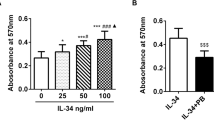
Abstract
The interleukin-1β-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and NF-κB signaling pathways are involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Ebosin, a novel exopolysaccharide (EPS), exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in rat collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing the production of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 and interleukin-1β. The aim of the present study was to assess the effects of ebosin on NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways mediated through interleukin-1β in rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs). Western blotting showed decreased production of phosphorylated p38, JNK1, JNK2, IKKα, IKKβ and IκB in the cytoplasm and NF-κB in the nucleus upon ebosin treatment. The DNA-binding activity of NF-κB in the cell nucleus was also inhibited by ebosin treatment, as demonstrated using an electrophoresis mobility gel shift assay. Analysis of the results of the immunofluorescence assay also showed a reduced amount of NF-κB in the nucleus of cells affected by ebosin. These results provided evidence for the effects of ebosin on both interleukin-1β-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in rat FLSs. In addition, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay demonstrated that ebosin reduces the levels of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-1 and MMP-3 and the chemokines, interleukin-8 and RANTES. Thus, the results of the present study provide further evidence for understanding the medicinal activity of ebosin at a molecular level, therefore nominating this EPS as a potential therapeutic candidate for the treatment of rheumatic arthritis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN . Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell 1996; 85: 307–310.
Burger D, Dayer JM, Palmer G, Gabay C . Is IL-1 a good therapeutic target in the treatment of arthritis? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2006; 20: 879–896.
Piecyk M, Anderson P . Signal transduction in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2001; 15: 789–803.
Kaminska B . MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 2005; 1754: 253–262.
Okamoto H, Cujec TP, Yamanaka H, Kamatani N . Molecular aspects of rheumatoid arthritis: role of transcription factors. FEBS J 2008; 275: 4463–4470.
Okamoto H, Yoshio T, Kaneko H, Yamanaka H . Inhibition of NF-κB signaling by Fasudil as a potential therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 82–92.
Lee YR, Lee JH, Noh EM, Kim EK, Song MY, Jung WS . Guggulsterone blocks IL-1β-mediated inflammatory responses by suppressing NF-kappaB activation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Life Sci 2008; 82: 1203–1209.
Turner-Brannen E, Choi KY, Lippert DN, Cortens JP, Hancock RE, El-Gabalawy H . Modulation of interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory responses by a synthetic cationic innate defence regulator peptide, IDR-1002, in synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 2011; 13: R129.
Jing C, Jianbo W, Yuan L, Rong J, Baoyi L . A new IL-1 receptor inhibitor 139A: fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and structure. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2003; 56: 87–90.
Zhang Y, Wang LF, Bai JY, Guan MJ, Jiang R, Li Y . Anti-inflammatory effect of Ebosin on rat collagen-induced arthritis through suppression production of interferon-1β, interferon-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. Eur J Inflamm 2013; 11: 677–688.
Cuzzocrea S, Mazzon E, Bevilaqua C, Costantino G, Britti D, Mazzulo G . Cloricromene, a coumarine derivative, protects against collagen-induced arthritis in Lewis rats. Br J Pharmacol 2000; 131: 1399–1407.
Bradford MM . A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976; 72: 248–254.
Yang JP, Merin JP, Nakano T, Kato T, Kitade Y, Okamoto T . Inhibition of the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB by gold compounds in vitro. FEBS Lett 1995; 361: 89–96.
Turner-Brannen E, Choi KY, Lippert DN, Cortens JP, Hancock RE, El-Gabalawy H . Modulation of interleukin-1α-induced inflammatory responses by a synthetic cationic innate defence regulator peptide, IDR-1002, in synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 2011; 13: R129.
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J . Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 2001; 81: 807–869.
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K . Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 2001; 22: 153–183.
van Loo G, Beyaert R . Negative regulation of NF-κB and its involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2011; 13: 221–231.
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F, Karin M . NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev 2012; 246: 379–400.
Vincenti MP, Coon CI, Brinckerhoff CE . Nuclear factor κB/p50 activates an element in the distal matrix metalloproteinase 1 promoter in interleukin-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 1998; 41: 1987–1994.
Konttinen YT, Ainola M, Valleala H, Ma J, Ida H, Mandelin J . Analysis of 16 different matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1 to MMP-20) in the synovial membrane: different profiles in trauma and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1999; 58: 691–697.
