Abstract
Purpose
To review and evaluate the effects of intravitreal bevacizumab injection (IVB) in centralserous chorioretinopathy (CSC) by meta-analysis.
Patients and methods
Clinical controlled studies that evaluated the effect of IVB in CSC were identified through systematic searches of Embase, PubMed, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. Data on the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) in logMAR and central macular thickness (CMT) in μm at baseline and 6 months after IVB were extracted and compared with those treated by simple observation.
Results
Four clinical controlled studies were included in the meta-analysis. The IVB injection group achieved better BCVA at a follow-up of 6 months. However, the analysis showed that there were no significant differences of BCVA at 6 months after injection between IVB group and the observation group (−0.02 logMAR, 95% CI −0.14 to 0.11, P=0.80). The analysis of the reduction in CMT revealed that the difference between groups was not statistically significant (−8.37 μm, 95% CI −97.26 to 80.52, P=0.85). No report assessed severe complications or side effects of IVB in patients with CSC.
Conclusions
Meta-analysis failed to verify the positive effect of IVB in CSC based on the epidemiological literature published to date.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) is a common retinopathy with an uncertain pathology, characterized by serous detachment of the neurosensory retina.1, 2, 3, 4 The disorder is usually self-limited, although some patients are left with permanent visual impairment because of pigment epithelium and photoreceptor damage, especially in chronic CSC.1, 2, 5, 6 Hypotheses include abnormal alterations at the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) level2, 3, 7 and choroidal vascular hyperpermeability, as demonstrated on indocyanine green angiography.7, 8, 9
CSC has a high spontaneous remission rate, but there is evidence of the benefit of early treatment.10, 11, 12 CSC with single, extrafoveal leaking point can be treated using focal photocoagulation to shorten the duration of symptoms without altering the final visual outcomes and the recurrent rate.13, 14, 15 This method, however, has a significant adverse effect such as symptomatic scotomas, secondary choroidal neovascularization (CNV), and so on.16, 17 Recently, photodynamic therapy (PDT) with verteporfin has been tried as an alternative treatment to reduce underlying choroidal hyperpermeability and congestion.18, 19 The effect of the vascular modulation was successful with visual improvement in most of patients. However, there is a risk of complications, including RPE atrophy, choriocapillary hypoperfusion, and the development of CNV, especially with standard-dose PDT.9, 20 Half-dose PDT seems to be effective and safe, but its long-term efficacy is unknown.
Bevacizumab (Avastin, Roche, Basel, Switzerland), a monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), is a new treatment that exerts antipermeability effects in diabetic macular edema and CNV.2, 21 There have been several off-label clinical trials of intravitreal bevacizumab injection (IVB) in CSC.1, 2, 13, 22, 23, 24, 25 Most showed positive results, with improved visual acuity and reduced subretinal fluid. However, these findings should be interpreted cautiously because of the self-limiting characteristics of CSC, which can show spontaneous improvement within months.1, 2, 12, 22, 23, 24, 25
Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis of the efficacy of IVB in terms of visual acuity and macular thickness to gain a better perspective regarding the therapeutic options in CSC.
Materials and methods
Search method
Three databases (PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane) were last searched on 20 August. ‘Central serous chorioretinopathy’, ‘bevacizumab’, and ‘avastin’ comprised the terms for the sensitive search. There was no restriction on study design but the eligible studies only covered those that were written in English. Duplicate articles were manually removed.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Published studies, regardless of sample size or study design, were included if the changes in the means and SDs from baseline to 6 months after injection were available for the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) in logMAR and central macular thickness (CMT) in μm. The follow-up period varied across the studies, and we chose to analyze the results at 6 months as this period was the most common to all of the included studies. The results of subjects who received IVB were extracted, and the treatment of controls was assigned as simple observation, PDT, or subthreshold laser. The primary outcomes were the change in BCVA and CMT from baseline after IVB. The mean difference and SD at the 6-month follow-up were calculated from the data in the included studies. Secondary outcomes were any reported complication of IVB in eyes with CSC. Case reports, interventional case series, and comments were reviewed but not subjected to analysis, and conference abstracts that had not been published were excluded (Table 1).
