Abstract
Purpose
Recent studies demonstrate that whole-genome sequencing enables detection of cryptic rearrangements in apparently balanced chromosomal rearrangements (also known as balanced chromosomal abnormalities, BCAs) previously identified by conventional cytogenetic methods. We aimed to assess our analytical tool for detecting BCAs in the 1000 Genomes Project without knowing which bands were affected.
Methods
The 1000 Genomes Project provides an unprecedented integrated map of structural variants in phenotypically normal subjects, but there is no information on potential inclusion of subjects with apparent BCAs akin to those traditionally detected in diagnostic cytogenetics laboratories. We applied our analytical tool to 1,166 genomes from the 1000 Genomes Project with sufficient physical coverage (8.25-fold).
Results
With this approach, we detected four reciprocal balanced translocations and four inversions, ranging in size from 57.9 kb to 13.3 Mb, all of which were confirmed by cytogenetic methods and polymerase chain reaction studies. One of these DNAs has a subtle translocation that is not readily identified by chromosome analysis because of the similarity of the banding patterns and size of exchanged segments, and another results in disruption of all transcripts of an OMIM gene.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates the extension of utilizing low-pass whole-genome sequencing for unbiased detection of BCAs including translocations and inversions previously unknown in the 1000 Genomes Project.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
A balanced chromosomal rearrangement (or balanced chromosomal abnormality, BCA) is a type of chromosomal structural variant (SV) involving chromosomal rearrangements (e.g., translocations, inversions, and insertions) without cytogenetically apparent gain or loss of chromatin. The incidence of balanced translocations has been estimated to range from 1/500 to 1/625 in the general population1,2,3 and the prevalence is well known to be increased in individuals with clinical anomalies.4,5,6,7 Based on the association of increased prevalence with abnormal clinical phenotypes, studies of BCAs such as those carried out in the Developmental Genome Anatomy Project (http://dgap.harvard.edu)5,6,8,9 among others7,10 have a high yield in identification of genetic disease due to gene disruption or dysregulation.
Current high-resolution methods (i.e., chromosomal microarray analysis and whole-exome sequencing) are generally insensitive to BCAs that are not accompanied by sizable genomic imbalances. Thus, detection of BCAs relies on conventional cytogenetic methods (i.e., G-banded karyotyping), which are limited to microscopic resolution (~3–10 Mb). More recently, whole-genome sequencing (WGS) using paired-end analysis has enabled molecular delineation of the breakpoints of BCAs at base-pair resolution but has been tested and validated only in DNA samples harboring previously recognized BCAs.
By utilizing WGS (mean 7.4-fold base coverage) and orthogonal techniques (i.e., long-read single-molecule sequencing), the 1000 Genomes Project (http://www.internationalgenome.org/data/) has established the most detailed catalog of human genetic variation, which in turn can be used for association studies relating genetic variation to disease. It provides an unprecedented integrated map of SVs from 2,054 individuals, including copy-number variants, inversions (<50 kb), and insertions,11,12 and serves as an indispensable reference for geographic and functional studies of human genetic variation. However, no information was available on the frequency of balanced translocations or inversions (>50 kb) in this resource of participants who were healthy at the time of enrollment. Our previous pilot study showed the feasibility of detecting BCAs with low-pass (or low-coverage) paired-end WGS in a blinded fashion.13 In the present study, we applied our analytical tool to WGS data released by the 1000 Genomes Project.11
Materials and methods
WGS data from the 1000 Genomes Project
Alignment files from 2,504 presumably healthy individuals were downloaded from the 1000 Genomes Project. Assessment of data quality and further analysis were carried out for each individual independently.
Minimum physical coverage requirement used in this study
As shown in our previous study,13 the minimum read-pair count was used to avoid false-negative detection of BCAs. This minimum number of read-pairs in a small-insert library (400 to 600 bp) was estimated as 120 million (50 bp), which is equivalent to four-fold base coverage from WGS. However, read length (35 to 100 bp) and insert size (200 to 600 bp, Figure 1a) were varied among samples from the 1000 Genomes Project.11 Therefore, physical coverage14 was included in the required selection criteria instead of the number of read-pairs (Figure 1b).
