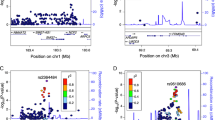
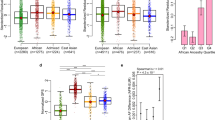
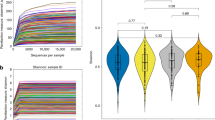
Abstract
Celiac sprue remains a model autoimmune disease for dissection of genetic and environmental influences on disease progression. The 2010 Congress of Autoimmunity included several key sessions devoted to genetics and environment. Several papers from these symposia were selected for in-depth discussion and publication. This issue is devoted to this theme. The goal is not to discuss genetic and environmental interactions, but rather to focus on key elements of diagnosis, the inflammatory response and the mechanisms of autoimmunity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM . History of celiac disease. J Am Diet Assoc 1959; 35: 1158–1162.
Schuppan D, Junker Y, Barisani D . Celiac disease: from pathogenesis to novel therapies. Gastroenterology 2009; 137: 1912–1933.
Catassi C, Rätsch IM, Gandolfi L, Pratesi R, Fabiani E, El Asmar R et al. Why is coeliac disease endemic in the people of the Sahara? Lancet 1999; 354: 647–648.
Marsh MN, Gluten, major histocompatibility complex, and the small intestine. A molecular and immunobiologic approach to the spectrum of gluten sensitivity (‘celiac sprue’). Gastroenterology 1992; 102: 330–354.
Jabri B, Sollid LM . Tissue-mediated control of immunopathology of coeliac disease. Nature Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 58–70.
Vorobjova T, Uibo O, Heilman K, Rägo T, Honkanen J, Vaarala O et al. Increased FOXP3 expression in small-bowel mucosa of children with coeliac disease and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Scand J Gastroenterol 2009; 44: 422–430.
Lindfors K, Mäki M, Kaukinen K . Transglutaminase 2-targeted autoantibodies in celiac disease: pathogenetic players in addition to diagnostic tools? Autoimmune Rev 2010; 9: 744–749.
Zhernakova A, Elbers CC, Ferwerda B, Romanos J, Trynka G, Dubois PC et al. Evolutionary and fuctional analysis of celiac risk loci reveals SH2B3 as a protective factor against bacterial infection. Am J Hum Gen 2010; 86: 970–977.
Trynka G, Wijmenga C, van Heel DA . A genetic perspective on coeliac disease. Trends Mol Med 2010; 16: 537–550.
Plot L, Amital H, Barzilai O, Ram M, Nicola B, Shoenfeld Y . Infections may have a protective role in the etiopathogenesis of celiac disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 2009; 1173: 670–674.
Ou G, Hedberg M, Hörstedt P, Baranov V, Forsberg G, Drobni M et al. Proximal small intestinal microbiota and identification of rod-shaped bacteria associated with childhood celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104: 3058–3067.
de Palma G, Cinova J, Stepankova R, Tuckova L, Sanz Y . Pivotal advance: Bifidobacteria and Gram-negative bacteria differentially influence immune responses in the proinflammatory milieu of celiac disease. J Leukoc Biol 2010; 87: 765–778.
Meresse B, Ripoche J, Heyman M, Cerf-Bensussan N . Celiac disease: from oral tolerance to intestinal inflammation, autoimmunity and lymphogenesis. Mucosal Immunol 2009; 2: 8–23.
Monteleone G, Pender SL, Alstead E, Hauer AC, Lionetti P, McKenzie C . Role of interferon alpha in promoting T helper cell type I responses in the small intestine in coeliac disease. Gut 2001; 48: 425–429.
Maiuri L, Ciacci C, Auricchio S, Brown V, Quarantino S, Londei M . Interleukin-15 mediates epithelial changes in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 996–1006.
Stene LC, Honeyman MC, Hoffenberg EJ, Haas JE, Sokol RJ, Emery L et al. Rotavirus infection frequency and risk of celiac disease autoimmunity in early childhood: a longitudinal study. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101: 2333–2340.
Lammers KM, Lu R, Brownley J, Lu B, Gerard C, Thomas K et al. Gliadin induces an increase in intestinal permeability and zonulin release by binding to chemokine receptor CXCR3. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 194–204.
Visser J, Rozing J, Sapone A, Lammers K, Fasano A . Tight junctions, intestinal permeability, and autoimmunity. Celiac disease and type 1 diabetes paradigms. Ann NY Acad Sci 2009; 1165: 195–205.
Stamnaes J, Dorum S, Fleckenstein B, Aeshlimann D, Solid LM . Gluten T cell epitope targeting by TG3 and TG6; implications for dermatitis herpetiformis and gluten ataxia. Amino Acids 2010; 39: 1183–1191.
Simpson M, Mojibian M, Barriga K, Scott FW, Fasano A, Rewers M et al. An exploration of Glo-3A antibdy levels in children at increased risk for type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2009; 10: 563–572.
Arnson Y, Shoenfeld Y, Amital H . Effects of tobacco smoke on immunity, inflammation and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J258–J265.
