Abstract
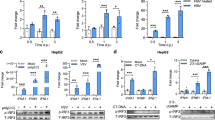
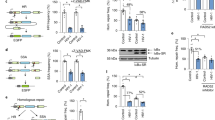
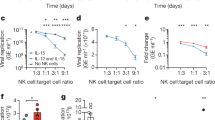
Natural killer (NK) cells are a major component of the host innate immune defense against various pathogens. Several viruses, including hepatitis C virus (HCV), have developed strategies to evade the NK-cell response. In our study, we found HCV infection could trigger DNA damage response by both ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ATM- and Rad3-related (ATR) pathways. Recent reports had revealed that NKG2D ligands (NK cell-activating ligands) were upregulated when a major DNA damage checkpoint pathway was activated. However, here we found that DNA damage response was activated but NKG2D ligands were downregulated upon HCV infection. Further studies showed that the protease NS3/4A of HCV which had been shown relation with immune invasion contributed to the reduced expression of NKG2D ligands. These findings provide a novel insight into the mechanisms evolved by HCV to escape from the NK cell response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, C., He, X., Ma, H. et al. Hepatitis C Virus Infection Downregulates the Ligands of the Activating Receptor NKG2D. Cell Mol Immunol 5, 475–478 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2008.60
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2008.60
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Natural killer cells and their exosomes in viral infections and related therapeutic approaches: where are we?
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Defining the role of natural killer cells in COVID-19
Nature Immunology (2023)
-
Liver-resident NK cells suppress autoimmune cholangitis and limit the proliferation of CD4+ T cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)
-
Natural killer group 2D receptor and its ligands in cancer immune escape
Molecular Cancer (2019)
-
Novel chemoimmunotherapeutic strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma based on a genome-wide association study
Scientific Reports (2016)