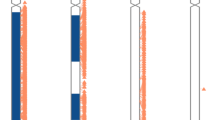
Distributions of the average insert sizes and quantity of read-pairs in 2,504 samples from the 1000 Genomes Project are shown in (a) and (b), respectively. Calculation of insert size and read-pair quantities were based on nonchimeric and uniquely mapped read-pairs. (c) Spectrum of balanced chromosomal abnormalities. Balanced translocations are indicated with red lines and the corresponding sample IDs are shown in red font in each affected chromosome in the outmost circle. Inversions are indicated in blue lines and sample IDs are shown in blue font. Chromosomal nucleotide positions and bands are shown according to the University of California, Santa Cruz Genome Viewer Table Browser. Panels (d–f) show validation of balanced translocations and (g) shows inversion by G-banded chromosome analysis. Ideograms of the balanced rearrangements (extracted from CyDAS http://www.cydas.org/OnlineAnalysis/WebExample4.aspx) are shown on the left, while the karyogram images are on the right, with the corresponding ideograms of the derivative chromosomes for reference. Breakpoint regions are indicated with red arrows. Sample name and the International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature description are shown below each.
We defined a chimeric read-pair if two ends aligned to different chromosomes (interchromosomal) or to the same chromosome (intrachromosomal) with an aligned distance larger than 10 kb.13,15 Physical coverage was estimated by counting the aligned distances from the nonchimeric and uniquely mapped read-pairs.13 In the present study, the minimum physical coverage of 8.25-fold, estimated based on 90 million read-pairs (data from our previous pilot study),13 was set to maximize inclusion of 1,166 of 2,504 samples (Supplementary Table 1 online). This was based on: (i) only 616 of 2,504 samples available for this study with 11-fold physical coverage (estimated based on 120 million read-pairs) and (ii) an increase in the false-negative detection rate in our previous study from 11.1% (1/9) with 90 million read-pairs to 33.3% (3/9) with only 60 million read-pairs.13
Data quality control and BCA detection
We filtered out low-quality reads (≥4% of mismatch rates) and extracted uniquely aligned reads in both ends for further analysis. Detection of chromosomal rearrangement is based on a four-step procedure, described in our previous study:13
-
1.
Event clustering: chimeric read-pairs were clustered by sorting the aligned coordinates (GRCh37/hg19) and any two read-pairs were considered to represent two distinct events if they were separated by a distance >10kb.
-
2.
Systematic error filtering: each event was filtered against a control data set, which was built up by using the events from all the 2,504 samples, and a false positive was filtered out if it was identified in >5% of subjects.
-
3.
Random error filtering: each event was filtered with a cluster property matrix (i.e., the number of supporting read-pairs and the average number of mismatches) with the reported parameters.
-
4.
Aligned orientations: each event was filtered based on q/p arm genetic exchange (joining type). As some of the samples had short read lengths (i.e., 35 bp), we further used Sanger sequencing results to fine-map the ligated sequences at the breakpoints.
Chromosome analysis and FISH validation
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed B lymphoblastoid (EBV-B) cell lines were obtained from the Coriell Institute (Camden, NJ) for validation. G-banded chromosome analysis was performed using standard protocols for more than 100 cells in each EBV-B cell line.16 Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed for NA18612 using standard procedures with bacterial artificial chromosome clones labeled by nick translation with SpectrumOrange, SpectrumRed or SpectrumGreen dUTP (Abbott Molecular, Des Plaines, IL).16,17 Bacterial artificial chromosome clones were selected from the University of California, Santa Cruz Genome Browser (https://genome.ucsc.edu/).
Molecular validation of balanced rearrangements
For samples with translocations and available EBV-B cell lines, genomic DNA was extracted using a commercial DNA extraction kit (Puregene, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). For samples identified with submicroscopic inversions, DNA samples were obtained from the Coriell Institute. Each DNA sample was quantified subsequently with the Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Life Technologies, Waltham, MA) for DNA quality measurement.
Genomic reference sequences (GRCh37/hg19) at a 1 kb distance from each putative breakpoint region (both upstream and downstream) were used for primer design with Primer3 Web (http://primer3.ut.ee/)and NCBI Primer-Blast (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/) (Supplementary Table 2). PCR amplification was performed simultaneously in cases and control (DNA from YH, a well-characterized normal EBV-B cell line18). PCR products were sequenced by Sanger sequencing on an ABI 3730 machine (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE)8,13,19 and sequencing results were aligned with BLAT (https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgBlat?command=start) for further confirmation of the balanced rearrangement and for mapping breakpoints at single-nucleotide level.
RNA preparation, library construction, and sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from each EBV-B cell line with a balanced translocation using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and subsequently treated with DNase I (Invitrogen).20 For each RNA sample, purity was evaluated with a Nano-Photometer spectrophotometer (Implen, Westlake Village, CA), concentration measured in a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (Life Technologies), and RNA integrity verified using an Agilent 2100 BioAnalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA).
