Abstract
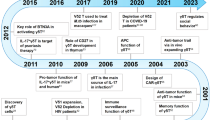
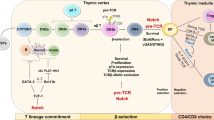
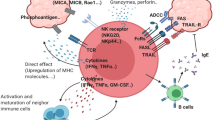
T lymphocytes bearing γ- and δ-chain T-cell receptor heterodimers are named γδ T cells. Interestingly, γδ and αβ T cells share the same progenitors, and they undergo a fate decision in the thymus. Functional differentiation of γδ T cells occurs both inside and outside the thymus. Antigen recognition of γδ T-cell receptors is very unique, and the responses frequently exhibit innate characteristics. Nevertheless, peripheral γδ T cells exert a number of effector and regulatory functions. γδ T cells rapidly produce cytokines like interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-17 and promote inflammation, partly due to the inherent epigenetic and transcriptional programs, which facilitates a quick and extensive response. Moreover, γδ T cells lyse target cells directly, and this is necessary for pathogen or tumor clearance. γδ T cells can even serve as regulatory cells, and may contribute to immune suppression. Orchestration of γδ T-cell and other immune cell interactions may be critical for host defense and immune regulation. Recently, γδ T cells have been used for immunotherapy for infectious diseases and malignancy. In this review, we summarize the abstracts presented at the recent γδ T cell Conference held from 19 to 21 May 2010, in Kiel, Germany (please see the website for details: http://www.gammadelta-conference.uni-kiel.de/index.html).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melichar HJ, Narayan K, Der SD, Hiraoka Y, Gardiol N, Jeannet G et al. Regulation of gammadelta versus alphabeta T lymphocyte differentiation by the transcription factor SOX13. Science 2007; 315: 230–233.
Lauritsen JP, Wong GW, Lee SY, Lefebvre JM, Ciofani M, Rhodes M et al. Marked induction of the helix–loop–helix protein Id3 promotes the gammadelta T cell fate and renders their functional maturation Notch independent. Immunity 2009; 31: 565–575.
Haks MC, Lefebvre JM, Lauritsen JP, Carleton M, Rhodes M, Miyazaki T et al. Attenuation of gammadelta TCR signaling efficiently diverts thymocytes to the alphabeta lineage. Immunity 2005; 22: 595–606.
Hayes SM, Li L, Love PE . TCR signal strength influences alphabeta/gammadelta lineage fate. Immunity 2005; 22: 583–593.
Kreslavsky T, Garbe AI, Krueger A, von Boehmer H . T cell receptor-instructed alphabeta versus gammadelta lineage commitment revealed by single-cell analysis. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 1173–1186.
Ciofani M, Knowles GC, Wiest DL, von Boehmer H, Zuniga-Pflucker JC . Stage-specific and differential notch dependency at the alphabeta and gammadelta T lineage bifurcation. Immunity 2006; 25: 105–116.
Garbe AI, Krueger A, Gounari F, Zuniga-Pflucker JC, von Boehmer H . Differential synergy of Notch and T cell receptor signaling determines alphabeta versus gammadelta lineage fate. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1579–1590.
Tanigaki K, Tsuji M, Yamamoto N, Han H, Tsukada J, Inoue H et al. Regulation of alphabeta/gammadelta T cell lineage commitment and peripheral T cell responses by Notch/RBP-J signaling. Immunity 2004; 20: 611–622.
Washburn T, Schweighoffer E, Gridley T, Chang D, Fowlkes BJ, Cado D et al. Notch activity influences the alphabeta versus gammadelta T cell lineage decision. Cell 1997; 88: 833–843.
Boyden LM, Lewis JM, Barbee SD, Bas A, Girardi M, Hayday AC et al. Skint1, the prototype of a newly identified immunoglobulin superfamily gene cluster, positively selects epidermal gammadelta T cells. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 656–662.
Silva-Santos B, Pennington DJ, Hayday AC . Lymphotoxin-mediated regulation of gammadelta cell differentiation by alphabeta T cell progenitors. Science 2005; 307: 925–928.
