Abstract
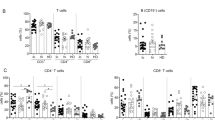
B cells play an important role in the clearance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and protection against reinfection. However, the functional characteristics of these cells that are associated with the outcome of chronic HBV infection remain unknown. We comprehensively investigated the frequency, phenotype, and function of peripheral B-cell subsets from CHB patients in different phases: immune tolerance (IT), immune activation (IA), immune clearance (IC), responders with HBsAg seroconversion (resolved patients, RP), and healthy controls (HC). IA patients displayed lower percentages of peripheral blood memory B cells compared with the other groups. Overall polyclonal activation of B cells, indicated by higher levels of activation markers and secretion of IgG and IgM, was observed in IA patients. This B-cell hyperactivation could be induced by increased IFN-α and soluble CD40 ligands in IA patients. Notably, the expression of the co-stimulator molecule CD80 and serum HBsAb and the frequency of HBsAg-specific B cells were significantly decreased in IT, IA, and IC patients compared with HC subjects. More importantly, the B-cell hyperactivation, co-stimulatory molecule downregulation and HBsAg-specific B-cell impairment were reversed in RP patients. The reversal of B-cell hyperactivation and functional impairment is associated with HBsAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2012; 57: 167–185.
Wang FS, Zhang Z . Host immunity influences disease progression and antiviral efficacy in humans infected with hepatitis B virus. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 3: 499–512.
Schurich A, Khanna P, Lopes AR et al. Role of the coinhibitory receptor cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 on apoptosis-prone CD8 T cells in persistent hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2011; 53: 1494–1503.
Bertoletti A, Ferrari C . Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections: towards restoration of immune control of viral infection. Gut 2011; 61: 1754–1764. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301073.
Zhang Z, Zhang JY, Wang LF, Wang FS . Immunopathogenesis and prognostic immune markers of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatology 2012; 27: 223–230.
Lo CM, Fung JT, Lau GK et al. Development of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen after liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2003; 37: 36–43.
Luo Y, Lo CM, Cheung CK, Lau GK, Fan ST, Wong J . Identification of hepatitis B virus-specific lymphocytes in human liver grafts from HBV-immune donors. Liver Transpl 2007; 13: 71–79.
Dahmen U, Li J, Dirsch O et al. Adoptive transfer of donor-derived immunity by liver transplantation: a potential avenue to prevent hepatitis B virus reinfection. J Viral Hepat 2003; 10: 31–36.
Schumann A, Lindemann M, Valentin-Gamazo C et al. Adoptive immune transfer of hepatitis B virus specific immunity from immunized living liver donors to liver recipients. Transplantation 2009; 87: 103–111.
Dervite I, Hober D, Morel P . Acute hepatitis B in a patient with antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen who was receiving rituximab. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 68–69.
Westhoff TH, Jochimsen F, Schmittel A et al. Fatal hepatitis B virus reactivation by an escape mutant following rituximab therapy. Blood 2003; 102: 1930.
Niscola P, Del Principe MI, Maurillo L et al. Fulminant B hepatitis in a surface antigen-negative patient with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia after rituximab therapy. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1840–1841.
Yeo W, Chan TC, Leung NW et al. Hepatitis B virus reactivation in lymphoma patients with prior resolved hepatitis B undergoing anticancer therapy with or without rituximab. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 605–611.
Maruyama T, McLachlan A, Iino S, Koike K, Kurokawa K, Milich DR . The serology of chronic hepatitis B infection revisited. J Clin Invest 1993; 91: 2586–2595.
Bocher WO, Herzog-Hauff S, Herr W et al. Regulation of the neutralizing anti-hepatitis B surface (HBs) antibody response in vitro in HBs vaccine recipients and patients with acute or chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol 1996; 105: 52–58.
Oliviero B, Cerino A, Varchetta S et al. Enhanced B-cell differentiation and reduced proliferative capacity in chronic hepatitis C and chronic hepatitis B virus infections. J Hepatol 2011; 55: 53–60.
Dusheiko GM, Hoofnagle JH, Cooksley WG, James SP, Jones EA . Synthesis of antibodies to hepatitis B virus by cultured lymphocytes from chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. J Clin Invest 1983; 71: 1104–1113.