For library construction, messenger RNA (mRNA) enrichment was performed with Oligo(dT)25 Dynabeads (Thermo Fisher Scientific) twice and purification was carried out with the Dynabeads mRNA Purification Kit (Invitrogen, no. 61006). The eluted mRNA was fragmented with Fragmentation Buffer Mix at 94°C for 10 min. Reverse transcription (RT) was performed with RT Buffer Mix and RT Enzyme Mix followed by double-strand cDNA (dscDNA) synthesis with Second Strand Buffer Mix and Second Strand Enzyme Mix. End repair, adaptor (with barcode) ligation, and PCR amplification were performed after dscDNA purification. Next, the purified double-stranded PCR products were heat denatured to a single strand and circularized with Splint Oligo Mix and Ligation Enzyme (MGIEasy mRNA Library Prep Kit, no. 85-05536-01, MGI Technology, Shenzhen, China). The single-strand circle DNA (ssCirc DNA) library was rolling circle amplified to construct the DNA nanoball, which was substantially loaded into a patterned nanoarray. Paired-end sequencing with 50 bp in each end (PE50) was carried out in a BGISeq-500 platform (BGI, Wuhan, China).21
RNA-seq data analysis
Paired-reads that passed standard quality control tests13,15 were simultaneously aligned to the human genome (GRCh37/hg19) using HISAT (Hierarchical Indexing for Spliced Alignment of Transcripts)22 and aligned to human transcriptome (RefSeq) via Bowtie.23 One base-pair mismatch was set in each alignment. Paired-end aligned reads were used for further analysis. Alignment files were transformed into Pileup files for determination of coverage with Samtools (mpileup). The expression of each gene in each sample was determined based on alignment files from the human transcriptome (RefSeq).
The gene expression of each sample was compared to data reported for 13 EBV-B controls present in the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project (http://www.gtexportal.org/home/).24
Validation of cryptic deletions
Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed for validation of the two cryptic deletions. Genomic reference sequences (GRCh37/hg19) of each deleted region were used for primer design with Primer3 Web and NCBI Primer-Blast (Supplementary Table 2). Melting curve analysis was carried out for each pair of primers to ensure specificity of the PCR amplification, and the standard curve method was used to determine PCR efficiency (within a range from 95% to 105%).
Each reaction was performed in quadruplicate in 10 μl of reaction mixture simultaneously in cases and control (DNA from YH EBV-B cell line13) on a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) with SYBR Premix Ex Taq Tli RNaseH Plus (Takara Biotechnology, Dalian, China) with the default setting of the reaction condition. The number of copies in each sample was determined by using the ΔΔCt method, which compared the Ct (cycle threshold) in a case with that in the control.25 Two independent pairs of primers (Supplementary Table 2) were used in quintuplicate for validation of each deletion.
Accession number
The accession number for the RNA-seq data reported in this paper is GSE94043 (NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus).
Code availability
All the programs relevant to this pipeline are available at https://sourceforge.net/projects/bca-analysis/files/.
Results
We assessed 1,166 samples with at least 8.25-fold physical coverage (Supplementary Table 1), using our previously reported approach with the same parameters.13 Four samples (HG02260, HG03729, NA18612, and NA20764) were identified as harboring balanced translocations (Figure 1a), and four samples (NA20759, HG04152, NA18959, and NA21133) showed inversions, the size of which ranged from 57.8 kb to 13.3 Mb (Figure 1a). Of the four cases with balanced translocations, two are female and two male, and they originate from different ethnic populations (Table 1).11 For the four cases with inversions, all are males and they also originate from different ethnic populations (Table 2).
G-banded karyotypes were observed to be directly consistent with the WGS data for samples HG02260, HG03729, NA20764, and NA20759 (Figure 1d–g), and those of NA18612 were consistent but much less obvious (Figure 2a, described below). Sanger results confirmed each rearrangement in all eight samples with BCAs (Table 1 and Table 2, next-generation cytogenetic nomenclature26 shown in Supplementary Table 3). Microhomology sequences were identified in eight of 16 breakpoints; this suggests that the rearrangements were mediated by microhomology-mediated end joining27 (Table Tables 1 and Table 2). The remaining eight breakpoints represented nonhomologous end joining28 (Table Tables 1 and Table 2).