Quality assessment
The quality of the included randomized clinical trials (RCTs) was evaluated using the Delphi list.26 Determined items were the following: randomization, allocation concealment, baseline similarity within groups, specified eligibility criteria, blinded outcome assessment, blinded care provider, blinded patient, point estimates and measure of variability presented, and intention-to-treat analysis.26 Quality scores were calculated, with a response of ‘yes’ given one point for each item and ‘not available’ or ‘no’ given zero points. Total scores are presented in Table 2.
Statistical analysis
The meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.1,27 with application of a random effect model. Heterogeneity was examined using the I2 statistic and was defined as significant at I2 <50%. Squares indicate mean difference estimates, and lines extending from the squares reveal the associated 95% intervals in the forest plot display. Confidence intervals that do not intersect the vertical line at 0 indicate statistical significance at the 0.05 level.
Sensitivity analysis
In order to assess the influence of two non-RCTs, and Snellen and ETDRS to logMAR conversion included in the meta-analysis, these studies were excluded and the analysis was performed. Sensitivity analyses were undertaken using the following subgroups to assess reliability: (1) all studies including two RCTs and two non-RCTs, and (2) two RCTs with logMAR visual acuity.
Results
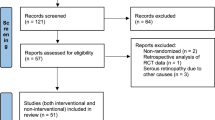
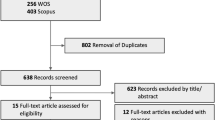
Result of search
The literature search yielded 155 articles, 50 from PubMed, 102 from EMBASE, and 3 from Cochrane Library. After excluding 138 ineligible articles because of various reasons such as duplicates from multiple databases, articles not matching the current topic, single case description, and different treatment modality, 17 studies were identified. There were 6 comparative studies, including 2 RCTs and 4 non-RCT studies (Table 3). The remaining 11 studies were interventional case series. After excluding 2 comparative studies because of the lack of data at 6 months of follow-up and the lack of observation group,28, 29 in total 112 patients were included in four comparative studies. Among those, 50 patients were in the treatment group with IVB as compared with 62 patients in the observation group.
Quality assessment
Nine criteria were used to judge the quality of two RCTs included in the meta-analysis. The two RTCs were of reasonable to good quality, and the mean quality score was 55.6%.
Characteristics of studies
The differences in the baseline BCVA, CMT, and demographics between the IVB and control groups were not significant in each of the included studies. However, the clinical heterogeneity among the included studies was considerable in several areas. As for the inclusion criteria, the two studies by Lim et al30 and Aydin31 recruited patients with acute CSC of <3-month duration, whereas the other studies included those with CSC of >3 months. The included studies used the different control groups: the three studies by Artunay et al,32 Lim et al,30 and Aydin31 used patients with observation, whereas the other studies by Semeraro et al29 and Lee et al28 used only those treated with PDT. Both the observation group and a group treated with a subthreshold laser were used as controls in the study by Koss et al.33 Moreover, four studies had consistent treatment arms comparing 1.25 mg/0.05 ml of IVB to the control group, whereas Artunay et al32 performed IVB with 2.5 mg/1.0 ml. Furthermore, Artunay et al,32 Lim et al,30 and Aydin31 simply evaluated the effect of IVB after a single injection, whereas the others allowed repeated treatment with the same modality, guided by BCVA, OCT, and fluorescein angiography (FA).
Visual acuity
Figure 1 shows the forest plot of the BCVA results of IVB and the observation group as a control. Examination of the forest plot demonstrated that, with the exception of the results shown by Aydin,31 the IVB injection group achieved better BCVA at a follow-up of 6 months. Meta-analysis of these data revealed no statistically significant differences between the two groups (−0.02 logMAR, 95% CI −0.14 to 0.11, P=0.80). Because heterogeneity (I2=68%) was substantial, a random effects model was used to present the data.
Central macular thickness
The forest plot showed that the IVB group was associated with more reduction in CMT than the control group. However, analysis of these data revealed that the difference between groups was not statistically significant (−8.37 μm, 95% CI −97.26 to 80.52, P=0.85; Figure 2).
