Abstract
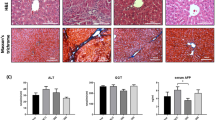
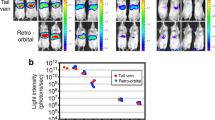
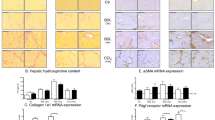
Capillarization of the sinusoid impedes the clearance of neurotoxic substances in liver fibrosis. These events may result in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurological and hepatic features of rats after bile duct ligation (BDL) supplemented with Manganese (BDL+Mn2+) were examined. The 4-week-old BDL rats had elevated levels of ammonia and were concomitantly fed with 1 mg ml−1 of MnCl2 in drinking water (BDL/Mn+2). Five out of fifteen rats were killed and the serum, liver and brain tissue (striatum and substantia nigra) were recovered. Of the remaining BDL/Mn+2-cirrhotic animals (n=10), five were injected with a combination of Adenovirus-human plasminogen activator (Ad-huPA) and Adenovirus-matrix metalloproteinase-8 (Ad-MMP-8) (3 × 1011+1.5 × 1011 vector particles per kg), and five with 4.5 × 1011 vector particles per kg of Adenovirus-β-galactosidase (Ad-β-Gal). This treatment was carried on for 10 days. The BDL/Mn+2 rats displayed tremor, rigidity and gait abnormalities, which improved notably with combinatorial gene therapy, as well as motor coordination. Liver fibrosis was evidently less after treatment with Ad-huPA+Ad-MMP-8 (25%). In the brain (striatum), Ad-huPA+Ad-MMP-8 treatment rendered higher concentrations of dopamine compared with Ad-β-Gal-treated encephalopathic rats (210 and 162 ng g−1 of tissue, respectively). The BDL/Mn+2 animals and controls treated with Ad-β-Gal showed abnormal morphology in astrocytes (gliosis) in striatum and substantia nigra, in which expressions of green fibrillar acidic protein and tyrosine hydroxylase were altered. These abnormalities decreased with Ad-huPA+Ad-MMP-8 treatment. Importantly, the latter animals showed an increment in sprouting of nervous fibers in substantia nigra. Combinatorial gene therapy improves neuroanatomical and neurochemical characteristics similar to human hepatic encephalopathy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miranda-Diaz A, Rincon AR, Salgado S, Vera-Cruz J, Galvez J, Islas MC et al. Improved effects of viral gene delivery of human uPA plus biliodigestive anastomosis induce recovery from experimental biliary cirrhosis. Mol Ther 2004; 9: 30–37.
Salgado S, Garcia J, Vera J, Siller F, Bueno M, Miranda A et al. Liver cirrhosis is reverted by urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene therapy. Mol Ther 2000; 2: 545–551.
Siller-López F, Sandoval A, Salgado S, Salazar A, Bueno M, García J et al. Treatment with human metalloproteinase-8 gene delivery ameliorates experimental rat liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2004; 126: 1122–1133.
Tucker HM, Kihiko-Ehmann M, Estust S . Urokinase-type plasminogen activator inhibits amyloid B neurotoxicity and fibrillogenesis via plasminogen. J Neurosci Res 2002; 70: 249–255.
Butterworth RF . Hepatic encephalopathy-a serious complication of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res Health 2003; 27: 143–145.
Montes S, Alcaraz-Zubeldia M, Muriel P, Rios C . Striatal manganese accumulation induces changes in dopamine metabolism in the cirrhotic rat. Brain Res 2001; 891: 123–129.
Jalan R, Shawcross D, Davies N . The molecular pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2003; 1471: 1–7.
Ong J, Mullen D . Hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001; 13: 3325–3334.
Butterworth RF . Neuronal cell death in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2007; 22: 309–320.
Hazell A . Astrocytes and manganese neurotoxicity. Neurochem Int 2002; 41: 271–277.
Hazell A, Butterworth R . Hepatic encephalopathy: an updateof pathophysiologic mechanism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1999; 222: 99–112.
Garcia-Bañuelos J, Siller-Lopez F, Miranda A, Aguilar AL, Aguilar-Cordova E, Armendariz-Borunda J . Cirrhotic rat livers with extensive fibrosis can be safely transduced with clinical-grade adenoviral vectors. Evidence of cirrhosis reversión. Gene Ther 2002; 9: 127–134.
Limuro Y, Nishio T, Morimoto T, Nitta T, Stefanovic B, Choi SK et al. Delivery of matrix metalloproteinase-1 attenuates established liver fibrosis in the rat. Gastroenterology 2003; 124: 445–458.
Sakaida I, Terai S, Yamamoto N, Aoyama KIT, Nishina H, Okita K . Transplantation of bone marrow cells reduces CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2004; 40: 1304–1311.
Xue F, Takahara T, Yata Y, Kuwabara Y, Shinno E, Nonome K et al. Hepatocyte growth factor gene therapy accelerates regeneration in cirrhotic mouse livers after hepatectomy. Gut 2003; 52: 694–700.
Layrargues GP, Rose C, Spahr L, Zayed J, Normandin L, Butterworth RF . Role of manganese in the pathogenesis of portal-systemic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 1998; 13: 311–317.
Jover R, Rodrigo R, Felipo V, Insausti R, Sáez-Valero J, García-Ayllón MS et al. Brain edema and inflammatory activation in bile duct ligated rats with diet-induced hyperammonemia: a model of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006; 43: 1257–1266.
Lieber A, Peeters MJ, Gown A, Perkins J, Kay MA . A modified urokinase plasminogen activator induces liver regeneration without bleeding. Human Gene Ther 1995; 6: 1029–1037.
Nyberg-Hoffman C, Shabram P, Li W, Giroux D, Aguilar-Cordova E . Sensitivity and reproducibility in adenoviral infectious titer determination. Nat Med 1997; 3: 808–811.
Mizuguchi H, Kay MA . Efficient construction of a recombinant adenovirusvectorby an improved in vitro ligation method. Human Gene Ther 1998; 9: 2577–2583.
Lotersztajn S, Julien B, Teixeira-Clerc F, Grenard P, Mallat A . Hepatic fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and drug targets. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2005; 45: 605–628.
Lee CM, Stewart L, Way LW . Postcholecystectomy abdominal bile collections. Arch Surg 2000; 135: 538–542; discussion 542–4.
Rojkind M, Gonzalez E . An improved method for determining specific radioactivities of proline-14C and hydroxyproline-14C in collagen and in noncollagenous proteins. Anal Biochem 1974; 57: 1–7.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by COECyT-Jal (code number 08-2004) and CONACyT 25474 awarded to JAB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gálvez-Gastélum, F., Garcia-Bañuelos, J., Beas-Zárate, C. et al. Combinatorial gene therapy induces regression of hepatic encephalopathy. Gene Ther 18, 88–94 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.107
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.107