Jensen KD, Su X, Shin S, Li L, Youssef S, Yamasaki S et al. Thymic selection determines gammadelta T cell effector fate: antigen-naive cells make interleukin-17 and antigen-experienced cells make interferon gamma. Immunity 2008; 29: 90–100.
Pennington DJ, Silva-Santos B, Shires J, Theodoridis E, Pollitt C, Wise EL et al. The inter-relatedness and interdependence of mouse T cell receptor gammadelta+ and alphabeta+ cells. Nat Immunol 2003; 4: 991–998.
Kreslavsky T, Savage AK, Hobbs R, Gounari F, Bronson R, Pereira P et al. TCR-inducible PLZF transcription factor required for innate phenotype of a subset of gammadelta T cells with restricted TCR diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 12453–12458.
Yin Z, Zhang DH, Welte T, Bahtiyar G, Jung S, Liu L et al. Dominance of IL-12 over IL-4 in gamma delta T cell differentiation leads to default production of IFN-gamma: failure to down-regulate IL-12 receptor beta 2-chain expression. J Immunol 2000; 164: 3056–3064.
Yin Z, Chen C, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH, Ray A, Craft J . T-Bet expression and failure of GATA-3 cross-regulation lead to default production of IFN-gamma by gammadelta T cells. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1566–1571.
Chen L, He W, Kim ST, Tao J, Gao Y, Chi H et al. Epigenetic and transcriptional programs lead to default IFN-gamma production by gammadelta T cells. J Immunol 2007; 178: 2730–2736.
Gao Y, Yang W, Pan M, Scully E, Girardi M, Augenlicht LH et al. Gamma delta T cells provide an early source of interferon gamma in tumor immunity. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 433–442.
He W, Hao J, Dong S, Gao Y, Tao J, Chi H et al. Naturally activated Vgamma4 gammadelta T cells play a protective role in tumor immunity through expression of eomesodermin. J Immunol 2010; 185: 126–133.
Subauste CS, Chung JY, Do D, Koniaris AH, Hunter CA, Montoya JG et al. Preferential activation and expansion of human peripheral blood gamma delta T cells in response to Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and their cytokine production and cytotoxic activity against T. gondii-infected cells. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 610–619.
Wang L, Das H, Kamath A, Bukowski JF . Human V gamma 2V delta 2 T cells produce IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha with an on/off/on cycling pattern in response to live bacterial products. J Immunol 2001; 167: 6195–6201.
Roark CL, French JD, Taylor MA, Bendele AM, Born WK, O'Brien RL . Exacerbation of collagen-induced arthritis by oligoclonal, IL-17-producing gamma delta T cells. J Immunol 2007; 179: 5576–5583.
Hamada S, Umemura M, Shiono T, Tanaka K, Yahagi A, Begum MD et al. IL-17A produced by gammadelta T cells plays a critical role in innate immunity against listeria monocytogenes infection in the liver. J Immunol 2008; 181: 3456–3463.
Roark CL, Simonian PL, Fontenot AP, Born WK, O'Brien RL . Gammadelta T cells: an important source of IL-17. Curr Opin Immunol 2008; 20: 353–357.
Martin B, Hirota K, Cua DJ, Stockinger B, Veldhoen M . Interleukin-17-producing gammadelta T cells selectively expand in response to pathogen products and environmental signals. Immunity 2009; 31: 321–330.
Sutton CE, Lalor SJ, Sweeney CM, Brereton CF, Lavelle EC, Mills KH . Interleukin-1 and IL-23 induce innate IL-17 production from gammadelta T cells, amplifying Th17 responses and autoimmunity. Immunity 2009; 31: 331–341.
Ribot JC, deBarros A, Pang DJ, Neves JF, Peperzak V, Roberts SJ et al. CD27 is a thymic determinant of the balance between interferon-gamma- and interleukin 17-producing gammadelta T cell subsets. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 427–436.
Prinz I, Sansoni A, Kissenpfennig A, Ardouin L, Malissen M, Malissen B . Visualization of the earliest steps of gammadelta T cell development in the adult thymus. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 995–1003.
O'Brien RL, Roark CL, Jin N, Aydintug MK, French JD, Chain JL et al. gammadelta T-cell receptors: functional correlations. Immunol Rev 2007; 215: 77–88.