Comparison among different treatment modalities was not possible because of the small number of available data on the subject.
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analyses of primary outcomes excluding two non-RCTs resulted in similar outcomes. The two non-RCTs included in this meta-analysis did not have an important impact: (1) (−0.02 logMAR, 95% CI −0.14 to 0.11, P=0.80) and (2) (−0.09 logMAR, 95% CI −0.20 to 0.01, P=0.09).
Adverse effects
There was no report of complications or side effects of IVB in patients with CSC in either the included or excluded studies except mild subconjuctival hemorrhage at the injection site.
Discussion
CSC is a self-limiting disease, but it can cause permanent photoreceptor damage or RPE atrophy that leads to visual impairment.34 The greater the understanding of the pathophysiology of CSC with advances in imaging, the more doubts about the so-called ‘benign’ nature of CSC. Several treatment modalities have been tried. Treatment with acetazolamide might shorten the duration of the disease without influencing the final visual acuity or recurrence rate.35 Other medical treatments such as mifepristone, aspirin, finasteride, and propanolol have been reported with good results but require well-designed randomized controlled study to evaluate their efficacy and safety.36, 37, 38, 39 One of the traditional treatments is focal laser photocoagulation, although its application is limited because of possible scotoma or secondary CNV when the RPE leak is close to the fovea.14 Some authors reported that laser photocoagulation was effective in shortening the duration of CSC and reducing the recurrence rate, whereas others reported no definite advantage in terms of the final vision or recurrence.2 PDT is another option for treatment of CSC, as choroidal hyperpermeability has been suggested as the underlying pathology, but foveal atrophy was reported as a possible complication and PDT is expensive.19, 40
Recently, anti-VEGF antibody has been used in CSC as an off-label method.1, 2, 3, 22, 23, 24, 28, 30, 32, 33, 41, 42, 43 Bevacizumab is a recombinant humanized full-length monoclonal antibody of VEGF that penetrates the retina and is transported into the photoreceptor outer segments, RPE, and choroid after intravitreal injection.44 The half-life of bevacizumab in the vitreous is 5.6 days, and it remains in the eye for 4 to 6 weeks.45 Many studies of other macular diseases have reported that the CMT starts decreasing or stabilizes in most eyes at 3–6 weeks.45, 46, 47, 48 The mechanism of IVB in the resolution of subretinal fluid in CSC is unknown, but might involve effects on choroidal vascular hyperpermeability.2, 3, 13
Considering the self-limiting characteristics of CSC, usually within 3–6 months, many of the clinical case studies selected patients with CSC of >3 months as subjects for IVB. Most case series reported no specific complications, although there is always some risk of postinjection endophthalmitis.49 Most studies reported that IVB might be effective in terms of improving visual acuity and reducing CMT without significant complications and can be considered an optional intervention,1, 2, 23, 24, 28, 32, 33 but these conclusions should be interpreted cautiously owing to the self-limiting nature of acute and even in chronic CSC. Moreover, it should be noted that the aqueous humor and plasma levels of VEGF were not significantly increased in patients with CSC compared with the healthy control group.50
Four studies were included in this meta-analysis. They compared the effects of IVB with simple observation. Nonrandomized studies were included, although it is usually better to exclude these from meta-analyses, because we believe that BCVA and CMT are not influenced by randomization. In this meta-analysis, the visual acuity at 6 months after injection was not significantly improved in the IVB group compared with simple observation, and the CMT was also not significantly reduced in the IVB group. Thus, a beneficial role of IVB in treating chronic or acute CSC can be discouraging.
