Abstract
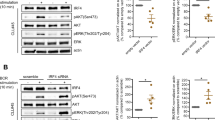
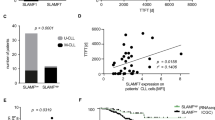
CD5 is constitutively expressed on T cells and a subset of mature normal and leukemic B cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Important functional properties are associated with CD5 expression in B cells, including signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation, IL-10 production and the promotion of B-lymphocyte survival and transformation. However, the pathway(s) by which CD5 influences the biology of B cells and its dependence on B-cell receptor (BCR) co-signaling remain unknown. In this study, we show that CD5 expression activates a number of important signaling pathways, including Erk1/2, leading to IL-10 production through a novel pathway independent of BCR engagement. This pathway is dependent on extracellular calcium (Ca2+) entry facilitated by upregulation of the transient receptor potential channel 1 (TRPC1) protein. We also show that Erk1/2 activation in a subgroup of CLL patients is associated with TRPC1 overexpression. In this subgroup of CLL patients, small inhibitory RNA (siRNA) for CD5 reduces TRPC1 expression. Furthermore, siRNAs for CD5 or for TRPC1 inhibit IL-10 production. These findings provide new insights into the role of CD5 in B-cell biology in health and disease and could pave the way for new treatment strategies for patients with B-CLL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berland R, Wortis HH . Origins and functions of B-1 cells with notes on the role of CD5. Annu Rev Immunol 2002; 20: 253–300.
Hardy RR, Hayakawa K, K . CD5B cells, a fetal B cell lineage. Adv Immunol 1994; 55: 297–339.
Hayakawa K, Formica AM, Colombo MJ, Ichikawa D, Shinton SA, Brill-Dashoff J et al. B cells generated by B-1 development can progress to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann NY Acad Sci 2015; 1362: 250–255.
Gary-Gouy H, Harriague J, Bismuth G, Platzer C, Schmitt C, Dalloul AH . Human CD5 promotes B-cell survival through stimulation of autocrine IL-10 production. Blood 2002; 100: 4537–4543.
Burdin N, Rousset F, Banchereau J . B-cell-derived IL-10: production and function. Methods 1997; 11: 98–111.
Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A . Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 2001; 19: 683–765.
Defrance T, Vanbervliet B, Brière F, Durand I, Rousset F, Banchereau J . Interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor beta cooperate to induce anti-CD40-activated naive human B cells to secrete immunoglobulin A. J Exp Med 1992; 175: 671–682.
Kitabayashi A, Hirokawa M, Miura AB . The role of interleukin-10 (IL-10) in chronic B-lymphocytic leukemia: IL-10 prevents leukemic cells from apoptotic cell death. Int J Hematol 1995; 62: 99–106.
Fayad L, Keating MJ, Reuben JM, O’Brien S, Lee BN, Lerner S et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with phenotypic characteristics and outcome. Blood 2001; 97: 256–263.
Gary-Gouy H, Sainz-Perez A, Marteau JB, Marfaing-Koka A, Delic J, Merle-Beral H et al. Natural phosphorylation of CD5 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells and analysis of CD5-regulated genes in a B cell line suggest a role for CD5 in malignant phenotype. J Immunol 2007; 179: 4335–4344.
Garaud S, Le Dantec C, de Mendoza AR, Mageed RA, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y . IL-10 production by B cells expressing CD5 with the alternative exon 1B. Ann NY Acad Sci 2009; 1173: 280–285.
Garaud S, Morva A, Lemoine S, Hillion S, Bordron A, Pers JO et al. CD5 promotes IL-10 production in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells through STAT3 and NFAT2 activation. J Immunol 2011; 186: 4835–4844.
Apollonio B, Scielzo C, Bertilaccio MT, Ten Hacken E, Scarfò L, Ranghetti P et al. Targeting B-cell anergy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013; 121: 3879–3888.
Li P, Grgurevic S, Liu Z, Harris D, Rozovski U, Calin GA et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 induces MicroRNA-155 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. PLoS One 2013; 8: e64678.
Sarrias MR, Grønlund J, Padilla O, Madsen J, Holmskov U, Lozano F . The scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain: an ancient and highly conserved protein module of the innate immune system. Crit Rev Immunol 2004; 24: 1–37.