Crowley MP, Reich Z, Mavaddat N, Altman JD, Chien Y . The recognition of the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule, T10, by the gammadelta T cell, G8. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 1223–1230.
Matis LA, Cron R, Bluestone JA . Major histocompatibility complex-linked specificity of gamma delta receptor-bearing T lymphocytes. Nature 1987; 330: 262–264.
Shin S, El-Diwany R, Schaffert S, Adams EJ, Garcia KC, Pereira P et al. Antigen recognition determinants of gammadelta T cell receptors. Science 2005; 308: 252–255.
Adams EJ, Strop P, Shin S, Chien YH, Garcia KC . An autonomous CDR3delta is sufficient for recognition of the nonclassical MHC class I molecules T10 and T22 by gammadelta T cells. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 777–784.
Porcelli S, Brenner MB, Greenstein JL, Balk SP, Terhorst C, Bleicher PA . Recognition of cluster of differentiation 1 antigens by human CD4−CD8-cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature 1989; 341: 447–450.
Spada FM, Grant EP, Peters PJ, Sugita M, Melian A, Leslie DS et al. Self-recognition of CD1 by gamma/delta T cells: implications for innate immunity. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 937–948.
Groh V, Steinle A, Bauer S, Spies T . Recognition of stress-induced MHC molecules by intestinal epithelial gammadelta T cells. Science 1998; 279: 1737–1740.
Tanaka Y, Morita CT, Nieves E, Brenner MB, Bloom BR . Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human gamma delta T cells. Nature 1995; 375: 155–158.
Scotet E, Martinez LO, Grant E, Barbaras R, Jeno P, Guiraud M et al. Tumor recognition following Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell receptor interactions with a surface F1-ATPase-related structure and apolipoprotein A–I. Immunity 2005; 22: 71–80.
Diefenbach A, Jamieson AM, Liu SD, Shastri N, Raulet DH . Ligands for the murine NKG2D receptor: expression by tumor cells and activation of NK cells and macrophages. Nat Immunol 2000; 1: 119–126.
Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J, Steinle A, Phillips JH, Lanier LL et al. Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 1999; 285: 727–729.
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH . The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 515–548.
Born WK, Yin Z, Hahn YS, Sun D, O'Brien RL . Analysis of gammadelta T cell functions in the mouse. J Immunol 2010; 184: 4055–4061.
Bonneville M, O'Brien RL, Born WK . Gammadelta T cell effector functions: a blend of innate programming and acquired plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 467–478.
Peng G, Wang HY, Peng W, Kiniwa Y, Seo KH, Wang RF . Tumor-infiltrating gammadelta T cells suppress T and dendritic cell function via mechanisms controlled by a unique Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Immunity 2007; 27: 334–348.
Vincent MS, Roessner K, Lynch D, Wilson D, Cooper SM, Tschopp J et al. Apoptosis of Fashigh CD4+ synovial T cells by Borrelia-reactive Fas-ligandhigh gammadelta T cells in Lyme arthritis. J Exp Med 1996; 184: 2109–2118.
Hayday AC . gammadelta cells: a right time and a right place for a conserved third way of protection. Annu Rev Immunol 2000; 18: 975–1026.
Vermijlen D, Brouwer M, Donner C, Liesnard C, Tackoen M, van Rysselberge M et al. Human cytomegalovirus elicits fetal gammadelta T cell responses in utero. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 807–821.
Mombaerts P, Arnoldi J, Russ F, Tonegawa S, Kaufmann SH . Different roles of alpha beta and gamma delta T cells in immunity against an intracellular bacterial pathogen. Nature 1993; 365: 53–56.
Shen Y, Zhou D, Qiu L, Lai X, Simon M, Shen L et al. Adaptive immune response of Vgamma2Vdelta2+ T cells during mycobacterial infections. Science 2002; 295: 2255–2258.
Hiromatsu K, Yoshikai Y, Matsuzaki G, Ohga S, Muramori K, Matsumoto K et al. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med 1992; 175: 49–56.
Dieli F, Caccamo N, Meraviglia S, Ivanyi J, Sireci G, Bonanno CT et al. Reciprocal stimulation of gammadelta T cells and dendritic cells during the anti-mycobacterial immune response. Eur J Immunol 2004; 34: 3227–3235.
