang J, Chen C et al. Widespread and stable pancreatic gene transfer by adeno-associated virus vectors via different routes. Diabetes 2006; 55: 875–884.
Ferrer J, Scott WE 3rd, Weegman BP, Suszynski TM, Sutherland DE, Hering BJ et al. Pig pancreas anatomy: implications for pancreas procurement, preservation, and islet isolation. Transplantation 2008; 86: 1503–1510.
Prasad KM, Yang Z, Bleich D, Nadler JL . Adeno-associated virus vector mediated gene transfer to pancreatic beta cells. Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1553–1561.
Yang YW, Kotin RM . Glucose-responsive gene delivery in pancreatic Islet cells via recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors. Pharm Res 2000; 17: 1056–1061.
Loiler SA, Conlon TJ, Song S, Tang Q, Warrington KH, Agarwal A et al. Targeting recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors to enhance gene transfer to pancreatic islets and liver. Gene Ther 2003; 10: 1551–1558.
Rehman KK, Wang Z, Bottino R, Balamurugan AN, Trucco M, Li J et al. Efficient gene delivery to human and rodent islets with double-stranded (ds) AAV-based vectors. Gene Ther 2005; 12: 1313–1323.
Burghardt B, Elkaer ML, Kwon TH, Racz GZ, Varga G, Steward MC et al. Distribution of aquaporin water channels AQP1 and AQP5 in the ductal system of the human pancreas. Gut 2003; 52: 1008–1016.
Marino CR, Matovcik LM, Gorelick FS, Cohn JA . Localization of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in pancreas. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: 712–716.
Strong TV, Boehm K, Collins FS . Localization of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mRNA in the human gastrointestinal tract by in situ hybridization. J Clin Invest 1994; 93: 347–354.
Rehman KK, Trucco M, Wang Z, Xiao X, Robbins PD . AAV8-mediated gene transfer of interleukin-4 to endogenous beta-cells prevents the onset of diabetes in NOD mice. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1409–1416.
Michl P, Gress TM . Current concepts and novel targets in advanced pancreatic cancer. Gut 2013; 62: 317–326.
Moran A, Diem P, Klein DJ, Levitt MD, Robertson RP . Pancreatic endocrine function in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 1991; 118: 715–723.
Larsen S, Hilsted J, Tronier B, Worning H . Pancreatic hormone secretion in chronic pancreatitis without residual beta-cell function. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988; 118: 357–364.
Nousia-Arvanitakis S, Tomita T, Desai N, Kimmel JR . Pancreatic polypeptide in cystic fibrosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1985; 109: 722–726.
Stern A, Davidson GP, Kirubakaran CP, Deutsch J, Smith A, Hansky J . Pancreatic polypeptide secretion. A marker for disturbed pancreatic function in cystic fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci 1983; 28: 870–873.
Ostedgaard LS, Rokhlina T, Karp PH, Lashmit P, Afione S, Schmidt M et al. A shortened adeno-associated virus expression cassette for CFTR gene transfer to cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 2952–2957.
Ostedgaard LS, Zabner J, Vermeer DW, Rokhlina T, Karp PH, Stecenko AA et al. CFTR with a partially deleted R domain corrects the cystic fibrosis chloride transport defect in human airway epithelia in vitro and in mouse nasal mucosa in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 3093–3098.
Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Edlund H . The morphogenesis of the pancreatic mesenchyme is uncoupled from that of the pancreatic epithelium in IPF1/PDX1-deficient mice. Development 1996; 122: 1409–1416.
Divekar A, Gutsol A, Dakshinamurti S . Transumbilical catheter intervention of ductus arteriosus in neonatal swine. J Invest Surg 2007; 20: 313–317.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Joseph Zabner for his helpful input on the manuscript. We would like to thank Maisam Abu-El-Haija, Shelby Burdette, Leah Reznikov, Hyder Chowdhry, Michael Rector, John Morgan and Benjamin Steines for their technical assistance with handling tissues, animal care/feedings, necropsies and the Gene Transfer Vector Core for virus production. This work was supported by the National institute of Health (NIH) DK084049 (AU); University of Iowa Biological Sciences Funding Program (AU), NIH/University of Iowa Center for Gene Therapy of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Genetic Diseases Pilot Grant (AU); NIH DK54759 (BD); NIH P01 HL51670 (PBM); Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Student Traineeship Grant (EB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffin, M., Restrepo, M., Abu-El-Haija, M. et al. A novel gene delivery method transduces porcine pancreatic duct epithelial cells. Gene Ther 21, 123–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.62
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.62