Abstract
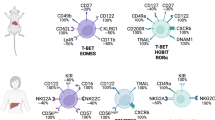
Natural killer (NK) cells represent a heterogeneous population of innate lymphocytes with phenotypically and functionally distinct subsets. In particular, recent studies have identified a unique subset of NK cells residing within the liver that are maintained as tissue-resident cells, confer antigen-specific memory responses and exhibit different phenotypical and developmental characteristics compared with conventional NK (cNK) cells. These findings have encouraged researchers to uncover tissue-resident NK cells at other sites, and detailed analyses have revealed that these tissue-resident NK cells share many similarities with liver-resident NK cells and tissue-resident memory T cells. Here, we present a brief historical perspective on the discovery of liver-resident NK cells and discuss their relationship to cNK cells and other emerging NK cell subsets and their potential functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vivier E, Raulet DH, Moretta A, Caligiuri MA, Zitvogel L, Lanier LL et al. Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells. Science 2011; 331: 44–49.
Sun C, Sun H, Zhang C, Tian Z . NK cell receptor imbalance and NK cell dysfunction in HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Immunol 2015; 12: 292–302.
Narni-Mancinelli E, Ugolini S, Vivier E . Tuning the threshold of natural killer cell responses. Curr Opin Immunol 2013; 25: 53–58.
Martin-Fontecha A, Thomsen LL, Brett S, Gerard C, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A et al. Induced recruitment of NK cells to lymph nodes provides IFN-gamma for T(H)1 priming. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 1260–1265.
Crome SQ, Lang PA, Lang KS, Ohashi PS . Natural killer cells regulate diverse T cell responses. Trends Immunol 2013; 34: 342–349.
Schuster IS, Wikstrom ME, Brizard G, Coudert JD, Estcourt MJ, Manzur M et al. TRAIL+ NK cells control CD4+ T cell responses during chronic viral infection to limit autoimmunity. Immunity 2014; 41: 646–656.
Yokoyama WM, Sojka DK, Peng H, Tian Z . Tissue-resident natural killer cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 2013; 78: 149–156.
Sojka DK, Tian Z, Yokoyama WM . Tissue-resident natural killer cells and their potential diversity. Semin Immunol 2014; 26: 127–131.
Spits H, Di Santo JP . The expanding family of innate lymphoid cells: regulators and effectors of immunity and tissue remodeling. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 21–27.
Spits H, Bernink JH, Lanier L . NK cells and type 1 innate lymphoid cells: partners in host defense. Nat Immunol 2016; 17: 758–764.
Erick TK, Brossay L . Phenotype and functions of conventional and non-conventional NK cells. Curr Opin Immunol 2016; 38: 67–74.
Peng H, Jiang X, Chen Y, Sojka DK, Wei H, Gao X et al. Liver-resident NK cells confer adaptive immunity in skin-contact inflammation. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 1444–1456.
Sojka DK, Plougastel-Douglas B, Yang L, Pak-Wittel MA, Artyomov MN, Ivanova Y et al. Tissue-resident natural killer (NK) cells are cell lineages distinct from thymic and conventional splenic NK cells. Elife 2014; 3: e01659.
Cortez VS, Cervantes-Barragan L, Robinette ML, Bando JK, Wang Y, Geiger TL et al. Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling Guides the Differentiation of Innate Lymphoid Cells in Salivary Glands. Immunity 2016; 44: 1127–1139.
O'Sullivan TE, Rapp M, Fan X, Weizman OE, Bhardwaj P, Adams NM et al. Adipose-Resident Group 1 Innate Lymphoid Cells Promote Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance. Immunity 2016; 45: 428–441.
Peng H, Wisse E, Tian Z . Liver natural killer cells: subsets and roles in liver immunity. Cell Mol Immunol 2016; 13: 328–336.
Kim S, Iizuka K, Kang HS, Dokun A, French AR, Greco S et al. In vivo developmental stages in murine natural killer cell maturation. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 523–528.
Takeda K, Cretney E, Hayakawa Y, Ota T, Akiba H, Ogasawara K et al. TRAIL identifies immature natural killer cells in newborn mice and adult mouse liver. Blood 2005; 105: 2082–2089.
Gordon SM, Chaix J, Rupp LJ, Wu J, Madera S, Sun JC et al. The transcription factors T-bet and Eomes control key checkpoints of natural killer cell maturation. Immunity 2012; 36: 55–67.
Burt BM, Plitas G, Zhao Z, Bamboat ZM, Nguyen HM, Dupont B et al. The lytic potential of human liver NK cells is restricted by their limited expression of inhibitory killer Ig-like receptors. J Immunol 2009; 183: 1789–1796.