Comparison with other treatment modalities was less valuable because of the relative lack of studies, and the role of IVB remains elusive. Semeraro et al29 reported that IVB group showed greater improvement in the mean BCVA compared with low-fluence PDT (300 mW/cm2 for 83 s, light dose 25 J/cm2) group at 9-month follow-up, although it was not statistically different. In contrast, it was reported by Lee et al28 that the mean BCVA was increased significantly more in standard PDT-treated group. Foveal thinning occurred more frequently in PDT group than in IVB group in both studies. Subthreshold laser photocoagulation (810 nm infrared diode) resulted superior to the IVB for resolution of SRF and BCVA improvement at 6 and 10 months after treatment in the study by Koss et al.33
Although our study confirmed the lack of efficacy of IVB for CSC over a 6-month period, the outcome of this treatment is still unknown. Despite the considerable available literature providing the possible efficacy of IVB for CSC, the majority of studies was simple interventional case series, and was not randomized. As a result, small sample sizes made it difficult to detect differences between the treatments and the observation. The second limitation is that the clinical heterogeneity among comparative studies was considerable in several areas, including inconsistency in inclusion criteria, and treatment protocols. The acute and chronic CSC were all subjected to the meta-analysis together. It would have been more meaningful meta-analysis to differentiate them, considering there might be inherent differences in the nature of acute and chronic CSC. However, chroidal vascular hyperpermeability is considered to be fundamental mechanisms for acute and chronic CSC, and the current treatment concept such as PDT or IVB is focused on modulating hyperpermeability in choroid. There has been language bias as the eligible studies only covered those that were written in English. Despite these limitations, this analysis makes an important contribution to the field because this study was the first meta-analysis to explore the use of intravitreal bevacizumab for CSC.
In conclusion, meta-analysis failed to verify the positive effect of IVB in CSC based on the epidemiological literature published to date. In the future, more studies using larger scales and better methodologies will help to clarify the uncertain relationship between CSC and IVB.

References
Seong HK, Bae JH, Kim ES, Han JR, Nam WH, Kim HK . Intravitreal bevacizumab to treat acute central serous chorioretinopathy: short-term effect. Ophthalmologica 2009; 223 (5): 343–347.
Torres-Soriano ME, Garcia-Aguirre G, Kon-Jara V, Ustariz-Gonzales O, Abraham-Marin M, Ober MD et al. A pilot study of intravitreal bevacizumab for the treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy (case reports). Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2008; 246 (9): 1235–1239.
Li XJ, Zhang JS . Intravitreal bevacizumab injection for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Chin Med J (Engl) 2010; 123 (15): 2145–2147.
Yannuzzi LA . Type-A behavior and central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 1987; 7 (2): 111–131.
Lafaut BA, Salati C, Priem H, De Laey JJ . Indocyanine green angiography is of value for the diagnosis of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy in elderly patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1998; 236 (7): 513–521.
Prunte C . Indocyanine green angiographic findings in central serous chorioretinopathy. Int Ophthalmol 1995; 19 (2): 77–82.
Guyer DR, Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS, Sorenson JA, Ho A, Orlock D . Digital indocyanine green videoangiography of central serous chorioretinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 1994; 112 (8): 1057–1062.
Prunte C, Flammer J . Choroidal capillary and venous congestion in central serous chorioretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 1996; 121 (1): 26–34.
Gemenetzi M, De Salvo G, Lotery AJ . Central serous chorioretinopathy: an update on pathogenesis and treatment. Eye (Lond) 2010; 24 (12): 1743–1756.
Shukla D, Kolluru C, Vignesh TP, Karthikprakash S, Kim R . Transpupillary thermotherapy for subfoveal leaks in central serous chorioretinopathy. Eye (Lond) 2008; 22 (1): 100–106.
Iida T, Yannuzzi LA, Spaide RF, Borodoker N, Carvalho CA, Negrao S . Cystoid macular degeneration in chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2003; 23 (1): 1–7 quiz 137-138.
Piccolino FC, de la Longrais RR, Ravera G, Eandi CM, Ventre L, Abdollahi A et al. The foveal photoreceptor layer and visual acuity loss in central serous chorioretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2005; 139 (1): 87–99.
Lim SJ, Roh MI, Kwon OW . Intravitreal bevacizumab injection for central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2010; 30 (1): 100–106.
Burumcek E, Mudun A, Karacorlu S, Arslan MO . Laser photocoagulation for persistent central serous retinopathy: results of long-term follow-up. Ophthalmology 1997; 104 (4): 616–622.
Wang M, Sander B, la Cour M, Larsen M . Clinical characteristics of subretinal deposits in central serous chorioretinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2005; 83 (6): 691–696.
