Abstract
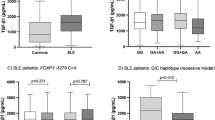
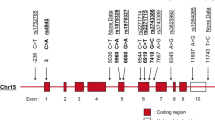
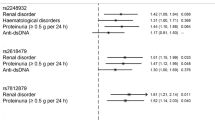
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors (LILRs) are inhibitory, stimulatory or soluble receptors encoded within the leukocyte receptor complex. Some LILRs are extensively polymorphic, and exhibit evidence for balancing selection and association with disease susceptibility. LILRA2 (LIR7/ILT1) is an activating receptor highly expressed in inflammatory tissues, and is involved in granulocyte and macrophage activation. In this study, we examined the association of LILRA2 and adjacently located LILRA1 with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA). Polymorphism screening detected a LILRA2 SNP (rs2241524 G>A) that disrupts splice acceptor site of intron 6. Case–control association studies on 273 Japanese SLE, 296 RA, 50 MPA and 284 healthy individuals revealed increase of genotype A/A in SLE (12.1%, odds ratio (OR) 1.82, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.02–3.24, P=0.041) and in MPA (16.0%, OR 2.52, 95% CI 1.07–5.96, P=0.049) compared with healthy individuals (7.0%). The risk allele caused an activation of a cryptic splice acceptor site that would lead to a novel LILRA2 isoform lacking three amino acids in the linker region (Δ419–421). Flow cytometry indicated that this isoform was expressed on the surface of monocytes. These findings suggested that LILRA2 Δ419–421 isoform encoded by the splice site SNP may play a role in SLE and MPA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Borges L, Hsu ML, Fanger N, Kubin M, Cosman D . A family of human lymphoid and myeloid Ig-like receptors, some of which bind to MHC class I molecules. J Immunol 1997; 159: 5192–5196.
Colonna M, Navarro F, Bellon T, Llano M, Garcia P, Samaridis J et al. A common inhibitory receptor for major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on human lymphoid and myelomonocytic cells. J Exp Med 1997; 186: 1809–1818.
Cosman D, Fanger N, Borges L, Kubin M, Chin W, Peterson L et al. A novel immunoglobulin superfamily receptor for cellular and viral MHC class I molecules. Immunity 1997; 7: 273–282.
Wende H, Colonna M, Ziegler A, Volz A . Organization of the leukocyte receptor cluster (LRC) on human chromosome 19q13.4. Mamm Genome 1999; 10: 154–160.
Wende H, Volz A, Ziegler A . Extensive gene duplications and a large inversion characterize the human leukocyte receptor cluster. Immunogenetics 2000; 51: 703–713.
Wilson MJ, Torkar M, Haude A, Milne S, Jones T, Sheer D et al. Plasticity in the organization and sequences of human KIR/ILT gene families. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 4778–4783.
Lindqvist AK, Steinsson K, Johanneson B, Kristjansdottir H, Arnasson A, Grondal G et al. A susceptibility locus for human systemic lupus erythematosus (hSLE1) on chromosome 2q. J Autoimmun 2000; 14: 169–178.
Moser KL, Neas BR, Salmon JE, Yu H, Gray-McGuire C, Asundi N et al. Genome scan of human systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for linkage on chromosome 1q in African-American pedigrees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 14869–14874.
Kubagawa H, Burrows PD, Cooper MD . A novel pair of immunoglobulin-like receptors expressed by B cells and myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 5261–5266.
Yamashita Y, Ono M, Takai T . Inhibitory and stimulatory functions of paired Ig-like receptor (PIR) family in RBL-2H3 cells. J Immunol 1998; 161: 4042–4047.
Ujike A, Takeda K, Nakamura A, Ebihara S, Akiyama K, Takai T . Impaired dendritic cell maturation and increased TH2 responses in PIR-B−/− mice. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 542–548.
Nakamura A, Kobayashi E, Takai T . Exacerbated graft-versus-host disease in Pirb−/− mice. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 623–629.
Cella M, Jarrossay D, Facchetti F, Alebardi O, Nakajima H, Lanzavecchia A et al. Plasmacytoid monocytes migrate to inflamed lymph nodes and produce large amounts of type I interferon. Nat Med 1999; 5: 919–923.
Nakajima H, Samaridis J, Angman L, Colonna M . Human myeloid cells express an activating ILT receptor (ILT1) that associates with Fc receptor γ-chain. J Immunol 1999; 162: 5–8.
Bleharski JR, Li H, Meinken C, Graeber TG, Ochoa MT, Yamamura M et al. Use of genetic profiling in leprosy to discriminate clinical forms of the disease. Science 2003; 301: 1527–1530.
Tedla N, Gibson K, McNeil HP, Cosman D, Borges L, Arm JP . The co-expression of activating and inhibitory leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors in rheumatoid synovium. Am J Pathol 2002; 160: 425–431.