Rosmaraki EE, Douagi I, Roth C, Colucci F, Cumano A, Di Santo JP . Identification of committed NK cell progenitors in adult murine bone marrow. Eur J Immunol 2001; 31: 1900–1909.
Hudspeth K, Donadon M, Cimino M, Pontarini E, Tentorio P, Preti M et al. Human liver-resident CD56(bright)/CD16(neg) NK cells are retained within hepatic sinusoids via the engagement of CCR5 and CXCR6 pathways. J Autoimmun 2016; 66: 40–50.
Marquardt N, Beziat V, Nystrom S, Hengst J, Ivarsson MA, Kekalainen E et al. Cutting edge: identification and characterization of human intrahepatic CD49a+ NK cells. J Immunol 2015; 194: 2467–2471.
Stegmann KA, Robertson F, Hansi N, Gill U, Pallant C, Christophides T et al. CXCR6 marks a novel subset of T-bet(lo)Eomes(hi) natural killer cells residing in human liver. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 26157.
Harmon C, Robinson MW, Fahey R, Whelan S, Houlihan DD, Geoghegan J et al. Tissue-resident Eomes(hi) T-bet(lo) CD56(bright) NK cells with reduced proinflammatory potential are enriched in the adult human liver. Eur J Immunol 2016; 46: 2111–2120.
Aw Yeang HX, Piersma SJ, Lin Y, Yang L, Malkova ON, Miner C et al. Cutting edge: human CD49e- NK cells are tissue resident in the liver. J Immunol 2017; 198: 1417–1422.
Tang L, Peng H, Zhou J, Chen Y, Wei H, Sun R et al. Differential phenotypic and functional properties of liver-resident NK cells and mucosal ILC1s. J Autoimmun 2016; 67: 29–35.
Paust S, Gill HS, Wang BZ, Flynn MP, Moseman EA, Senman B et al. Critical role for the chemokine receptor CXCR6 in NK cell-mediated antigen-specific memory of haptens and viruses. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 1127–1135.
Cuff AO, Robertson FP, Stegmann KA, Pallett LJ, Maini MK, Davidson BR et al. Eomeshi NK cells in human liver are long-lived and do not recirculate but can be replenished from the circulation. J Immunol 2016; 197: 4283–4291.
Peng H, Tian Z . Re-examining the origin and function of liver-resident NK cells. Trends Immunol 2015; 36: 293–299.
Mackay LK, Minnich M, Kragten NA, Liao Y, Nota B, Seillet C et al. Hobit and Blimp1 instruct a universal transcriptional program of tissue residency in lymphocytes. Science 2016; 352: 459–463.
Daussy C, Faure F, Mayol K, Viel S, Gasteiger G, Charrier E et al. T-bet and Eomes instruct the development of two distinct natural killer cell lineages in the liver and in the bone marrow. J Exp Med 2014; 211: 563–577.
Male V, Nisoli I, Kostrzewski T, Allan DS, Carlyle JR, Lord GM et al. The transcription factor E4bp4/Nfil3 controls commitment to the NK lineage and directly regulates Eomes and Id2 expression. J Exp Med 2014; 211: 635–642.
Yu X, Wang Y, Deng M, Li Y, Ruhn KA, Zhang CC et al. The basic leucine zipper transcription factor NFIL3 directs the development of a common innate lymphoid cell precursor. Elife 2014; 3.
Yang Q, Li F, Harly C, Xing S, Ye L, Xia X et al. TCF-1 upregulation identifies early innate lymphoid progenitors in the bone marrow. Nat Immunol 2015; 16: 1044–1050.
Constantinides MG, Gudjonson H, McDonald BD, Ishizuka IE, Verhoef PA, Dinner AR et al. PLZF expression maps the early stages of ILC1 lineage development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2015; 112: 5123–5128.
Klose CS, Flach M, Mohle L, Rogell L, Hoyler T, Ebert K et al. Differentiation of type 1 ILCs from a common progenitor to all helper-like innate lymphoid cell lineages. Cell 2014; 157: 340–356.
Fan X, Rudensky AY . Hallmarks of tissue-resident lymphocytes. Cell 2016; 164: 1198–1211.
Victorino F, Sojka DK, Brodsky KS, McNamee EN, Masterson JC, Homann D et al. Tissue-resident NK cells mediate ischemic kidney injury and are not depleted by anti-Asialo-GM1 antibody. J Immunol 2015; 195: 4973–4985.
Tayade C, Fang Y, Black GP, V Jr AP, Erlebacher A, Croy BA . Differential transcription of Eomes and T-bet during maturation of mouse uterine natural killer cells. J Leukoc Biol 2005; 78: 1347–1355.
Mueller SN, Mackay LK . Tissue-resident memory T cells: local specialists in immune defence. Nat Rev Immunol 2016; 16: 79–89.