Ross A, Ross AH, Mohamed Q . Review and update of central serous chorioretinopathy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2011; 22 (3): 166–173.
Wang M, Munch IC, Hasler PW, Prunte C, Larsen M . Central serous chorioretinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol 2008; 86 (2): 126–145.
Cardillo Piccolino F, Eandi CM, Ventre L, Rigault de la Longrais RC, Grignolo FM . Photodynamic therapy for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2003; 23 (6): 752–763.
Chan WM, Lam DS, Lai TY, Tam BS, Liu DT, Chan CK . Choroidal vascular remodelling in central serous chorioretinopathy after indocyanine green guided photodynamic therapy with verteporfin: a novel treatment at the primary disease level. Br J Ophthalmol 2003; 87 (12): 1453–1458.
Inoue R, Sawa M, Tsujikawa M, Gomi F . Association between the efficacy of photodynamic therapy and indocyanine green angiography findings for central serous chorioretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2010; 149 (3): 441–446. e441–e442.
Wu L, Martinez-Castellanos MA, Quiroz-Mercado H, Arevalo JF, Berrocal MH, Farah ME et al. Twelve-month safety of intravitreal injections of bevacizumab (Avastin): results of the Pan-American Collaborative Retina Study Group (PACORES). Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2008; 246 (1): 81–87.
Lim JW, Kim MU . The efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab for idiopathic central serous chorioretinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2011; 249 (7): 969–974.
Schaal KB, Hoeh AE, Scheuerle A, Schuett F, Dithmar S . Intravitreal bevacizumab for treatment of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Eur J Ophthalmol 2009; 19 (4): 613–617.
Inoue M, Kadonosono K, Watanabe Y, Kobayashi S, Yamane S, Arakawa A . Results of one-year follow-up examinations after intravitreal bevacizumab administration for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Ophthalmologica 2011; 225 (1): 37–40.
Lee ST, Adelman RA . The treatment of recurrent central serous chorioretinopathy with intravitreal bevacizumab. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 2011; 27 (6): 611–614.
Verhagen AP, de Vet HC, de Bie RA, Kessels AG, Boers M, Bouter LM et al. The Delphi list: a criteria list for quality assessment of randomized clinical trials for conducting systematic reviews developed by Delphi consensus. J Clin Epidemiol 1998; 51 (12): 1235–1241.
Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Version 5.1. The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration: Copenhagen, 2011.
Lee JY, Chae JB, Yang SJ, Kim JG, Yoon YH . Intravitreal bevacizumab versus the conventional protocol of photodynamic therapy for treatment of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol 2011; 89 (3): e293–e294.
Semeraro F, Romano MR, Danzi P, Morescalchi F, Costagliola C . Intravitreal bevacizumab versus low-fluence photodynamic therapy for treatment of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2012; 56 (6): 608–612.
Lim JW, Ryu SJ, Shin MC . The effect of intravitreal bevacizumab in patients with acute central serous chorioretinopathy. Korean J Ophthalmol 2010; 24 (3): 155–158.
Aydin E . The efficacy of intravitreal bevacizumab for acute central serous chorioretinopathy. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 2013; 29 (1): 10–13.
Artunay O, Yuzbasioglu E, Rasier R, Sengul A, Bahcecioglu H . Intravitreal bevacizumab in treatment of idiopathic persistent central serous chorioretinopathy: a prospective, controlled clinical study. Curr Eye Res 2010; 35 (2): 91–98.
Koss MJ, Beger I, Koch FH . Subthreshold diode laser micropulse photocoagulation versus intravitreal injections of bevacizumab in the treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy. Eye (Lond) 2012; 26 (2): 307–314.
Hussain D, Gass JD . Idiopathic central serous chorioretinopathy. Indian J Ophthalmol 1998; 46 (3): 131–137.
Pikkel J, Beiran I, Ophir A, Miller B . Acetazolamide for central serous retinopathy. Ophthalmology 2002; 109 (9): 1723–1725.
Nielsen JS, Weinreb RN, Yannuzzi L, Jampol LM . Mifepristone treatment of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2007; 27 (1): 119–122.
