Abstract
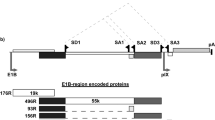
The limitations of the current oncolytic adenoviruses for cancer therapy include insufficient potency and poor distribution of the virus throughout the tumor mass. To address these problems, we generated an oncolytic adenovirus expressing the hyperfusogenic form of the gibbon-ape leukemia virus (GALV) envelope glycoprotein under the control of the adenovirus major late promoter. The oncolytic properties of the new fusogenic adenovirus, ICOVIR16, were analyzed both in vitro and in vivo, and compared with that of its non-fusogenic counterpart, ICOVIR15. Our results indicate that GALV expression by ICOVIR16 induced extensive syncytia formation and enhanced tumor cell killing in a variety of tumor cell types. When injected intratumorally or intravenously into mice with large pre-established melanoma or pancreatic tumors, ICOVIR16 rapidly reduced tumor burden, and in some cases, resulted in complete eradication of the tumors. Importantly, GALV expression induced tumor cell fusion in vivo and enhanced the spreading of the virus throughout the tumor. Taken together, these results indicate that GALV expression can improve the antitumoral potency of an oncolytic adenovirus and suggest that ICOVIR16 is a promising candidate for clinical evaluation in patients with cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemany R, Balague C, Curiel DT . Replicative adenoviruses for cancer therapy. Nat Biotechnol 2000; 18: 723–727.
Aghi M, Martuza RL . Oncolytic viral therapies - the clinical experience. Oncogene 2005; 24: 7802–7816.
Ottolino-Perry K, Diallo JS, Lichty BD, Bell JC, McCart JA . Intelligent design: combination therapy with oncolytic viruses. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 251–263.
Gros A, Guedan S . Adenovirus release from the infected cell as a key factor for adenovirus oncolysis. Open Gene Ther J 2010; 3: 24–30.
Chu RL, Post DE, Khuri FR, Van Meir EG . Use of replicating oncolytic adenoviruses in combination therapy for cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 5299–5312.
Gros A, Puig C, Guedan S, Rojas JJ, Alemany R, Cascallo M . Verapamil enhances the antitumoral efficacy of oncolytic adenoviruses. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 903–911.
Homicsko K, Lukashev A, Iggo RD . RAD001 (everolimus) improves the efficacy of replicating adenoviruses that target colon cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 6882–6890.
Alonso MM, Jiang H, Yokoyama T, Xu J, Bekele NB, Lang FF et al. Delta-24-RGD in combination with RAD001 induces enhanced anti-glioma effect via autophagic cell death. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 487–493.
Cody JJ, Douglas JT . Armed replicating adenoviruses for cancer virotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2009; 16: 473–488.
Ganesh S, Gonzalez Edick M, Idamakanti N, Abramova M, Vanroey M, Robinson M et al. Relaxin-expressing, fiber chimeric oncolytic adenovirus prolongs survival of tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 4399–4407.
Kim JH, Lee YS, Kim H, Huang JH, Yoon AR, Yun CO . Relaxin expression from tumor-targeting adenoviruses and its intratumoral spread, apoptosis induction, and efficacy. J Natl Cancer Inst 2006; 98: 1482–1493.
Guedan S, Rojas JJ, Gros A, Mercade E, Cascallo M, Alemany R . Hyaluronidase Expression by an Oncolytic Adenovirus Enhances Its Intratumoral Spread and Suppresses Tumor Growth. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 1275–1283.
Bristol JA, Zhu M, Ji H, Mina M, Xie Y, Clarke L et al. In vitro and in vivo activities of an oncolytic adenoviral vector designed to express GM-CSF. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 755–764.
Lee YS, Kim JH, Choi KJ, Choi IK, Kim H, Cho S et al. Enhanced antitumor effect of oncolytic adenovirus expressing interleukin-12 and B7-1 in an immunocompetent murine model. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 5859–5868.
Post DE, Sandberg EM, Kyle MM, Devi NS, Brat DJ, Xu Z et al. Targeted cancer gene therapy using a hypoxia inducible factor dependent oncolytic adenovirus armed with interleukin-4. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6872–6881.