Berkun Y, Padeh S . Environmental factors and the geoepidemiology of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A319–A324.
Bhat A, Naguwa S, Cheema G, Gershwin ME . The epidemiology of transverse myelitis. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A395–A399.
Biggioggero M, Meroni PL . The geoepidemiology of the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A299–A304.
Borchers AT, Naguwa SM, Keen CL, Gershwin ME . The implications of autoimmunity and pregnancy. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J287–J299.
Borchers AT, Naguwa SM, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME . The geoepidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A277–A287.
Borchers AT, Uibo R, Gershwin ME . The geoepidemiology of type 1 diabetes. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A355–A365.
Brooks WH, Le Dantec C, Pers JO, Youinou P, Renaudineau Y . Epigenetics and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J207–J219.
Chandran V, Raychaudhuri SP . Geoepidemiology and environmental factors of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J314–J321.
Chang C . The immune effects of naturally occurring and synthetic nanoparticles. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J234–J246.
Chang C, Gershwin ME . Drugs and autoimmunity—a contemporary review and mechanistic approach. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J266–J275.
Chen M, Daha MR, Kallenberg CG . The complement system in systemic autoimmune disease. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J276–J286.
Chen M, Kallenberg CG . The environment, geoepidemiology and ANCA-associated vasculitides. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A293–A298.
Deane S, Teuber SS, Gershwin ME . The geoepidemiology of immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A342–A349.
Ehrenfeld M . Geoepidemiology: the environment and spondyloarthropathies. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A325–A329.
Hemminki K, Li X, Sundquist J, Sundquist K . The epidemiology of Graves' disease: evidence of a genetic and an environmental contribution. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J307–J313.
Hoffmann MH, Trembleau S, Muller S, Steiner G . Nucleic acid-associated autoantigens: pathogenic involvement and therapeutic potential. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J178–J206.
Invernizzi P . Geoepidemiology of autoimmune liver diseases. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J300–J306.
Lambert JF, Nydegger UE . Geoepidemiology of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A350–A354.
Leung PS, Shu SA, Kenny TP, Wu PY, Tao MH . Development and validation of gene therapies in autoimmune diseases: epidemiology to animal models. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A400–A405.
Lleo A, Invernizzi P, Gao B, Podda M, Gershwin ME . Definition of human autoimmunity–autoantibodies versus autoimmune disease. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A259–A266.
Logan I, Bowlus CL . The geoepidemiology of autoimmune intestinal diseases. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A372–A378.
Mackay IR . Travels and travails of autoimmunity: a historical journey from discovery to rediscovery. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A251–A258.
Maverakis E, Miyamura Y, Bowen MP, Correa G, Ono Y, Goodarzi H . Light, including ultraviolet. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J247–J257.
Mavragani CP, Moutsopoulos HM . The geoepidemiology of Sjogren's syndrome. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A305–A310.
Meyer A, Levy Y . Chapter 33: geoepidemiology of myasthenia gravis. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A383–A386.
Meyer N, Misery L . Geoepidemiologic considerations of auto-immune pemphigus. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A379–A382.
Milo R, Kahana E . Multiple sclerosis: geoepidemiology, genetics and the environment. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A387–A394.
Powell JJ, Faria N, Thomas-McKay E, Pele LC . Origin and fate of dietary nanoparticles and microparticles in the gastrointestinal tract. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J226–J233.
Prieto S, Grau JM . The geoepidemiology of autoimmune muscle disease. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A330–A334.
Ranque B, Mouthon L . Geoepidemiology of systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A311–A318.
Round JL, O'Connell RM, Mazmanian SK . Coordination of tolerogenic immune responses by the commensal microbiota. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J220–J225.
Sands J, Tuscano JM . Geoepidemiology and autoimmune manifestations of lymphoproliferative disorders. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A335–A341.
Segelmark M, Hellmark T . Autoimmune kidney diseases. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A366–A371.
Selmi C . The worldwide gradient of autoimmune conditions. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A247–A250.
Selmi C, Tsuneyama K . Nutrition, geoepidemiology, and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A267–A270.
Shapira Y, Agmon-Levin N, Shoenfeld Y . Defining and analyzing geoepidemiology and human autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J168–J177.
Stojanovich L . Stress and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A271–A276.
Tobon GJ, Youinou P, Saraux A . The environment, geo-epidemiology, and autoimmune disease: rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 2010; 9: A288–A292.
Tomer Y . Hepatitis C and interferon induced thyroiditis. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J322–J326.
Youinou P, Pers JO, Gershwin ME, Shoenfeld Y . Geo-epidemiology and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J163–J167.
Zeki AA, Schivo M, Chan AL, Hardin KA, Kenyon NJ, Albertson TE, et al. Geoepidemiology of COPD and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: J327–J338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uibo, R., Tian, Z. & Gershwin, M. Celiac disease: a model disease for gene–environment interaction. Cell Mol Immunol 8, 93–95 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.62
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.62
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The impact of perinatal immune development on mucosal homeostasis and chronic inflammation
Nature Reviews Immunology (2012)