O'Brien RL, Happ MP, Dallas A, Palmer E, Kubo R, Born WK . Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell 1989; 57: 667–674.
French JD, Roark CL, Born WK, O'Brien RL . gammadelta T cell homeostasis is established in competition with alphabeta T cells and NK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 14741–14746.
Constant P, Davodeau F, Peyrat MA, Poquet Y, Puzo G, Bonneville M et al. Stimulation of human gamma delta T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science 1994; 264: 267–270.
Girardi M, Oppenheim DE, Steele CR, Lewis JM, Glusac E, Filler R et al. Regulation of cutaneous malignancy by gammadelta T cells. Science 2001; 294: 605–609.
Girardi M, Glusac E, Filler RB, Roberts SJ, Propperova I, Lewis J et al. The distinct contributions of murine T cell receptor (TCR)gammadelta+ and TCRalphabeta+ T cells to different stages of chemically induced skin cancer. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 747–755.
Kabelitz D, Wesch D, He W . Perspectives of gammadelta T cells in tumor immunology. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5–8.
Jameson J, Ugarte K, Chen N, Yachi P, Fuchs E, Boismenu R et al. A role for skin gammadelta T cells in wound repair. Science 2002; 296: 747–749.
Jameson JM, Cauvi G, Witherden DA, Havran WL . A keratinocyte-responsive gamma delta TCR is necessary for dendritic epidermal T cell activation by damaged keratinocytes and maintenance in the epidermis. J Immunol 2004; 172: 3573–3579.
Sharp LL, Jameson JM, Cauvi G, Havran WL . Dendritic epidermal T cells regulate skin homeostasis through local production of insulin-like growth factor 1. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 73–79.
Girardi M, Lewis JM, Filler RB, Hayday AC, Tigelaar RE . Environmentally responsive and reversible regulation of epidermal barrier function by gammadelta T cells. J Invest Dermatol 2006; 126: 808–814.
Toulon A, Breton L, Taylor KR, Tenenhaus M, Bhavsar D, Lanigan C et al. A role for human skin-resident T cells in wound healing. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 743–750.
Zaba LC, Cardinale I, Gilleaudeau P, Sullivan-Whalen M, Suarez-Farinas M, Fuentes-Duculan J et al. Amelioration of epidermal hyperplasia by TNF inhibition is associated with reduced Th17 responses. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 3183–3194.
Taylor KR, Mills RE, Costanzo AE, Jameson JM . Gammadelta T cells are reduced and rendered unresponsive by hyperglycemia and chronic TNFalpha in mouse models of obesity and metabolic disease. PLoS One 2010; 5: e11422.
Chiplunkar S, Dhar S, Wesch D, Kabelitz D . gammadelta T cells in cancer immunotherapy: current status and future prospects. Immunotherapy 2009; 1: 663–678.
Bouet-Toussaint F, Cabillic F, Toutirais O, Le Gallo M, Thomas de la Pintiere C, Daniel P et al. Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell-mediated recognition of human solid tumors. Potential for immunotherapy of hepatocellular and colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2008; 57: 531–539.
Bonneville M, Scotet E . Human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells: promising new leads for immunotherapy of infections and tumors. Curr Opin Immunol 2006; 18: 539–546.
Nedellec S, Bonneville M, Scotet E . Human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells: from signals to functions. Semin Immunol 2010; 22: 199–206.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Mark Bartlam and Dr Dieter Kabelitz for editing the manuscript. We are grateful to the organizers, Dr Dieter Kabelitz and Dr Daniela Wesch; they made this conference unforgettable. Due to the length of this report, we sincerely apologize to those participants for not mentioning their exciting results here. This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB914801) and the National Outstanding Young Scientist Award of National Natural Science Foundation of China (30725015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, J., Wu, X., Xia, S. et al. Current progress in γδ T-cell biology. Cell Mol Immunol 7, 409–413 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.50
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.50
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor affects the distribution and clonality of TRGV and TRDV repertoire of T cells and graft-versus-host disease
Journal of Translational Medicine (2011)