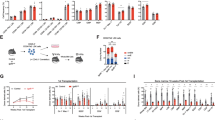
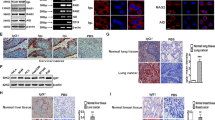
Abstract
Recently, immunoglobulins (Igs) were unexpectedly found to be expressed in epithelial cancers. Immunoglobulin class switching or class switch recombination (CSR) is a natural biological process that alters a B cell’s production of antibodies (immunoglobulins) from one class to another. However, the mechanism of CSR of Ig genes in cancer is still unknown. Here, we confirmed by detecting the hallmark of CSR that the Igα gene in cancer underwent CSR. Then we focused on activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a crucial factor for initiating CSR. Further studies using tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α stimulation and specific inhibitor of NF-κB revealed that TNF-α could increase AID expression through NF-κB signaling. Finally, we demonstrated that AID could co-localize with protein kinase A and bind to the switching (Sα) region of the Igα gene. Overexpression of AID obviously enhanced Igα heavy chain expression and its binding ability to the Sα region. These findings indicated that TNF-α-induced AID expression is involved with CSR in cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao Y, Sun Y, Poirier S, Winterstein D, Hegamyer G, Seed J, et al. Isolation and partial characterization of a transformation-associated sequence from human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Carcinog 1991; 4: 297–307.
Hu D, Zheng H, Liu H, Li M, Ren W, Liao W, et al. Immunoglobulin expression and its biological significance in cancer cells. Cell Mol Immunol 2008; 5: 319–324.
Chen Z, Qiu X, Gu J . Immunoglobulin expression in non-lymphoid lineage and neoplastic cells. Am J Pathol 2009; 174: 1139–1148.
Qiu X, Zhu X, Zhang L, Mao Y, Zhang J, Hao P, et al. Human epithelial cancers secrete immunoglobulin g with unidentified specificity to promote growth and survival of tumor cells. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6488–6495.
Zheng H, Li M, Liu H, Ren W, Hu DS, Shi Y, et al. Immunoglobulin alpha heavy chain derived from human epithelial cancer cells promotes the access of S phase and growth of cancer cells. Cell Biol Int 2007; 31: 82–87.
Li M, Zheng H, Duan Z, Liu H, Hu D, Bode A, et al. Promotion of cell proliferation and inhibition of ADCC by cancerous immunoglobulin expressed in cancer cell lines. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 54–61.
Liu HD, Zheng H, Li M, Hu DS, Tang M, Cao Y . Upregulated expression of kappa light chain by Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via NF-kappaB and AP-1 pathways. Cell Signal 2007; 19: 419–427.
Liu H, Zheng H, Duan Z, Hu D, Li M, Liu S, et al. LMP1-augmented kappa intron enhancer activity contributes to upregulation expression of Ig kappa light chain via NF-kappaB and AP-1 pathways in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer 2009; 8: 92.
Zhu X, Wu L, Zhang L, Hao P, Zhang S, Huang J, et al. Distinct regulatory mechanism of immunoglobulin gene transcription in epithelial cancer cells. Cell Mol Immunol 2010; 7: 279–286.
Liu H, Duan Z, Zheng H, Hu D, Li M, Tao Y, et al. EBV-encoded LMP1 upregulates Igκ 3′enhancer activity and Igkappa expression in nasopharyngeal cancer cells by activating the Ets-1 through ERKs signaling. PLoS One 2012; 7: e32624.
Zheng H, Li M, Ren W, Zeng L, Liu HD, Hu D, et al. Expression and secretion of immunoglobulin alpha heavy chain with diverse VDJ recombinations by human epithelial cancer cells. Mol Immunol 2007; 44: 2221–2227.
Zheng J, Huang J, Mao Y, Liu S, Sun X, Zhu X, et al. Immunoglobulin gene transcripts have distinct VHDJH recombination characteristics in human epithelial cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 13610–13619.
Stavnezer J, Guikema JE, Schrader CE . Mechanism and regulation of class switch recombination. Annu Rev Immunol 2008; 26: 261–292.
Vuong BQ, Lee M, Kabir S, Irimia C, Macchiarulo S, McKnight GS, et al. Specific recruitment of protein kinase A to the immunoglobulin locus regulates class-switch recombination. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 420–426.
Longerich S, Basu U, Alt F, Storb U . AID in somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination. Curr Opin Immunol 2006; 18: 164–174.
Pan-Hammarstrom Q, Zhao Y, Hammarstrom L . Class switch recombination: a comparison between mouse and human. Adv Immunol 2007; 93: 1–61.
Schrader CE, Linehan EK, Mochegova SN, Woodland RT, Stavnezer J . Inducible DNA breaks in Ig S regions are dependent on AID and UNG. J Exp Med 2005; 202: 561–568.
Maul RW, Saribasak H, Martomo SA, McClure RL, Yang W, Vaisman A, et al. Uracil residues dependent on the deaminase AID in immunoglobulin gene variable and switch regions. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 70–76.
Yadav A, Olaru A, Saltis M, Setren A, Cerny J, Livak F . Identification of a ubiquitously active promoter of the murine activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AICDA) gene. Mol Immunol 2006; 43: 529–541.