Caccavale A, Romanazzi F, Imparato M, Negri A, Morano A, Ferentini F . Low-dose aspirin as treatment for central serous chorioretinopathy. Clin Ophthalmol 2010; 4: 899–903.
Tatham A, Macfarlane A . The use of propranolol to treat central serous chorioretinopathy: an evaluation by serial OCT. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 2006; 22 (2): 145–149.
Forooghian F, Meleth AD, Cukras C, Chew EY, Wong WT, Meyerle CB . Finasteride for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2011; 31 (4): 766–771.
Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS, Gross NE, Spaide RF, Costa D, Huang SJ et al. Indocyanine green angiography-guided photodynamic therapy for treatment of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy: a pilot study. Retina 2003; 23 (3): 288–298.
Mehany SA, Shawkat AM, Sayed MF, Mourad KM . Role of Avastin in management of central serous chorioretinopathy. Saudi J Ophthalmol 2010; 24 (3): 69–75.
Jamil AZ, Rahman FU, Iqbal K, Ansari HM, Iqbal W, Mirza KA . Intravitreal bevacizumab in central serous chorioretinopathy. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2012; 22 (6): 363–366.
Entezari M, Ramezani A, Yaseri M . Intravitreal bevacizumab for treatment of refractory central serous choroidoretinopathy. Korean J Ophthalmol 2012; 26 (2): 139–142.
Heiduschka P, Fietz H, Hofmeister S, Schultheiss S, Mack AF, Peters S et al. Penetration of bevacizumab through the retina after intravitreal injection in the monkey. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48 (6): 2814–2823.
Scott IU, Edwards AR, Beck RW, Bressler NM, Chan CK, Elman MJ et al. A phase II randomized clinical trial of intravitreal bevacizumab for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 2007; 114 (10): 1860–1867.
Soheilian M, Ramezani A, Obudi A, Bijanzadeh B, Salehipour M, Yaseri M et al. Randomized trial of intravitreal bevacizumab alone or combined with triamcinolone versus macular photocoagulation in diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 2009; 116 (6): 1142–1150.
Haritoglou C, Kook D, Neubauer A, Wolf A, Priglinger S, Strauss R et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) therapy for persistent diffuse diabetic macular edema. Retina 2006; 26 (9): 999–1005.
Fang X, Sakaguchi H, Gomi F, Oshima Y, Sawa M, Tsujikawa M et al. Efficacy and safety of one intravitreal injection of bevacizumab in diabetic macular oedema. Acta Ophthalmol 2008; 86 (7): 800–805.
Sharma S, Johnson D, Abouammoh M, Hollands S, Brissette A . Rate of serious adverse effects in a series of bevacizumab and ranibizumab injections. Can J Ophthalmol 2012; 47 (3): 275–279.
Lim JW, Kim MU, Shin MC . Aqueous humor and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8 in patients with central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2010; 30 (9): 1465–1471.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Seung Ah Chung for providing very useful materials.
Author Contributions
Design of the study (Y-RC and KL); conduct of the study (Y-RC and EJS); preparation of the manuscript (Y-RC and KL); review and approval of the manuscript (KL and HML).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, YR., Seo, E., Lew, H. et al. Lack of positive effect of intravitreal bevacizumab in central serous chorioretinopathy: meta-analysis and review. Eye 27, 1339–1346 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.236
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.236
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparing treatment outcomes in randomized controlled trials of central serous chorioretinopathy
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2023)
-
Stellungnahme von BVA, DOG und RG zur Chorioretinopathia centralis serosa (CCS)
Der Ophthalmologe (2022)
-
Statement of the Professional Association of Ophthalmologists in Germany (BVA), the German Society of Ophthalmology (DOG) and the German Retina Society (RG) on central serous chorioretinopathy
Die Ophthalmologie (2022)
-
Ranibizumab non-response in pachychoroid neovasculopathy: Effects of switching to aflibercept
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Clinical efficacy of eplerenone versus placebo for central serous chorioretinopathy: study protocol for the VICI randomised controlled trial
Eye (2019)