Barnaba V, Valesini G, Levrero M et al. Immunoregulation of the in vitro anti-HBs antibody synthesis in chronic HBsAg carriers and in recently boosted anti-hepatitis B vaccine recipients. Clin Exp Immunol 1985; 60: 259–266.
Barnaba V, Levrero M, Ruberti G et al. In vitro anti-HBs antibody synthesis from anti-hepatitis B vaccine recipients. Clin Exp Immunol 1987; 70: 283–288.
Zhang Z, Xu X, Lu J et al. B and T lymphocyte attenuator down-regulation by HIV-1 depends on type I interferon and contributes to T-cell hyperactivation. J Infect Dis 2011; 203: 1668–1678.
Moir S, Fauci AS . Pathogenic mechanisms of B-lymphocyte dysfunction in HIV disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 122: 12–19.
Moir S, Fauci AS . B cells in HIV infection and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 235–245.
Chu CM, Sheen IS, Yeh CT, Hsieh SY, Tsai SL, Liaw YF . Serum levels of interferon-alpha and -gamma in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Dig Dis Sci 1995; 40: 2107–2112.
Gora-Gebka M, Liberek A, Szydlowska-Lysiak W, Bako W, Korzon M . Serum interleukin 6 and interleukin 12 levels in children with chronic hepatitis HBV treated with interferon alpha. Ann Hepatol 2003; 2: 92–97.
Zhang Z, Zou ZS, Fu JL et al. Severe dendritic cell perturbation is actively involved in the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. J Hepatol 2008; 49: 396–406.
Dustin LB, Rice CM . Flying under the radar: the immunobiology of hepatitis C. Annu Rev Immunol 2007; 25: 71–99.
Moir S, Ho J, Malaspina A et al. Evidence for HIV-associated B cell exhaustion in a dysfunctional memory B cell compartment in HIV-infected viremic individuals. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 1797–1805.
Wu C, Liu Y, Zhao Q et al. Soluble CD40 ligand-activated human peripheral B cells as surrogated antigen presenting cells: a preliminary approach for anti-HBV immunotherapy. Virol J 2010; 7: 370.
Chisari FV, Ferrari C . Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol 1995; 13: 29–60.
Maruyama T, Iino S, Koike K, Yasuda K, Milich DR . Serology of acute exacerbation in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 1993; 105: 1141–1151.
Chang JJ, Wightman F, Bartholomeusz A et al. Reduced hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific CD4+ T-cell responses in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-HBV-coinfected individuals receiving HBV-active antiretroviral therapy. J Virol 2005; 79: 3038–3051.
Maini MK, Boni C, Lee CK et al. The role of virus-specific CD8(+) cells in liver damage and viral control during persistent hepatitis B virus infection. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 1269–1280.
Boni C, Penna A, Ogg GS et al. Lamivudine treatment can overcome cytotoxic T-cell hyporesponsiveness in chronic hepatitis B: new perspectives for immune therapy. Hepatology 2001; 33: 963–971.
Chen L, Zhang Z, Chen W et al. B7-H1 up-regulation on myeloid dendritic cells significantly suppresses T cell immune function in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Immunol 2007; 178: 6634–6641.
Jaroszewicz J, Calle SB, Wursthorn K et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infection: a European perspective. J Hepatol 2010; 52: 514–522.
Nguyen T, Thompson AJ, Bowden S et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen levels during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B: a perspective on Asia. J Hepatol 2010; 52: 508–513.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Grand Program on Key Infectious Disease (2013ZX10002001-001-003, 2012ZX10002-007-002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81373137), the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2012CB519005), and the National Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars (81222024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Shang, Q., Chen, X. et al. Reversal of B-cell hyperactivation and functional impairment is associated with HBsAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients. Cell Mol Immunol 12, 309–316 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.25
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.25
This article is cited by
-
Peg-IFNα combined with hepatitis B vaccination contributes to HBsAg seroconversion and improved immune function
Virology Journal (2024)
-
Hepatitis B virus–associated diffuse large B cell lymphoma: epidemiology, biology, clinical features and HBV reactivation
Holistic Integrative Oncology (2023)
-
Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection
Nature Reviews Immunology (2022)
-
Long-term safety of rituximab in rheumatic patients with previously resolved hepatitis B virus infection
Internal and Emergency Medicine (2022)
-
T follicular helper cells improve the response of patients with chronic hepatitis B to interferon by promoting HBsAb production
Journal of Gastroenterology (2022)