(a) Validation from chromosome analysis. Ideograms of the derivative balanced translocation chromosomes are shown with the corresponding G-banded chromosome pairs. Breakpoint regions are indicated with red arrows. (b) PCR validations of the junction of DNA sequences from the two derivative chromosomes are indicated by red arrows; both of them are absent in the negative control (indicated by red arrows correspondingly). (c) Validation from FISH. Bacterial artificial chromosome probes are shown with the targeted bands (16q24.3 in SpectrumOrange, 17p13.3 in SpectrumRed, and 17q25.1 in SpectrumGreen). Derivative chromosomes and normal chromosomes are designated with arrows. (d) In the der(17), the genomic location of antisense gene CFDP1 (NM_006324) is shown with the breakpoint mapping in intron 6 (red dotted line). RNA-seq read-pairs align to the region (expressed as coverage) proximal to the breakpoint in seq[GRCh37/hg19] 16q23.1(75,336,134_75,336,138). It includes the intergenic region in 17q24.2 and the partial intron 6 of CFDP1 (NM_006324) in 16q23.1 (two grey dotted lines), indicating the aberrant splicing of intron 6. (e) Transcript coverage was plotted with the paired-end aligned reads (RNA-seq). The coverage of each coordinate is divided by the average coverage in this transcript, and subsequently normalized coverage with the average coverage from the other three EBV-B cell lines from the 1000 Genomes Project. The black arrow indicates the low expression in exon 7 that is the absence of exon 7 in the disrupted transcript.
Subtle balanced translocation identified by WGS
Breakpoints of the t(16;17)(q23.1;q24.2) (NA18612, Figure 2b) were located in bands 16q23.1 and 17q24.2, representing translocated segments of 15.0 Mb and 16.2 Mb, respectively. Owing to similarity of the G-banding pattern and size in the exchanged segments, chromosome analysis did not readily identify the translocation (Figure 2a). Therefore, metaphase FISH17 was performed using bacterial artificial chromosome probes (SpectrumOrange: RP11-7D23 at 16q24.3, SpectrumGreen: RP11-526M7 at 17q25.1, and SpectrumRed: RP11-135N5 at 17p13.3) in more than 100 cells, confirming the t(16;17) (Figure 2c).
Gene disruptions by the breakpoints of balanced translocations
Of the four cell lines with balanced translocations, the eight breakpoints disrupted six genes (Table 1, Figure Figures 2d and Figure 3a), which in four cases resulted in disruption of all transcripts in the derivative chromosomes of the breakpoints. In contrast, none of the breakpoints from the four cases with inversions disrupted any gene (Table 2).
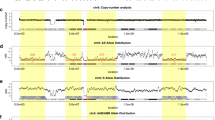
(a–c) NRXN3 disruption in 46,XX,t(9;14)(q34.2;q31.1) (HG02260). (a and b) Genomic locations of NRXN3 and RXRA are shown with breakpoints indicated by red dotted lines. (c) NRXN3 and RXRA expression for the four cases from the 1000 Genomes Project and for 13 reported EBV-B normal control cell lines (the GTEx project). Gene expression for NRXN3 and RXRA in HG02260 is indicated with red arrows. Panels (d and e) show cryptic deletions involved at the breakpoints in translocation 46,XY,t(3;17)(q24;p13.3) (HG03729). Two cryptic deletions of seq[GRCh37/hg19] 3q24(143,817,430_143,822,651)x1 and seq[GRCh37/hg19] 17p13.3(2,910,366_2,914,751)x1 were detected by a read-depth difference algorithm and were further confirmed by quantitative PCR. The deleted regions are shown on a yellow background with a red arrow while the normal copy-ratio (diploid) is shown on a blue background with a blue arrow (figure extracted from Integrative Genomics Viewer (http://software.broadinstitute.org/software/igv/)). Two independent pairs of primers (Supplementary Table 2) were used to perform qPCR in quintuplicate for validation of each deletion. The bars in cyan show the relative quantification of HG03729, while the bars in blue indicate the negative control. Panels (f and g) show potential disruption of interaction between promoter and enhancer from rearrangement in 46,XY,t(16;17)(q23.1;q24.2) (NA18612) in H1-hESC. (f) Genes and the ChIP-seq data from the ENCODE Project are shown in terms of the genomic location. Each cell line with H3K4Me3 and H3K27Ac33 is labeled with arrows in red and black, respectively. The breakpoint in seq[GRCh37/hg19] 17q24.2(64,953,078_64,953,079) is shown by a green vertical line, while the candidate promoters and enhancers are indicated with orange and blue arrows, respectively. The region of potential enhancer in H1-hESC is highlighted in DNase I Hypersensitivity Clusters34 in a blue rectangle (DHS region). The figure below is an enlarged image of the potential enhancer region in H1-hESC. Enrichment of H3K4Me1 and absence of H3K4Me3 support a potential active enhancer in this region,33,39 while enrichment of DNA-binding sequence motifs also indicates the candidate region of the interaction for regulatory elements.33 (g) Gene expression level (RPKM, Reads per kilobase per million) of the four cases and 13 EBV-B normal control samples (GTEx project).24