Nagaoka H, Tran TH, Kobayashi M, Aida M, Honjo T . Preventing AID, a physiological mutator, from deleterious activation: regulation of the genomic instability that is associated with antibody diversity. Int Immunol 2010; 22: 227–235.
Gourzi P, Leonova T, Papavasiliou FN . Viral induction of AID is independent of the interferon and the Toll-like receptor signaling pathways but requires NF-kappaB. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 259–265.
Ishikawa C, Nakachi S, Senba M, Sugai M, Mori N . Activation of AID by human T-cell leukemia virus Tax oncoprotein and the possible role of its constitutive expression in ATL genesis. Carcinogenesis 2011; 32: 110–119.
Endo Y, Marusawa H, Kinoshita K, Morisawa T, Sakurai T, Okazaki IM, et al. Expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase in human hepatocytes via NF-kappaB signaling. Oncogene 2007; 26: 5587–5595.
Machida K, Cheng KT, Sung VM, Shimodaira S, Lindsay KL, Levine AM, et al. Hepatitis C virus induces a mutator phenotype: enhanced mutations of immunoglobulin and protooncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 4262–4267.
Matsumoto Y, Marusawa H, Kinoshita K, Endo Y, Kou T, Morisawa T, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection triggers aberrant expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase in gastric epithelium. Nat Med 2007; 13: 470–476.
Cerutti A, Zan H, Schaffer A, Bergsagel L, Harindranath N, Max EE, et al. CD40 ligand and appropriate cytokines induce switching to IgG, IgA, and IgE and coordinated germinal center and plasmacytoid phenotypic differentiation in a human monoclonal IgM+IgD+ B cell line. J Immunol 1998; 160: 2145–2157.
Cerutti A, Zan H, Kim EC, Shah S, Schattner EJ, Schaffer A, et al. Ongoing in vivo immunoglobulin class switch DNA recombination in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J Immunol 2002; 169: 6594–6603.
Kinoshita K, Harigai M, Fagarasan S, Muramatsu M, Honjo T . A hallmark of active class switch recombination: transcripts directed by I promoters on looped-out circular DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 12620–12623.
Hu Y, Ericsson I, Doseth B, Liabakk NB, Krokan HE, Kavli B . Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) is localized to subnuclear domains enriched in splicing factors. Exp Cell Res 2014; 322: 178–192.
Dorsett Y, McBride KM, Jankovic M, Gazumyan A, Thai TH, Robbiani DF, et al. MicroRNA-155 suppresses activation-induced cytidine deaminase-mediated Myc-Igh translocation. Immunity 2008; 28: 630–638.
Teng G, Hakimpour P, Landgraf P, Rice A, Tuschl T, Casellas R, et al. MicroRNA-155 is a negative regulator of activation-induced cytidine deaminase. Immunity 2008; 28: 621–629.
de Yebenes VG, Belver L, Pisano DG, Gonzalez S, Villasante A, Croce C, et al. miR-181b negatively regulates activation-induced cytidine deaminase in B cells. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 2199–2206.
Basu U, Chaudhuri J, Phan RT, Datta A, Alt FW . Regulation of activation induced deaminase via phosphorylation. Adv Exp Med Biol 2007; 596: 129–137.
Cheng HL, Vuong BQ, Basu U, Franklin A, Schwer B, Astarita J, et al. Integrity of the AID serine-38 phosphorylation site is critical for class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 2717–2722.
McBride KM, Gazumyan A, Woo EM, Barreto VM, Robbiani DF, Chait BT, et al. Regulation of hypermutation by activation-induced cytidine deaminase phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 8798–8803.
McBride KM, Gazumyan A, Woo EM, Schwickert TA, Chait BT, Nussenzweig MC . Regulation of class switch recombination and somatic mutation by AID phosphorylation. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 2585–2594.
Chaudhuri J, Alt FW . Class-switch recombination: interplay of transcription, DNA deamination and DNA repair. Nat Rev Immunol 2004; 4: 541–552.
Basu U, Chaudhuri J, Alpert C, Dutt S, Ranganath S, Li G, et al. The AID antibody diversification enzyme is regulated by protein kinase A phosphorylation. Nature 2005; 438: 508–511.
de Yebenes VG, Ramiro AR . Activation-induced deaminase: light and dark sides. Trends Mol Med 2006; 12: 432–439.
Pasqualucci L, Kitaura Y, Gu H, Dalla-Favera R . PKA-mediated phosphorylation regulates the function of activation-induced deaminase (AID) in B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 395–400.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Gu Jiang (Department of Pathology, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, China) for providing the HeLa S3 cell line. We also thank Professor Songqing Fan (The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China) for quantifying the immunohistochemistry results.
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863) of China (No. 2006AA02A404) and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 30772465, No. 30973399).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology’s website. (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, Z., Zheng, H., Liu, H. et al. AID expression increased by TNF-α is associated with class switch recombination of Igα gene in cancers. Cell Mol Immunol 13, 484–491 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.26