Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Breast feeding in infancy may be associated with reduced cardiovascular morbidity in adulthood. We examined the association between breast feeding in infancy and arterial function and structure in adulthood in a population-based cohort of Finnish adults.
Subjects/Methods:
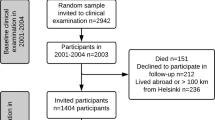
Noninvasive ultrasound was used to measure brachial artery flow-mediated dilatation (FMD), carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) and carotid artery compliance (CAC) in 1667 young adults participating in the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study with data on early nutrition.
Results:
Maximal FMD was higher in breast-fed men compared to formula-fed men (7.2±4.0 vs 5.9±3.4%, P=0.029) while no differences were seen between breast-fed and formula-fed women (8.9±4.5 vs 8.8±5.0%, P=0.84). In men, the multivariable correlates of FMD included the group variable for breast feeding (P=0.014), birth weight (P=0.043), waist circumference (P<0.001) and baseline brachial artery diameter (P<0.001). In women, the multivariable correlates of FMD were birth weight (P=0.02), waist circumference (P<0.001) and brachial artery baseline diameter (P<0.001). Breast feeding was not significantly associated with IMT or CAC in multivariable models.
Conclusions:
Adult men who have been breast fed have better brachial endothelial function compared to men who have been formula fed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkerblom HK, Viikari J, Uhari M, Räsänen L, Byckling T, Louhivuori K et al. (1985). Atherosclerosis precursors in Finnish children and adolescents. I. General description of the cross-sectional study of 1980, and an account of the children's and families' state of health. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 318, 49–63.
Barker DJ, Gluckman PD, Godfrey KM, Harding JE, Owens JA, Robinson JS (1993). Fetal nutrition and cardiovascular disease in adult life. Lancet 341, 938–941.
Blacher J, Pannier B, Guerin AP, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM (1998). Carotid arterial stiffness as a predictor of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in end-stage renal disease. Hypertension 32, 570–574.
Burke GL, Evans GW, Riley WA, Sharrett AR, Howard G, Barnes RW et al. (1995). Arterial wall thickness is associated with prevalent cardiovascular disease in middle-aged adults. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Stroke 26, 386–391.
Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM, Spiegelhalter DJ, Miller OI, Sullivan ID et al. (1992). Noninvasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet 340, 1111–1115.
Davis PH, Dawson JD, Riley WA, Lauer RM (2001). Carotid intimal-medial thickness is related to cardiovascular risk factors measured from childhood through middle age: the Muscatine Study. Circulation 104, 2815–2819.
Engler MM, Engler MB, Kroetz DL, Boswell KD, Neeley E, Krassner SM (1999). The effects of a diet rich in docosahexaenoic acid on organ and vascular fatty acid composition in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 61, 289–295.
Fall CH, Barker DJ, Osmond C, Winter PD, Clark PM, Hales CN (1992). Relation of infant feeding to adult serum cholesterol concentration and death from ischaemic heart disease. BMJ 304, 801–805.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972). Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18, 499–502.
Gillman MW, Rifas-Shiman SL, Camargo Jr CA, Berkey CS, Frazier AL, Rockett HR et al. (2001). Risk of overweight among adolescents who were breastfed as infants. JAMA 285, 2461–2467.
Hales CN, Barker DJ (1992). Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: the thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Diabetologia 35, 595–601.
Järvisalo MJ, Juonala M, Raitakari OT (2006). Assessment of inflammatory markers and endothelial function. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 9, 547–552.
Järvisalo MJ, Raitakari M, Toikka JO, Putto-Laurila A, Rontu R, Laine S et al. (2004). Endothelial dysfunction and increased arterial intima-media thickness in children with type 1 diabetes. Circulation 109, 1750–1755.
Juonala M, J MJ, Mäki-Torkko N, K M, Viikari JSA, Raitakari OT (2005). Risk factors identified in childhood and decreased carotid artery elasticity in adulthood. The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Circulation 112, 1486–1493.
Juonala M, Viikari JS, Hutri-K N, Pietik M, Jokinen E, Taittonen L et al. (2004a). The 21-year follow-up of the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study: risk factor levels, secular trends and east-west difference. J Intern Med 255, 457–468.
Juonala M, Viikari JS, Laitinen T, Marniemi J, Helenius H, Rönnemaa T et al. (2004b). Interrelations between brachial endothelial function and carotid intima-media thickness in young adults: the cardiovascular risk in young Finns Study. Circulation 110, 2918–2923.
Kark JD, Troya G, Friedlander Y, Slater PE, Stein Y (1984). Validity of maternal reporting of breast feeding history and the association with blood lipids in 17 year olds in Jerusalem. J Epidemiol Community Health 38, 218–225.
Kling PJ, Sullivan TM, Roberts RA, Philipps AF, Koldovsky O (1998). Human milk as a potential enteral source of erythropoietin. Pediatr Res 43, 216–221.
Koldovsky O (1996). The potential physiological significance of milk-borne hormonally active substances for the neonate. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 1, 317–323.