The breakpoint in seq[GRCh37/hg19] 16q23.1(75,336,134_75,336,138) (NA18612, Figure 2d) disrupts the gene encoding craniofacial development protein 1 (CFDP1, NM_006324), resulting in aberrant splicing of intron 6 and an absence of expression of exon 7. This disruption is supported by observation of RNA-seq reads mapping in the nonexonic region (Figure 2d) and decreased expression of exon 7 (Figure 2e). Although CFDP1 has been reported to be necessary for cell survival and differentiation during tooth morphogenesis in organ culture,29 it is unlikely to be haploinsufficient (haploinsufficiency score = 14.9%, DECIPHER (https://decipher.sanger.ac.uk)).30
In contrast, the seq[GRCh37/hg19] 14q31.1(79,839,173_79,839,174) breakpoint of 46,XX,t(9;14)(q34.2;q31.1) (HG02260) (Figure 3a) disrupts all transcripts of neurexin 3 (NRXN3), which is likely to be haploinsufficient (haploinsufficiency score = 0.3%).30 However, expression of NRXN3 was not detectable among any of the EBV-B cell lines including cases or controls (Figure 3c).24
Cryptic deletions
The 3q24 breakpoint of 46,XY,t(3;17)(q24;p13.3) (HG03729) was found to include a 5.2 kb deletion, seq[GRCh37/hg19] 3q24(143,817,430_143,822,651)x1, while the 17p13.3 breakpoint has a 4.4 kb deletion, seq[GRCh37/hg19] 17p13.3(2,910,366_2,914,751)x1 (Table 1, Figure 3d). Neither deletion was reported previously11 and both were confirmed by quantitative PCR (Figure 3d).
Positional effects
Previous studies show that genes in proximity to the breakpoints of a structural variant (i.e., balanced translocation) may be misexpressed, which is defined as a positional effect.5 One mechanism for a positional effect is the disruption of topological associated domains (TADs) by the SV’s breakpoints.6,9,31 Here, we used boundaries predicted from the human IMR90 fibroblast cell line (GRCh37/hg19)31 for our study, as TADs are highly conserved across different cell types and across species.32
Eight TADs were disrupted by the breakpoints from the four translocations. Thirty-four genes are located in these eight disrupted TADs, and expression was observed in 16 of these genes in normal EBV-B cell lines (Supplementary Table 4). However, misexpression was not observed in any of these 34 genes from our RNA-seq data (Supplementary Table 4), even though 2 of these genes are predicted to probably be haploinsufficient (Supplementary Table 4). The published ChIP-seq data from the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE https://www.encodeproject.org)33 in EBV-B cell line GM12878 indicate that 22 of the 34 genes have a candidate promoter (indicated by H3K4Me3) near a potential active regulatory element (indicated by H3K27Ac).31,33 In addition, as shown by the accessible chromatin landscape,34 19 of the 34 genes have highly associated DNA I hypersensitive sites (DHSs) and each has at least one DHS located in the same partial TAD as the gene and the predicted promoter.
The breakpoint in seq[GRCh37/hg19] 17q24.2(64,953,078_64,953,079) is likely to be located between the CACNG4 promoter (indicated by H3K4Me3) and its potential enhancer (indicated by H3K27Ac 31,33 and DHSs,34 Figure 3f) in a human embryonic stem-cell line (H1-hESC).33 These data suggest that the translocation would probably result in disruption of the interaction between the promoter and enhancer for CACNG4 32 in this particular cell line. However, misexpression of CACNG4 was not observed in our RNA-seq data from the EBV-B cell line (Figure 3g). Both the candidate promoter and the enhancer for CACNG4 were probably located downstream of the breakpoint33 in the EBV-B cell line GM12878 (control EBV-B cell line, Figure 3f).
Discussion
BCAs, including translocations and inversions, known to cause reproductive problems and/or an abnormal phenotype, are currently detected mainly by G-banded chromosome analysis. However, subtle or cryptic BCAs are not detectable by current methods but may contribute to birth defects in offspring of the carriers, owing to unbalanced segregations.35 In the present study, by utilizing existing genomic data from the 1000 Genomes Project, we demonstrated the feasibility of using WGS in the detection of BCAs in samples without prior knowledge of their existence.
