Abstract
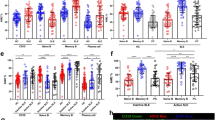
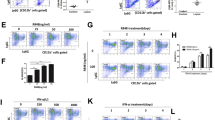
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by B-cell hyperreactivity. The Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) signaling pathway is abnormally activated in SLE B cells. CyclinD3 (CCND3) plays an important role in B-cell proliferation, development, and differentiation. Although previous studies focused on the B cell-intrinsic role of TLR7 for the development of spontaneous germinal centers, the influence of TLR7 on CCND3 in SLE B cells is still not clear. Here, we used a B-cell profiling chip and found that CCND3 was related to SLE and significantly elevated in SLE B cells. Moreover, we determined that the expression level of CCND3 was higher, while miR-15b was significantly lower in the B cells from SLE patients and B6.MRL-Faslpr/J lupus mice compared to normal subjects. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the activation of TLR7 dramatically increased CCND3 expression but significantly decreased miR-15b in B cells in vitro and we identified that CCND3 is a direct target of miR-15b. To further confirm our results, we established another lupus model by topically treating C57BL/6 (B6) mice with the TLR-7 agonist imiquimod (IMQ) for 8 weeks according to the previously described protocol. Expectedly, topical treatment with IMQ also significantly increased CCND3 and decreased miR-15b in B cells of B6 mice. Taken together, our results identified that the activation of TLR7 increased CCND3 expression via the downregulation of miR-15b in B cells; thus, these findings suggest that extrinsic factor-induced CCND3 expression may contribute to the abnormality of B cell in SLE.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Z, Davidson A . Taming lupus-a new understanding of pathogenesis is leading to clinical advances. Nat Med 2012; 18: 871–882.
Allen CD, Okada T, Cyster JG . Germinal-center organization and cellular dynamics. Immunity 2007; 27: 190–202.
Luzina IG, Atamas SP, Storrer CE, daSilva LC, Kelsoe G, Papadimitriou JC et al. Spontaneous formation of germinal centers in autoimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol 2001; 70: 578–584.
Cappione A, 3rd, Anolik JH, Pugh-Bernard A, Barnard J, Dutcher P, Silverman G et al. Germinal center exclusion of autoreactive B cells is defective in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 3205–3216.
Vinuesa CG, Sanz I, Cook MC . Dysregulation of germinal centres in autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 845–857.
Linterman MA, Rigby RJ, Wong RK, Yu D, Brink R, Cannons JL et al. Follicular helper T cells are required for systemic autoimmunity. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 561–576.
Cato MH, Chintalapati SK, Yau IW, Omori SA, Rickert RC . Cyclin D3 is selectively required for proliferative expansion of germinal center B cells. Mol Cell Biol 2011; 31: 127–137.
Peled JU, Yu JJ, Venkatesh J, Bi E, Ding BB, Krupski-Downs M et al. Requirement for cyclin D3 in germinal center formation and function. Cell Res 2010; 20: 631–646.
Sherr CJ . D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem Sci 1995; 20: 187–190.
Yokogawa M, Takaishi M, Nakajima K, Kamijima R, Fujimoto C, Kataoka S et al. Epicutaneous application of toll-like receptor 7 agonists leads to systemic autoimmunity in wild-type mice: a new model of systemic Lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014; 66: 694–706.
Cooper AB, Sawai CM, Sicinska E, Powers SE, Sicinski P, Clark MR et al. A unique function for cyclin D3 in early B cell development. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 489–497.
Moller MB, Nielsen O, Pedersen NT . Cyclin D3 expression in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Correlation with other cell cycle regulators and clinical features. Am J Clin Pathol 2001; 115: 404–412.
Xu C, Fu H, Gao L, Wang L, Wang W, Li J et al. BCR-ABL/GATA1/miR-138 mini circuitry contributes to the leukemogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2014; 33: 44–54.
Watanuki J, Hatakeyama K, Sonoki T, Tatetsu H, Yoshida K, Fujii S et al. Bone marrow large B cell lymphoma bearing cyclin D3 expression: clinical, morphologic, immunophenotypic, and genotypic analyses of seven patients. Int J Hematol 2009; 90: 217–225.
Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T . Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol 2001; 2: 675–680.
Hua Z, Hou B . TLR signaling in B-cell development and activation. Cell Mol Immunol 2013; 10: 103–106.
Celhar T, Magalhaes R, Fairhurst AM . TLR7 and TLR9 in SLE: when sensing self goes wrong. Immunol Res 2012; 53: 58–77.
Christensen SR, Shupe J, Nickerson K, Kashgarian M, Flavell RA, Shlomchik MJ . Toll-like receptor 7 and TLR9 dictate autoantibody specificity and have opposing inflammatory and regulatory roles in a murine model of lupus. Immunity 2006; 25: 417–428.
Pisitkun P, Deane JA, Difilippantonio MJ, Tarasenko T, Satterthwaite AB, Bolland S . Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science 2006; 312: 1669–1672.
Subramanian S, Tus K, Li QZ, Wang A, Tian XH, Zhou J et al. A Tlr7 translocation accelerates systemic autoimmunity in murine lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006; 103: 9970–9975.
Santiago-Raber ML, Kikuchi S, Borel P, Uematsu S, Akira S, Kotzin BL et al. Evidence for genes in addition to Tlr7 in the Yaa translocation linked with acceleration of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2008; 181: 1556–1562.
Hwang SH, Lee H, Yamamoto M, Jones LA, Dayalan J, Hopkins R et al. B cell TLR7 expression drives anti-RNA autoantibody production and exacerbates disease in systemic lupus erythematosus-prone mice. J Immunol 2012; 189: 5786–5796.
Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R . Regulation of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Science 2010; 327: 291–295.
Jackson SW, Scharping NE, Kolhatkar NS, Khim S, Schwartz MA, Li QZ et al. Opposing impact of B cell-intrinsic TLR7 and TLR9 signals on autoantibody repertoire and systemic inflammation. J Immunol 2014; 192: 4525–4532.
Soni C, Wong EB, Domeier PP, Khan TN, Satoh T, Akira S et al. B cell-intrinsic TLR7 signaling is essential for the development of spontaneous germinal centers. J Immunol 2014; 193: 4400–4414.
Browne EP . Toll-like receptor 7 controls the anti-retroviral germinal center response. PLoS Pathog 2011; 7: e1002293.
He L, Hannon GJ . MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 522–531.
Pauley KM, Cha S, Chan EK . MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 2009; 32: 189–194.
Rusca N, Monticelli S . MiR-146a in immunity and disease. Mol Biol Int 2011; 2011: 437301.
Shen N, Liang D, Tang Y, de Vries N, Tak PP . MicroRNAs – novel regulators of systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2012; 8: 701–709.
Stagakis E, Bertsias G, Verginis P, Nakou M, Hatziapostolou M, Kritikos H et al. Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to human lupus disease activity and pathogenesis: miR-21 regulates aberrant T cell responses through regulation of PDCD4 expression. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 1496–1506.
Chauhan SK, Singh VV, Rai R, Rai M, Rai G . Differential microRNA profile and post-transcriptional regulation exist in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with distinct autoantibody specificities. J Clin Immunol 2014; 34: 491–503.
Fan H, Liu F, Dong G, Ren D, Xu Y, Dou J et al. Activation-induced necroptosis contributes to B-cell lymphopenia in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5: e1416.
Ronnblom L, Eloranta ML, Alm GV . The type I interferon system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 408–420.
Jenks SA, Sanz I . Altered B cell receptor signaling in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 2009; 8: 209–213.
Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Sanjo H, Hoshino K et al. Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 196–200.
Gorden KKB, Qiu X, Battiste JJL, Wightman PPD, Vasilakos JP, Alkan SS . Oligodeoxynucleotides differentially modulate activation of TLR7 and TLR8 by imidazoquinolines. J Immunol 2006; 177: 8164–8170.
De Luca G, Ferretti R, Bruschi M, Mezzaroma E, Caruso M . Cyclin D3 critically regulates the balance between self-renewal and differentiation in skeletal muscle stem cells. Stem Cells 2013; 31: 2478–2491.
De Santa F, Albini S, Mezzaroma E, Baron L, Felsani A, Caruso M . pRb-dependent cyclin D3 protein stabilization is required for myogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 7248–7265.
Becker AM, Dao KH, Han BK, Kornu R, Lakhanpal S, Mobley AB et al. SLE peripheral blood B cell, T cell and myeloid cell transcriptomes display unique profiles and each subset contributes to the interferon signature. PLoS One 2013; 8: e67003.
Garaud JC, Schickel JN, Blaison G, Knapp AM, Dembele D, Ruer-Laventie J et al. B cell signature during inactive systemic lupus is heterogeneous: toward a biological dissection of lupus. PLoS One 2011; 6: e23900.
Toro-Dominguez D, Carmona-Saez P, Alarcon-Riquelme ME . Shared signatures between rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren inverted question marks syndrome uncovered through gene expression meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther 2014; 16: 489.
Wang H, Peng W, Ouyang X, Li W, Dai Y . Circulating microRNAs as candidate biomarkers in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Transl Res 2012; 160: 198–206.
Dai Y, Sui W, Lan H, Yan Q, Huang H, Huang Y . Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in renal biopsies of lupus nephritis patients. Rheumatol Int 2009; 29: 749–754.
Jacobi AM, Reiter K, Mackay M, Aranow C, Hiepe F, Radbruch A et al. Activated memory B cell subsets correlate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: delineation by expression of CD27, IgD, and CD95. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58: 1762–1773.
Park J, Moon S, Lee J, Park J, Lee D, Jung K et al. Bone marrow analysis of immune cells and apoptosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2014; 23: 975–985.
Liu Z, Zou Y, Davidson A . Plasma cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: the long and short of it all. Eur J Immunol 2011; 41: 588–591.
Hutcheson J, Scatizzi JC, Siddiqui AM, Haines GK, 3rd, Wu T, Li QZ et al. Combined deficiency of proapoptotic regulators Bim and Fas results in the early onset of systemic autoimmunity. Immunity 2008; 28: 206–217.
Xu M, Hou R, Sato-Hayashizaki A, Man R, Zhu C, Wakabayashi C et al. Cd72(c) is a modifier gene that regulates Fas(lpr)-induced autoimmune disease. J Immunol 2013; 190: 5436–5445.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project number: 31370899) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Project number: 2015PY007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology's website (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, D., Liu, F., Dong, G. et al. Activation of TLR7 increases CCND3 expression via the downregulation of miR-15b in B cells of systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol 13, 764–775 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.48
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.48
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
High expression of GPR50 promotes the proliferation, migration and autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Escape from X chromosome inactivation and female bias of autoimmune diseases
Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
TLR7, a third signal for the robust generation of spontaneous germinal center B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
Ligation of CD180 inhibits IFN-α signaling in a Lyn-PI3K-BTK-dependent manner in B cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2017)
-
Notch-Hes-1 axis controls TLR7-mediated autophagic death of macrophage via induction of P62 in mice with lupus
Cell Death & Disease (2016)