Gary-Gouy H, Bruhns P, Schmitt C, Dalloul A, Daëron M, Bismuth G . The pseudo-immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif of CD5 mediates its inhibitory action on B-cell receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 548–556.
Gary-Gouy H, Lang V, Sarun S, Boumsell L, Bismuth G . In vivo association of CD5 with tyrosine-phosphorylated ZAP-70 and p21 phospho-zeta molecules in human CD3+ thymocytes. J Immunol 1997; 159: 3739–3747.
Tibaldi E, Brunati AM, Zonta F, Frezzato F, Gattazzo C, Zambello R et al. Lyn-mediated SHP-1 recruitment to CD5 contributes to resistance to apoptosis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1768–1781.
Perez-Villar JJ, Whitney GS, Bowen MA, Hewgill DH, Aruffo AA, Kanner SB . CD5 negatively regulates the T-cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathway: involvement of SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 2903–2912.
Bauch A, Campbell KS, Reth M . Interaction of the CD5 cytoplasmic domain with the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase IIdelta. Eur J Immunol 1998; 28: 2167–2177.
Raman C, Kuo A, Deshane J, Litchfield DW, Kimberly RP . Regulation of casein kinase 2 by direct interaction with cell surface receptor CD5. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 19183–19189.
Wong SC, Chew WK, Tan JE, Melendez AJ, Francis F, Lam KP . Peritoneal CD5+ B-1 cells have signaling properties similar to tolerant B cells. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 30707–30715.
Gary-Gouy H, Harriague J, Dalloul A, Donnadieu E, Bismuth G . CD5-negative regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathways originates from tyrosine residue Y429 outside an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif. J Immunol 2002; 168: 232–239.
Hippen KL, Tze LE, Behrens TW . CD5 maintains tolerance in anergic B cells. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 883–890.
Parikh K, Poppema S, Peppelenbosch MP, Visser L . Extracellular ligation-dependent CD45RB enzymatic activity negatively regulates lipid raft signal transduction. Blood 2009; 113: 594–603.
Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S, Stein H, Jaffe ES . The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011; 117: 5019–5032.
Gross HJ, Merling A, Moldenhauer G, Schwartz-Albiez R . Ecto-sialyltransferase of human B lymphocytes reconstitutes differentiation markers in the presence of exogenous CMP-N-acetyl neuraminic acid. Blood 1996; 87: 5113–5126.
Loisel S, André PA, Golay J, Buchegger F, Kadouche J, Cérutti M et al. Antitumour effects of single or combined monoclonal antibodies directed against membrane antigens expressed by human B cells leukaemia. Mol Cancer 2011; 10: 42.
Devauchelle-Pensec V, Cagnard N, Pers JO, Youinou P, Saraux A, Chiocchia G . Gene expression profile in the salivary glands of primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients before and after treatment with rituximab. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 2262–2271.
Richards JD, Davé SH, Chou CH, Mamchak AA, DeFranco AL . Inhibition of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway blocks a subset of B cell responses to antigen. J Immunol 2001; 166: 3855–3864.
Nédellec S, Renaudineau Y, Bordron A, Berthou C, Porakishvili N, Lydyard PM et al. B cell response to surface IgM cross-linking identifies different prognostic groups of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients. J Immunol 2005; 174: 3749–3756.
Roa NS, Ordoñez-Rueda D, Chávez-Rios JR, Raman C, García-Zepeda EA, Lozano F et al. The carboxy-terminal region of CD5 is required for c-CBL mediated TCR signaling downmodulation in thymocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 432: 52–59.
Buhl AM, Pleiman CM, Rickert RC, Cambier JC . Qualitative regulation of B cell antigen receptor signaling by CD19: selective requirement for PI3-kinase activation, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate production and Ca2+ mobilization. J Exp Med 1997; 186: 1897–1910.
Chen J, Fang Y . A novel pathway regulating the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 64: 1071–1077.
Frank DA, Mahajan S, Ritz J . B lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia contain signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3 constitutively phosphorylated on serine residues. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 3140–3148.
Muggen AF, Pillai SY, Kil LP, van Zelm MC, van Dongen JJ, Hendriks RW et al. Basal Ca(2+) signaling is particularly increased in mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2015; 29: 321–328.