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Vozhilla N, Park ES, Gupta P, Fisher PB . Dual cancer-specific targeting strategy cures primary and distant breast carcinomas in nude mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 14034–14039.
Wildner O, Blaese RM, Morris JC . Therapy of colon cancer with oncolytic adenovirus is enhanced by the addition of herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 410–413.
Morris JC, Wildner O . Therapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with an oncolytic adenovirus expressing HSV-tk. Mol Ther 2000; 1: 56–62.
Cascante A, Abate-Daga D, Garcia-Rodriguez L, Gonzalez JR, Alemany R, Fillat C . GCV modulates the antitumoural efficacy of a replicative adenovirus expressing the Tat8-TK as a late gene in a pancreatic tumour model. Gene Therapy 2007; 14: 1471–1480.
Bateman A, Bullough F, Murphy S, Emiliusen L, Lavillette D, Cosset FL et al. Fusogenic membrane glycoproteins as a novel class of genes for the local and immune-mediated control of tumor growth. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 1492–1497.
Bateman AR, Harrington KJ, Kottke T, Ahmed A, Melcher AA, Gough MJ et al. Viral fusogenic membrane glycoproteins kill solid tumor cells by nonapoptotic mechanisms that promote cross presentation of tumor antigens by dendritic cells. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 6566–6578.
Errington F, Jones J, Merrick A, Bateman A, Harrington K, Gough M et al. Fusogenic membrane glycoprotein-mediated tumour cell fusion activates human dendritic cells for enhanced IL-12 production and T-cell priming. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 138–149.
Ebert O, Shinozaki K, Kournioti C, Park MS, Garcia-Sastre A, Woo SL . Syncytia induction enhances the oncolytic potential of vesicular stomatitis virus in virotherapy for cancer. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 3265–3270.
Fu X, Tao L, Jin A, Vile R, Brenner MK, Zhang X . Expression of a fusogenic membrane glycoprotein by an oncolytic herpes simplex virus potentiates the viral antitumor effect. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 748–754.
Simpson GR, Han Z, Liu B, Wang Y, Campbell G, Coffin RS . Combination of a fusogenic glycoprotein, prodrug activation, and oncolytic herpes simplex virus for enhanced local tumor control. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 4835–4842.
Li H, Haviv YS, Derdeyn CA, Lam J, Coolidge C, Hunter E et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-mediated syncytium formation is compatible with adenovirus replication and facilitates efficient dispersion of viral gene products and de novo-synthesized virus particles. Hum Gene Ther 2001; 12: 2155–2165.
Ahmed A, Jevremovic D, Suzuki K, Kottke T, Thompson J, Emery S et al. Intratumoral expression of a fusogenic membrane glycoprotein enhances the efficacy of replicating adenovirus therapy. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 1663–1671.
Guedan S, Gros A, Cascallo M, Vile R, Mercade E, Alemany R . Syncytia formation affects the yield and cytotoxicity of an adenovirus expressing a fusogenic glycoprotein at a late stage of replication. Gene Therapy 2008; 15: 1240–1245.
Rojas JJ, Guedan S, Searle PF, Martinez-Quintanilla J, Gil-Hoyos R, Alcayaga-Miranda F et al. Minimal RB-responsive E1A promoter modification to attain potency, selectivity, and transgene-arming capacity in oncolytic adenoviruses. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 1960–1971.
Gros A, Martinez-Quintanilla J, Puig C, Guedan S, Mollevi DG, Alemany R et al. Bioselection of a gain of function mutation that enhances adenovirus 5 release and improves its antitumoral potency. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 8928–8937.
Linardakis E, Bateman A, Phan V, Ahmed A, Gough M, Olivier K et al. Enhancing the efficacy of a weak allogeneic melanoma vaccine by viral fusogenic membrane glycoprotein-mediated tumor cell-tumor cell fusion. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 5495–5504.