Colonna M, Samaridis J, Cella M, Angman L, Allen RL, O'Callaghan CA et al. Human myelomonocytic cells express an inhibitory receptor for classical and nonclassical MHC class I molecules. J Immunol 1998; 160: 3096–3100.
Shiroishi M, Tsumoto K, Amano K, Shirakihara Y, Colonna M, Braud VM et al. Human inhibitory receptors Ig-like transcript 2 (ILT2) and ILT4 compete with CD8 for MHC class I binding and bind preferentially to HLA-G. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 8856–8861.
Tedla N, Bandeira-Melo C, Tassinari P, Sloane DE, Samplaski M, Cosman D et al. Activation of human eosinophils through leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 1174–1179.
Sloane DE, Tedla N, Awoniyi M, Macglashan Jr DW, Borges L, Austen KF et al. Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors: novel innate receptors for human basophil activation and inhibition. Blood 2004; 104: 2832–2839.
Huynh OA, Hampartzoumian T, Arm JP, Hunt J, Borges L, Ahern M et al. Down-regulation of leucocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor expression in the synovium of rheumatoid arthritis patients after treatment with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Rheumatology 2007; 46: 742–751.
Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K, Kim S, Suematsu A, Kobayashi E et al. Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature 2004; 428: 758–763.
Tsuchiya N, Kyogoku C, Miyashita R, Kuroki K . Diversity of human immune system multigene families and its implication in the genetic background of rheumatic diseases. Curr Med Chem 2007; 14: 431–439.
Tsuchiya N, Honda Z, Tokunaga K . Role of B cell inhibitory receptor polymorphisms in systemic lupus erythematosus: a negative times a negative makes a positive. J Hum Genet 2006; 51: 741–750.
Miyashita R, Tsuchiya N, Yabe T, Kobayashi S, Hashimoto H, Ozaki S et al. Association of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genotypes with microscopic polyangiitis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 992–997.
Kuroki K, Tsuchiya N, Shiroishi M, Rasubala L, Yamashita Y, Matsuta K et al. Extensive polymorphisms of LILRB1 (ILT2, LIR1) and their association with HLA-DRB1 shared epitope negative rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 2469–2480.
Hirayasu K, Ohashi J, Kashiwase K, Takanashi M, Satake M, Tokunaga K et al. Long-term persistence of both functional and non-functional alleles at the leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor A3 (LILRA3) locus suggests balancing selection. Hum Genet 2006; 119: 436–443.
Kyogoku C, Tsuchiya N . A compass that points to lupus: genetic studies on type I interferon pathway. Genes Immun 2007; 8: 445–455.
Reumaux D, Duthilleul P, Roos D . Pathogenesis of diseases associated with antineutrophil cytoplasm autoantibodies. Hum Immunol 2004; 65: 1–12.
Takahashi S, Fossati L, Iwamoto M, Merino R, Motta R, Kobayakawa T et al. Imbalance towards Th1 predominance is associated with acceleration of lupus-like autoimmune syndrome in MRL mice. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 1597–1604.
Ohashi J, Yamamoto S, Tsuchiya N, Hatta Y, Komata T, Matsushita M et al. Comparison of statistical power between 2 × 2 allele frequency and allele positivity tables in case-control studies of complex disease genes. Ann Hum Genet 2001; 65: 197–206.
Tsuchiya N, Kobayashi S, Kawasaki A, Kyogoku C, Arimura Y, Yoshida M et al. Genetic background of Japanese patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: association of HLA-DRB1*0901 with microscopic polyangiitis. J Rheumatol 2003; 30: 1534–1540.
Tsuchiya N, Kobayashi S, Hashimoto H, Ozaki S, Tokunaga K . Association of HLA-DRB1*0901-DQB1*0303 haplotype with microscopic polyangiitis in Japanese. Genes Immun 2006; 7: 81–84.
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988; 31: 315–324.
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1982; 25: 1271–1277.
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum 1994; 37: 187–192.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr Jun Ohashi (The University of Tokyo) and Dr Ryosuke Kimura (Tokai University) for their helpful suggestions. Sequence accession number: The nucleotide sequence data reported in this paper have been submitted to the DDBJ database and have been assigned the accession numbers AB375279-AB375302. This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas ‘Applied Genomics’ from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, Takeda Science Foundation and Japan Rheumatism Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamegano, K., Kuroki, K., Miyashita, R. et al. Association of LILRA2 (ILT1, LIR7) splice site polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus and microscopic polyangiitis. Genes Immun 9, 214–223 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.5
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between the AKT1 single nucleotide polymorphism (rs2498786, rs2494752 and rs5811155) and microscopic polyangiitis risk in a Chinese population
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2023)
-
An immunogenetic perspective of ANCA-associated vasculitides
Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation (2022)
-
Genetics of ANCA-associated vasculitis: role in pathogenesis, classification and management
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2022)
-
Functional and genetic diversity of leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor and implication for disease associations
Journal of Human Genetics (2015)
-
Genetics of ANCA-associated Vasculitides
Current Rheumatology Reports (2014)