Healy JI, Dolmetsch RE, Timmerman LA, Cyster JG, Thomas ML, Crabtree GR et al. Different nuclear signals are activated by the B cell receptor during positive versus negative signaling. Immunity 1997; 6: 419–428.
Chumley MJ, Dal Porto JM, Cambier JC . The unique antigen receptor signaling phenotype of B-1 cells is influenced by locale but induced by antigen. J Immunol 2002; 169: 1735–1743.
Sims GP, Ettinger R, Shirota Y, Yarboro CH, Illei GG, Lipsky PE . Identification and characterization of circulating human transitional B cells. Blood 2005; 105: 4390–4398.
Limnander A, Depeille P, Freedman TS, Liou J, Leitges M, Kurosaki T et al. STIM1, PKC-delta and RasGRP set a threshold for proapoptotic Erk signaling during B cell development. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 425–433.
Limnander A, Zikherman J, Lau T, Leitges M, Weiss A, Roose JP . Protein kinase Cdelta promotes transitional B cell-negative selection and limits proximal B cell receptor signaling to enforce tolerance. Mol Cell Biol 2014; 34: 1474–1485.
Muzio M, Apollonio B, Scielzo C, Frenquelli M, Vandoni I, Boussiotis V et al. Constitutive activation of distinct BCR-signaling pathways in a subset of CLL patients: a molecular signature of anergy. Blood 2008; 112: 188–195.
Kawauchi K, Ogasawara T, Yasuyama M . Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase through B-cell antigen receptor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Int J Hematol 2002; 75: 508–513.
Cheng S, Ma J, Guo A, Lu P, Leonard JP, Coleman M et al. BTK inhibition targets in vivo CLL proliferation through its effects on B-cell receptor signaling activity. Leukemia 2014; 28: 649–657.
Garaud S, Le Dantec C, Berthou C, Lydyard PM, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y . Selection of the alternative exon 1 from the cd5 gene down-regulates membrane level of the protein in B lymphocytes. J Immunol 2008; 181: 2010–2018.
Mori Y, Wakamori M, Miyakawa T, Hermosura M, Hara Y, Nishida M et al. Transient receptor potential 1 regulates capacitative Ca(2+) entry and Ca(2+) release from endoplasmic reticulum in B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 2002; 195: 673–681.
Roedding AS, Li PP, Warsh JJ . Characterization of the transient receptor potential channels mediating lysophosphatidic acid-stimulated calcium mobilization in B lymphoblasts. Life Sci 2006; 80: 89–97.
Yildirim E, Carey MA, Card JW, Dietrich A, Flake GP, Zhang Y et al. Severely blunted allergen-induced pulmonary Th2 cell response and lung hyperresponsiveness in type 1 transient receptor potential channel-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2012; 303: L539–L549.
O’Shea JJ, Laurence A, McInnes IB . Back to the future: oral targeted therapy for RA and other autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2013; 9: 173–182.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from Arthritis Research-UK to RAM and by grants from the “Cancéropole Grand Ouest”, the “Région Bretagne” and the “Ligue contre le cancer” to YR. We thank Catherine Riou and Professor Valérie Ugo (Brest) for the clinical material and Ms Simone Forest and Geneviève Michel for helping with typing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information for this article can be found on the Cellular & Molecular Immunology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garaud, S., Taher, T., Debant, M. et al. CD5 expression promotes IL-10 production through activation of the MAPK/Erk pathway and upregulation of TRPC1 channels in B lymphocytes. Cell Mol Immunol 15, 158–170 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2016.42
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2016.42
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The frequencies of peripheral blood CD5+CD19+ B cells, CD3−CD16+CD56+ NK, and CD3+CD56+ NKT cells and serum interleukin-10 in patients with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology (2022)
-
Upregulation of TRPC5 in hippocampal excitatory synapses improves memory impairment associated with neuroinflammation in microglia knockout IL-10 mice
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2021)
-
Wnt5a enhances proliferation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and ERK1/2 phosphorylation via a ROR1/DOCK2-dependent mechanism
Leukemia (2021)
-
Upregulated SOCC and IP3R calcium channels and subsequent elevated cytoplasmic calcium signaling promote nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting autophagy
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2021)
-
CD5 and B lymphocyte responses: multifaceted effects through multitudes of pathways and channels
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)