In the present study, we set a cutoff of 8.25-fold physical coverage to maximize the inclusion of 1,166 of 2,504 samples, based on the evaluation of the false-negative rate in our previous study (11.1%, with 90 million read-pairs with insert sizes ranging from 400 to 600 bp).13 The exclusion of more than half of all samples (n = 1,338) is because of the smaller insert size generated (259.1 ± 93.5 bp, Figure 1a); the number of nonchimeric and uniquely mapped read-pairs was 97.0 ± 40.2 million, although the base coverage reached 7.4-fold on average. Thus, detection of BCAs can be improved by using larger inserts to increase physical coverage, thereby increasing the number of supporting read-pairs for the potential BCAs.
The prevalence of reciprocal balanced translocations in this dataset is one in 291.5 (0.34%, 4/1,166), which is higher than the rate reported estimated by G-banded chromosome analysis.1,2,3 This estimate may be biased because of the limited sample size (N = 1,166). However, the reported incidences may be underestimated, as cryptic or subtle rearrangements such as that observed for 46,XY,t(16;17)(q23.1;q24.2) (NA18612) may not be readily identified by conventional G-banded chromosome analysis (Figure 3). Another explanation might be that the detection of rearrangements was based on WGS of EBV-B cell line-derived DNAs, which might have EBV-B-specific genomic variants owing to the introduction of genomic instability by EBV infection or the conditions of cell culture.36 However, as the EBV-B specific genomic variants frequently exist as mosaics,36 given the 100% consistency of more than 100 metaphases in each sample in the present study, and as the WGS data of these samples used for our analysis were generated from early batches of EBV-B cell lines in the 1000 Genomes Project, balanced translocations detected probably represent the true events in the subjects’ peripheral blood samples. Nonetheless, our approach reports the true events existing in the tested EBV-B cell lines.
In addition to the detection of balanced translocations, the microscopic inversion and three submicroscopic inversions identified (Table 2) were each unique to a single subject among all 1,166 samples analyzed. One explanation of not identifying common or recurrent inversions is that they may be mediated by repetitive elements28 that might not be detected by sequencing with a small-insert library.37 Sequencing with a mate-pair library (or a large-insert library) might be able to overcome such a challenge and can also greatly reduce the sequencing cost by reducing the read-pair amount required.13,19 Nonetheless, the identification of both balanced translocations and inversions underscores the importance of using low-pass WGS for nucleotide-level precision of chromosomal rearrangements in cytogenetic diagnoses, and brings us a step closer to implementation of sequencing as the first-tier test.
Gene disruptions were observed in six of the eight breakpoints in four cases with balanced translocations, and NRXN3, a probably haploinsufficient gene, was disrupted (HG02260). Heterozygous deletion of NRXN3 is reported in autism spectrum disorder.38 Although this participant in the 1000 Genomes Project is assumed to be healthy at the time of enrollment, a possible explanation for the apparent absence of autism spectrum disorder in this presumed normal individual would be lack of penetrance,38 in the absence of a positive comprehensive medical assessment or some technical failure in the process.
Two cryptic deletions involving both breakpoints were identified in t(3;17)(q24;p13.3) (HG03729) and neither of them had previously been reported.11 Two possible reasons for missed detection in the previous study11 are: (i) only a limited number of reads mapping in these regions (Figure 3d) resulting in insufficiently sensitive read-depth differences for identification, and (ii) absence of intrachromosomal aligned read-pairs supporting these two deletions. Genomic imbalance commonly involves the breakpoint of balanced translocations, and some of them are known to be pathogenic or likely pathogenic,6 thus indicating the importance of identification.
No aberration in gene expression resulted from a positional effect, such as disruption of TADs, as observed in our EBV-B cell line-derived RNA-seq data from four cases with balanced translocations. One explanation is that expression was only observed in 16 of the 34 genes in normal EBV-B cell lines (Supplementary Table 4), and an effect of dysregulated lower expression cannot be detected for genes without detectable expression in the EBV-B cell lines.24 In addition, another reason would be the proximate interaction between promoter and enhancer: (i) 22 of the 34 genes have a candidate promoter near a potential active regulatory element31,33 and (ii) 19 of the 34 genes have highly associated DHSs,34 and each of them has at least one DHS located in the same partial TAD as the gene and the predicted promoter, indicating that some residual interactions remain between promoter and regulatory elements; thus, the disruption of TADs is probably insufficient to alter the gene expression. The data from RNA expression provide evidence for confirming potential effects attributed to a chromosomal rearrangement, indicating the importance of combining RNA expression analysis with identification of BCAs based on DNA samples for clinical interpretation.
