Abstract
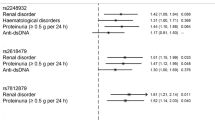
UHRF1BP1 encodes a highly conserved protein with unknown function. Previously, a coding variant in this gene was found to be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in populations of European ancestry (rs11755393, R454Q, P=2.22 × 10−8, odds ratio=1.17). In this study, by a combination of genome-wide study and replication involving a total of 1230 patients and 3144 controls, we confirmed the association of this coding variant to SLE in Hong Kong Chinese. We also identified another coding variant in this gene that independently contributes to SLE susceptibility (rs13205210, M1098T, P=4.44 × 10−9, odds ratio=1.49). Cross-population confirmation establishes the involvement of this locus in SLE and indicates that distinct alleles are contributing to disease susceptibility.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnett FC, Shulman LE . Studies in familial systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976; 55: 313–322.
Ramos-Niembro F, Alarcon-Segovia D . Familial aspects of mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD). I. Occurrence of systemic lupus erythematosus in another member in two families and aggregation of MCTD in another family. J Rheumatol 1978; 5: 433–440.
Sestak AL, Shaver TS, Moser KL, Neas BR, Harley JB . Familial aggregation of lupus and autoimmunity in an unusual multiplex pedigree. J Rheumatol 1999; 26: 1495–1499.
Mok CC, Lau CS . Lupus in Hong Kong Chinese. Lupus 2003; 12: 717–722.
Wong SN, Tse KC, Lee TL, Lee KW, Chim S, Lee KP et al. Lupus nephritis in Chinese children—a territory-wide cohort study in Hong Kong. Pediatr Nephrol 2006; 21: 1104–1112.
Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B, Taylor KE, Ortmann W, Garnier S et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 900–909.
Gateva V, Sandling JK, Hom G, Taylor KE, Chung SA, Sun X et al. A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1228–1233.
Han JW, Zheng HF, Cui Y, Sun LD, Ye DQ, Hu Z et al. Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1234–1237.
Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 204–210.
Yang W, Shen N, Ye DQ, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Qian XX et al. Genome-wide association study in Asian populations identifies variants in ETS1 and WDFY4 associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1000841.
Siu HO, Yang W, Lau CS, Chan TM, Wong RW, Wong WH et al. Association of a haplotype of IRF5 gene with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese. J Rheumatol 2008; 35: 360–362.
Yang W, Ng P, Zhao M, Hirankarn N, Lau CS, Mok CC et al. Population differences in SLE susceptibility genes: STAT4 and BLK, but not PXK, are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Genes Immun 2009; 10: 219–226.
Yang W, Zhao M, Hirankarn N, Lau CS, Mok CC, Chan TM et al. ITGAM is associated with disease susceptibility and renal nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese and Thai. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18: 2063–2070.
Chang YK, Yang W, Zhao M, Mok CC, Chan TM, Wong RW et al. Association of BANK1 and TNFSF4 with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Genes Immun 2009; 10: 414–420.
Kim I, Kim YJ, Kim K, Kang C, Choi CB, Sung YK et al. Genetic studies of systemic lupus erythematosus in Asia: where are we now? Genes Immun 2009; 10: 421–432.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D . Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. NatGenet 2006; 38: 904–909.
Unoki M, Nishidate T, Nakamura Y . ICBP90, an E2F-1 target, recruits HDAC1 and binds to methyl-CpG through its SRA domain. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7601–7610.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by the generous donation from Shun Tak District Min Yuen Tong of Hong Kong (to YLL). WY thanks support from Research Grant Council of the Hong Kong Government (GRF HKU781709M). YZ is supported by Edward the Sai Kim Hotung Paediatric Education and Research Fund and University Postgraduate Studentship. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, W., Mok, C. et al. Two missense variants in UHRF1BP1 are independently associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Genes Immun 12, 231–234 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2010.66
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2010.66
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association study identifies FBN2 as a novel locus associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Thai population
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2020)
-
Genetic association analyses implicate aberrant regulation of innate and adaptive immunity genes in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Nature Genetics (2015)
-
Meta-analysis of two Chinese populations identifies an autoimmune disease risk allele in 22q11.21 as associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2015)