Thomas MA, Spencer JF, La Regina MC, Dhar D, Tollefson AE, Toth K et al. Syrian hamster as a permissive immunocompetent animal model for the study of oncolytic adenovirus vectors. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 1270–1276.
Bortolanza S, Alzuguren P, Bunuales M, Qian C, Prieto J, Hernandez-Alcoceba R . Human adenovirus replicates in immunocompetent models of pancreatic cancer in Syrian hamsters. Hum Gene Ther 2007; 18: 681–690.
Bett AJ, Prevec L, Graham FL . Packaging capacity and stability of human adenovirus type 5 vectors. J Virol 1993; 67: 5911–5921.
Cascallo M, Alonso MM, Rojas JJ, Perez-Gimenez A, Fueyo J, Alemany R . Systemic toxicity-efficacy profile of ICOVIR-5, a potent and selective oncolytic adenovirus based on the pRB pathway. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 1607–1615.
Bridge E, Ketner G . Redundant control of adenovirus late gene expression by early region 4. J Virol 1989; 63: 631–638.
Suzuki K, Alemany R, Yamamoto M, Curiel DT . The presence of the adenovirus E3 region improves the oncolytic potency of conditionally replicative adenoviruses. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3348–3359.
Wang Y, Hallden G, Hill R, Anand A, Liu TC, Francis J et al. E3 gene manipulations affect oncolytic adenovirus activity in immunocompetent tumor models. Nat Biotechnol 2003; 21: 1328–1335.
Edwards SJ, Dix BR, Myers CJ, Dobson-Le D, Huschtscha L, Hibma M et al. Evidence that replication of the antitumor adenovirus ONYX-015 is not controlled by the p53 and p14(ARF) tumor suppressor genes. J Virol 2002; 76: 12483–12490.
Villanueva A, Garcia C, Paules AB, Vicente M, Megias M, Reyes G et al. Disruption of the antiproliferative TGF-beta signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 1998; 17: 1969–1978.
Cotten M, Saltik M, Kursa M, Wagner E, Maass G, Birnstiel ML . Psoralen treatment of adenovirus particles eliminates virus replication and transcription while maintaining the endosomolytic activity of the virus capsid. Virology 1994; 205: 254–261.
Cascallo M, Gros A, Bayo N, Serrano T, Capella G, Alemany R . Deletion of VAI and VAII RNA genes in the design of oncolytic adenoviruses. Hum Gene Ther 2006; 17: 929–940.
Acknowledgements
We thank Blanca Luena for her technical assistance in animal experiments; Jordi Martínez-Quintanilla, Marta Gimenez-Alexandre and Cristina Puig for technical assistance; and Lynda Coughlan (University of Glasgow, UK) for extensive revision of this manuscript. S Guedan and JJ Rojas were supported by a pre-doctoral fellowship (FI) granted by the Generalitat de Catalunya. This work was supported by a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science, BIO2008-04692-C03-01 and received partial support from the Generalitat de Catalunya SGR0500008 and 2009SGR1212. R Alemany belongs to the Network of Cooperative Research on Cancer (C03-10), Instituto de Salud Carlos III of the Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo, Government of Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guedan, S., Grases, D., Rojas, J. et al. GALV expression enhances the therapeutic efficacy of an oncolytic adenovirus by inducing cell fusion and enhancing virus distribution. Gene Ther 19, 1048–1057 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.184
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.184
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Use of cell fusion proteins to enhance adenoviral vector efficacy as an anti-cancer therapeutic
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
Construction of a replication-competent retroviral vector for expression of the VSV-G envelope glycoprotein for cancer gene therapy
Archives of Virology (2020)
-
Programming CAR T cells to enhance anti-tumor efficacy through remodeling of the immune system
Frontiers of Medicine (2020)
-
Expression of the fusogenic p14 FAST protein from a replication-defective adenovirus vector does not provide a therapeutic benefit in an immunocompetent mouse model of cancer
Cancer Gene Therapy (2016)
-
Enhancing the bystander killing effect of an oncolytic HSV by arming it with a secretable apoptosis activator
Gene Therapy (2015)