We observed a potential disruption of an interaction between the promoter and an enhancer for the 17q24.2 breakpoint (NA18612) in H1-hESC, which serves as a reference for disease association prediction.31 However, misexpression of CACNG4 was not observed in our RNA-seq data from the EBV-B cell line (Figure 3g). One explanation is that both the candidate promoter and the enhancer for CACNG4 are probably located downstream of the breakpoint33 in the EBV-B-derived cell line (GM12878, Figure 3f). Because another sample type from this subject is not obtainable for further validation, this case (NA18612) argues that peripheral blood is commonly considered a valuable sample type for disease studies for reasons beyond its simple availability.
Overall, this study is the first reported investigation utilizing low-pass WGS to explore detection of BCAs among samples from the 1000 Genomes Project without previously known chromosomal abnormalities. In addition, disruption of genes, cryptic imbalances, and potential disruption of promoter and enhancer interaction were observed in the four cases with balanced translocations, demonstrating the advantage of detecting the breakpoints in BCAs by molecular methods via paired-end sequencing and Sanger sequencing. These observations have important implications for a new dawn of improved diagnostics in clinical cytogenetics.
References
Mackie Ogilvie C, Scriven PN. Meiotic outcomes in reciprocal translocation carriers ascertained in 3-day human embryos. Eur J Hum Genet 2002;10:801–806.
Oliver-Bonet M, Navarro J, Carrera M, Egozcue J, Benet J. Aneuploid and unbalanced sperm in two translocation carriers evaluation of the genetic risk. Mol Hum Reprod 2002;8:958–963.
Van Dyke DL, Weiss L, Roberson JR, Babu VR. The frequency and mutation rate of balanced autosomal rearrangements in man estimated from prenatal genetic studies for advanced maternal age. Am J Hum Genet 1983;35:301–308.
Warburton D. De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes identified at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet 1991;49:995–1013.
Talkowski ME, Rosenfeld JA, Blumenthal I et al. Sequencing chromosomal abnormalities reveals neurodevelopmental loci that confer risk across diagnostic boundaries. Cell 2012;149:525–537.
Redin C, Brand H, Collins RL et al. The genomic landscape of balanced cytogenetic abnormalities associated with human congenital anomalies. Nat Genet 2017;49:36–45.
De Gregori M, Ciccone R, Magini P et al. Cryptic deletions are a common finding in “balanced” reciprocal and complex chromosome rearrangements: a study of 59 patients. J Med Genet 2007;44:750–762.
Talkowski ME, Ordulu Z, Pillalamarri V et al. Clinical diagnosis by whole-genome sequencing of a prenatal sample. N Engl J Med 2012;367:2226–2232.
Ordulu Z, Kammin T, Brand H et al. Structural chromosomal rearrangements require nucleotide-level resolution: lessons from next-generation sequencing in prenatal diagnosis. Am J Hum Genet 2016;99:1015–1033.
Nilsson D, Pettersson M, Gustavsson P et al. Whole-genome sequencing of cytogenetically balanced chromosome translocations identifies potentially pathological gene disruptions and highlights the importance of microhomology in the mechanism of formation. Hum Mutat 2017;38:180–192.
Sudmant PH, Rausch T, Gardner EJ et al. An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes. Nature 2015;526:75–81.
1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015;526:68–74.
Dong Z, Jiang L, Yang C et al. A robust approach for blind detection of balanced chromosomal rearrangements with whole-genome low-coverage sequencing. Hum Mutat 2014;35:625–636.
Ekblom R, Wolf JB. A field guide to whole-genome sequencing, assembly and annotation. Evol Appl 2014;7:1026–1042.
Dong Z, Zhang J, Hu P et al. Low-pass whole-genome sequencing in clinical cytogenetics: a validated approach. Genet Med 2016;18:940–948.
Ou Z, Stankiewicz P, Xia Z et al. Observation and prediction of recurrent human translocations mediated by NAHR between nonhomologous chromosomes. Genome Res 2011;21:33–46.
Gui B, Yao Z, Li Y et al. Chromosomal analysis of blastocysts from balanced chromosomal rearrangement carriers. Reproduction 2016;151:455–464.
Wang J, Wang W, Li R et al. The diploid genome sequence of an Asian individual. Nature 2008;456:60–65.