Leeson CP, Kattenhorn M, Deanfield JE, Lucas A (2001a). Duration of breast feeding and arterial distensibility in early adult life: population based study. BMJ 322, 643–647.
Leeson CP, Kattenhorn M, Morley R, Lucas A, Deanfield JE (2001b). Impact of low birth weight and cardiovascular risk factors on endothelial function in early adult life. Circulation 103, 1264–1268.
Leeson CP, Whincup PH, Cook DG, Donald AE, Papacosta O, Lucas A et al. (1997). Flow-mediated dilation in 9- to 11-year-old children: the influence of intrauterine and childhood factors. Circulation 96, 2233–2238.
Martin RM, Ebrahim S, Griffin M, Davey-Smith G, Nicolaides AN, Georgiou N et al. (2005). Breastfeeding and atherosclerosis: intima-media thickness and plaques at 65-year follow-up of the Boyd Orr cohort. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25, 1482–1488.
Martin RM, Ness AR, Gunnell D, Emmett P, Davey-Smith G (2004). Does breast-feeding in infancy lower blood pressure in childhood? The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Circulation 109, 1259–1266.
Martyn CN, Barker DJ, Jespersen S, Greenwald S, Osmond C, Berry C (1995). Growth in utero, adult blood pressure, and arterial compliance. Br Heart J 73, 116–121.
Mikkilä V, Räsänen L, Raitakari OT, Pietinen P, Viikari J (2004). Longitudinal changes in diet from childhood into adulthood with respect to risk of cardiovascular diseases: the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Eur J Clin Nutr 58, 1038–1045.
Mott GE, Lewis DS, Jackson EM, McMahan CA (1996). Preweaning diet programs postweaning plasma thyroxine concentrations in baboons. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 212, 342–348.
Mullen MJ, Kharbanda RK, Cross J, Donald AE, Taylor M, Vallance P et al. (2001). Heterogenous nature of flow-mediated dilatation in human conduit arteries in vivo: relevance to endothelial dysfunction in hypercholesterolemia. Circ Res 88, 145–151.
O'Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson Jr SK (1999). Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med 340, 14–22.
Owen CG, Whincup PH, Gilg JA, Cook DG (2003). Effect of breast feeding in infancy on blood pressure in later life: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 327, 1189–1195.
Owen CG, Whincup PH, Odoki K, Gilg JA, Cook DG (2002). Infant feeding and blood cholesterol: a study in adolescents and a systematic review. Pediatrics 110, 597–608.
Pettitt DJ, Forman MR, Hanson RL, Knowler WC, Bennett PH (1997). Breastfeeding and incidence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians. Lancet 350, 166–168.
Raitakari OT (1999). Imaging of subclinical atherosclerosis in children and young adults. Ann Med 31 (Suppl 1), 33–40.
Raitakari OT, Celermajer DS (2000). Testing for endothelial dysfunction. Ann Med 32, 293–304.
Raitakari OT, Juonala M, Kähönen M, Taittonen L, Laitinen T, Mäki-Torkko N et al. (2003). Cardiovascular risk factors in childhood and carotid artery intima-media thickness in adulthood—the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. JAMA 290, 2277–2283.
Ravelli AC, van der Meulen JH, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Bleker OP (2000). Infant feeding and adult glucose tolerance, lipid profile, blood pressure, and obesity. Arch Dis Child 82, 248–252.
Ristimäki A, Ylikorkala O, Pesonen K, Perheentupa J, Viinikka L (1991). Human milk stimulates prostacyclin production by cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72, 623–627.
Ross R, Glomset J, Harker L (1977). Response to injury and atherogenesis. Am J Pathol 86, 675–684.
Singhal A, Cole TJ, Fewtrell M, Lucas A (2004). Breastmilk feeding and lipoprotein profile in adolescents born preterm: follow-up of a prospective randomised study. Lancet 363, 1571–1578.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Academy of Finland (grants 77841 and 210283), the Social Insurance Institution of Finland, the Turku University Foundation, Special Federal Grants for the Turku University Hospital, the Juho Vainio Foundation, the Finnish Foundation of Cardiovascular Research, the Lydia Maria Julin Foundation, Research Foundation of Instrumentarium, Research Foundation of Orion Corporation, the Maud Kuistila Foundation, the Emil Aaltonen Foundation, the Finnish Medical Foundation and the Finnish Cultural Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Järvisalo, M., Hutri-Kähönen, N., Juonala, M. et al. Breast feeding in infancy and arterial endothelial function later in life. The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Eur J Clin Nutr 63, 640–645 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2008.17
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2008.17
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Influence of breastfeeding and postnatal nutrition on cardiovascular remodeling induced by fetal growth restriction
Pediatric Research (2016)
-
Influence of breastfeeding on retinal vessel calibers in school-age children. The Generation R Study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2016)
-
When and how to start prevention of atherosclerosis? Lessons from the Cardiovascular Risk in the Young Finns Study and the Special Turku Coronary Risk Factor Intervention Project
Pediatric Nephrology (2012)