Abstract
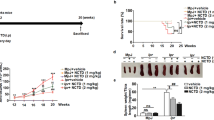
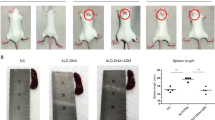
Recent evidence indicates that artesunate has immunomodulatory properties that might be useful for treating autoimmune disease. In this study, we conducted a pilot study and explored the effect and mechanism of artesunate on the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus using an MRL/lpr murine model. MRL/lpr mice were divided into control, cyclophosphamide (CTX) and artesunate treatment groups. Blood was collected to measure serum levels of creatinine, antinuclear antibody (ANA) and anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibody. Twenty-four-hour urine was collected to measure levels of proteinuria. The concentration of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) in serum and urine was measured. The expression of MCP-1 in kidney was detected by Western blot and immunohistochemistry assay, respectively. The expression of B cell activating factor (BAFF) in spleen was determined by real time-PCR and immunoblotting. We found that artesunate significantly increased the survival rate, body weight and blood leukocyte counts, and reduced the serum levels of ANA and anti-dsDNA antibody titer, 24 h urinary protein, and serum creatinine. Our results indicated that artesunate could decrease MCP-1, major pro-inflammation cytokine, in serum, urine and kidney. We also found that the level of BAFF, the major B cell activation factor, was decreased in artesunate treated MRL/lpr mice. Its efficacy was comparable with that of CTX in this study. Taken together, we have demonstrated that artesunate can inhibit the progression of disease and reverse the pathologic lesion of lupus nephritis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, O., Zhang, H., Gu, Z. et al. A Pilot Study of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Mechanism of Artesunate in the MRL/lpr Murine Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol 6, 461–467 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2009.58
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2009.58
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Artemisinin derivative SM934 in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: therapeutic effects and molecular mechanisms
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2022)
-
9,10-Anhydrodehydroartemisinin Attenuates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Inhibiting Th1 and Th17 Cell Differentiation
Inflammation (2021)
-
Unexpected mechanism of colitis amelioration by artesunate, a natural product from Artemisia annua L.
Inflammopharmacology (2020)
-
Protective mechanism of artemisinin on rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells against apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide via activation of c-Raf-Erk1/2-p90rsk-CREB pathway
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2019)
-
Artemisinins—a Promising New Treatment for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Descriptive Review
Current Rheumatology Reports (2018)