Talkowski ME, Ernst C, Heilbut A et al. Next-generation sequencing strategies enable routine detection of balanced chromosome rearrangements for clinical diagnostics and genetic research. Am J Hum Genet 2011;88:469–481.
Zhang B, Zhang W, Nie RE et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis of chemosensory genes in two sister leaf beetles provides insights into chemosensory speciation. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2016;79:108–118.
Goodwin S, McPherson JD, McCombie WR. Coming of age: ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nat Rev Genet 2016;17:333–351.
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Method. 2015;12:357–360.
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 2009;10:R25.
GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat Gene 2013;45:580–585.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001;25:402–408.
Ordulu Z, Wong KE, Currall BB et al. Describing sequencing results of structural chromosome rearrangements with a suggested next-generation cytogenetic nomenclature. Am J Hum Genet 2014;94:695–709.
Sfeir A, Symington LS. Microhomology-mediated end joining: a back-up survival mechanism or dedicated pathway? Trends Biochem Sci 2015;40:701–714.
Carvalho CM, Lupski JR. Mechanisms underlying structural variant formation in genomic disorders. Nat Rev Genet 2016;17:224–238.
Diekwisch TG, Luan X. CP27 function is necessary for cell survival and differentiation during tooth morphogenesis in organ culture. Gene 2002;287:141–147.
Huang N, Lee I, Marcotte EM, Hurles ME. Characterising and predicting haploinsufficiency in the human genome. PLoS Genet 2010;6:e1001154.
Lupiáñez DG, Kraft K, Heinrich V et al. Disruptions of topological chromatin domains cause pathogenic rewiring of gene-enhancer interactions. Cell 2015;161:1012–1025.
Dixon JR, Selvaraj S, Yue F et al. Topological domains in mammalian genomes identified by analysis of chromatin interactions. Nature 2012;485:376–380.
Rosenbloom KR, Sloan CA, Malladi VS et al. ENCODE data in the UCSC Genome Browser: year 5 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2013;41(Database issue):D56–63.
Thurman RE, Rynes E, Humbert R et al. The accessible chromatin landscape of the human genome. Nature 2012;489:75–82.
Ledbetter DH, Martin CL. Cryptic telomere imbalance: a 15-year update. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2007;145C:327–334.
Shirley MD, Baugher JD, Stevens EL et al. Chromosomal variation in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Mutat 2012;33:1075–1086.
Meyerson M, Gabriel S, Getz G. Advances in understanding cancer genomes through second-generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 2010;11:685–696.
Vaags AK, Lionel AC, Sato D et al. Rare deletions at the neurexin 3 locus in autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet 2012;90:133–141.
Shlyueva D, Stampfel G, Stark A. Transcriptional enhancers: from properties to genome-wide predictions. Nat Rev Genet 2014;15:272–286.
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81370715, 81300075), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2014A030313795), the Guangdong Enterprise Key Laboratory of Human Disease Genomics (No. 2011A060906007), the Shenzhen Municipal Government of China (No. CXZZ20150330171838997), Shenzhen Engineering Laboratory for Birth Defects Screening (DRC-SZ [2011]861), Shenzhen Key Laboratory of genomics (No. CXB200903110066A) and Health and Medical Research Fund (HMRF, Project 04152666). C.C.M. acknowledges funding through NIH/NIGMS GM061354. We thank the 1000 Genomes Project for releasing the WGS data for this study, and Feng Yue and Bo Zhang from Pennsylvania State University for sharing with us the predicted TADs from the human IMR90 fibroblast cell line (in the GRCh37/hg19 version). This study was approved by the institutional review board of the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z., Wang, H., Chen, H. et al. Identification of balanced chromosomal rearrangements previously unknown among participants in the 1000 Genomes Project: implications for interpretation of structural variation in genomes and the future of clinical cytogenetics. Genet Med 20, 697–707 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.170
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.170
This article is cited by
-
Evaluation of genetic risk of apparently balanced chromosomal rearrangement carriers by breakpoint characterization
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2024)
-
Mate-pair genome sequencing reveals structural variants for idiopathic male infertility
Human Genetics (2023)
-
A high-throughput real-time PCR tissue-of-origin test to distinguish blood from lymphoblastoid cell line DNA for (epi)genomic studies
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Deciphering the complexity of simple chromosomal insertions by genome sequencing
Human Genetics (2021)
-
High-throughput long paired-end sequencing of a Fosmid library by PacBio
Plant Methods (2019)