Ahmed S, Pakozdi A, Koch AE . Regulation of interleukin-1β-induced chemokine production and matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation by epigallocatechin-3-gallate in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 2393–2401.
Monaco C, Andreakos E, Kiriakidis S, Feldmann M, Paleolog E . T-cell-mediated signalling in immune, inflammatory and angiogenic processes: the cascade of events leading to inflammatory diseases. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 2004; 3: 35–42.
Schwartsburd PM . Chronic inflammation as inductor of procancer microenvironment: pathogenesis of dysregulated feedback control. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2003; 22: 95–102.
Heller RA, Schena M, Chai A, Shalon D, Bedilion T, Gilmore J . Discovery and analysis of inflammatory disease-related genes using cDNA microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997; 94: 2150–2155.
Feldmann M, Maini RN . TNF defined as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Nat Med 2003; 9: 1245–1250.
Laws A, Gu Y, Marshall V . Biosynthesis, characterization and design of bacterial exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria. Biotechnol Adv 2001; 19: 597–625.
Boels IC, Ramos A, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM . Functional analysis of the Lactoccus lactis GalU and GalE genes and their impact on sugar nucleotide and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 2001; 67: 3033–3040.
Boels IC, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM . Engineering of carbon distribution between glycolysis and sugar nucleotide biosynthesis in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 2003; 69: 1129–1135.
Lima LF, Habu S, Gern JC, Nascimento BM, Parada JL, Noseda MD . Production and characterization of the exopolysaccharides produced by Agaricus brasiliensis in submerged fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2008; 151: 283–294.
Fernandes MB, Habu S, de Lima MA, Thomaz-Soccol V, Soccol CR . Influence of drying methods over in vitro antitumoral effects of exopolysaccharides produced by Agaricus blazei LPB 03 on submerged fermentation. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 2011; 34: 253–261.
Jin M, Lu Z, Huang M, Wang Y, Wang Y . Effects of Se-enriched polysaccharides produced by Enterobacter cloacae Z0206 on alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2012; 50: 348–352.
Joo JH, Yun JW . Structure and molecular characterization of extracellular polysaccharides produced by Trichoderma erinaceum DG-312. J Mol Biotechnol 2005; 15: 1250–1257.
Nowak B, Ciszek-Lenda M, Sróttek M, Gamian A, Kontny E, Górska-Fraczek S . Lactobacillus rhamnosus exopolysaccharide ameliorates arthritis induced by the systemic injection of collagen and lipopolysaccharide in DBA/1 mice. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2012; 60: 211–220.
Sweeney SE, Firestein GS . Signal transduction in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2004; 16: 231–237.
Han Z, Boyle DL, Chang L, Bennett B, Karin M, Yang L . c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 73–81.
Inoue T, Hammaker D, Boyle DL, Firestein GS . Regulation of JNK by MKK-7 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 2127–2135.
Shin M, Yan C, Boyd D . An inhibitor of c-jun aminoterminal kinase (SP600125) represses c-Jun activation, DNA-binding and PMA-inducible 92-kDa type IV collagenase expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002; 1589: 311–316.
Triantaphyllopoulos K, Madden L, Rioja I, Essex D, Buckton J, Malhotra R . In vitro target validation and in vivo efficacy of p38 MAP kinase inhibition in established chronic collagen-induced arthritis model: a pre-clinical study. Clin Exp Heumatol 2010; 28: 176–185.
Kim EK, Choi EJ . Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1802: 396–405.
Beloueche-Babari M, Jackson LE, Al-Saffar NM, Workman P, Leach MO, Ronen SM . Magnetic resonance spectroscopy monitoring of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling inhibition. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 3356–3563.
May MJ, Ghosh S . Signal transduction through NF-kappa B. Immunol Today 1998; 19: 80–88.
Sweeney SE, Firestein GS . Rheumatoid arthritis: regulation of synovial inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2004; 36: 372–378.
Thornton S, Duwel LE, Boivin GP, Ma Y, Hirsch R . Association of the course of collagen-induced arthritis with distinct patterns of cytokine and chemokine messenger RNA expression. Arthritis Rheum 1999; 42: 1109–1118.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported through a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 30530830) and a grant from the National Key Project of New Drug Study of China (2012ZX09301002-001-023-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Bai, L. et al. Effect of ebosin on modulating interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory responses in rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cell Mol Immunol 13, 584–592 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.36
This article is cited by
-
Ebosin: a potential therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis and autoinflammatory syndromes
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)