Schenkel JM, Masopust D . Tissue-resident memory T cells. Immunity 2014; 41: 886–897.
Mackay LK, Kallies A . Transcriptional regulation of tissue-resident lymphocytes. Trends Immunol 2017; 38: 94–103.
Marcus A, Raulet DH . Evidence for natural killer cell memory. Curr Biol 2013; 23: R817–R820.
O'Leary JG, Goodarzi M, Drayton DL, von Andrian UH . T cell- and B cell-independent adaptive immunity mediated by natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 507–516.
Li T, Wang J, Wang Y, Chen Y, Wei H, Sun R et al. Respiratory influenza virus infection induces memory-like liver NK cells in mice. J Immunol 2017; 198: 1242–1252.
Paust S, von Andrian UH . Natural killer cell memory. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 500–508.
Horst AK, Neumann K, Diehl L, Tiegs G . Modulation of liver tolerance by conventional and nonconventional antigen-presenting cells and regulatory immune cells. Cell Mol Immunol 2016; 13: 277–292.
Grakoui A, Crispe IN . Presentation of hepatocellular antigens. Cell Mol Immunol 2016; 13: 293–300.
Ju C, Tacke F . Hepatic macrophages in homeostasis and liver diseases: from pathogenesis to novel therapeutic strategies. Cell Mol Immunol 2016; 13: 316–327.
Shuai Z, Leung MW, He X, Zhang W, Yang G, Leung PS et al. Adaptive immunity in the liver. Cell Mol Immunol 2016; 13: 354–368.
Tian Z, Chen Y, Gao B . Natural killer cells in liver disease. Hepatology 2013; 57: 1654–1662.
Hou X, Zhou R, Wei H, Sun R, Tian Z . NKG2D-retinoic acid early inducible-1 recognition between natural killer cells and Kupffer cells in a novel murine natural killer cell-dependent fulminant hepatitis. Hepatology 2009; 49: 940–949.
Radaeva S, Sun R, Jaruga B, Nguyen VT, Tian Z, Gao B . Natural killer cells ameliorate liver fibrosis by killing activated stellate cells in NKG2D-dependent and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-dependent manners. Gastroenterology 2006; 130: 435–452.
Gur C, Doron S, Kfir-Erenfeld S, Horwitz E, Abu-Tair L, Safadi R et al. NKp46-mediated killing of human and mouse hepatic stellate cells attenuates liver fibrosis. Gut 2012; 61: 885–893.
Gao B, Radaeva S, Park O . Liver natural killer and natural killer T cells: immunobiology and emerging roles in liver diseases. J Leukoc Biol 2009; 86: 513–528.
Cai L, Zhang Z, Zhou L, Wang H, Fu J, Zhang S et al. Functional impairment in circulating and intrahepatic NK cells and relative mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin Immunol 2008; 129: 428–437.
Hoechst B, Voigtlaender T, Ormandy L, Gamrekelashvili J, Zhao F, Wedemeyer H et al. Myeloid derived suppressor cells inhibit natural killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via the NKp30 receptor. Hepatology 2009; 50: 799–807.
Yang Y, Han Q, Hou Z, Zhang C, Tian Z, Zhang J . Exosomes mediate hepatitis B virus (HBV) transmission and NK-cell dysfunction. Cell Mol Immunol 2017; 14: 465–475.
Peppa D, Gill US, Reynolds G, Easom NJ, Pallett LJ, Schurich A et al. Up-regulation of a death receptor renders antiviral T cells susceptible to NK cell-mediated deletion. J Exp Med 2013; 210: 99–114.
Krueger PD, Narayanan S, Surette FA, Brown MG, Sung SJ, Hahn YS . Murine liver-resident group 1 innate lymphoid cells regulate optimal priming of anti-viral CD8+ T cells. J Leukoc Biol 2017; 101: 329–338.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (#81761128013, 81571522, 91642105, 81361120388, 31300727, 91542114, 91442112, 91542000 and 81330071) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (973 Basic Science Project 2013CB944902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H., Sun, R. Liver-resident NK cells and their potential functions. Cell Mol Immunol 14, 890–894 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.72
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.72
This article is cited by
-
Early life gut microbiota sustains liver-resident natural killer cells maturation via the butyrate-IL-18 axis
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Synergistic anti-inflammatory effect of gut microbiota and lithocholic acid on liver fibrosis
Inflammation Research (2022)
-
Innate-like Lymphocytes and Innate Lymphoid Cells in Asthma
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2020)
-
Tissue-resident memory-like ILCs: innate counterparts of TRM cells
Protein & Cell (2020)
-
Tissue-resident lymphocytes: from adaptive to innate immunity
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2019)