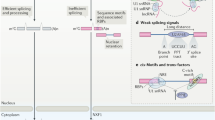
Abstract
One of the major challenges in cancer gene therapy is the identification of functionally relevant tumor-specific genes as the therapeutic targets. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small, 22–25 nucleotides, endogenously expressed noncoding RNA. miRNAs are important genetic regulators: one miRNA can possibly target multiple genes and they can function as tumor promoters (oncogenic miRNAs, oncomirs) or tumor suppressors (anti-oncomirs). Therefore, the identification of misregulated miRNAs in cellular signaling pathways related to oncogenesis can have profound implications for cancer therapy. The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) converts epithelial cells into mesenchymal cells, a normal embryological process that frequently get activated during cancer invasion and metastasis. Recent evidence also supports the presence of a small subset of self-renewing, stem-like cells within the tumor mass that possess the capacity to seed new tumors and they have been termed ‘cancer stem cells (CSC)’. Conceivably, these CSCs could provide a resource for cells that cause therapy resistance. Although the cell origin of CSCs remains to be fully elucidated, a growing body of evidence has demonstrated that the biology of EMT and CSCs is tightly linked with the sequences and compositions of miRNA molecules. Therefore, targeting miRNAs involved in EMT and CSCs regulation can provide novel miRNA-based therapeutic strategies in oncology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V . The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993; 75: 843–854.
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G . Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993; 75: 855–862.
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000; 408: 86–89.
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP . An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2001; 294: 858–862.
Lee RC, Ambros V . An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 2001; 294: 862–864.
Negrini M, Ferracin M, Sabbioni S, Croce CM . MicroRNAs in human cancer: from research to therapy. J Cell Sci 2007; 120: 1833–1840.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 15524–15529.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005; 435: 828–833.
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT . c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005; 435: 839–843.
Chen C-Z . MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1768–1771.
Chang S, Wang RH, Akagi K, Kim KA, Martin BK, Cavallone L et al. Tumor suppressor BRCA1 epigenetically controls oncogenic microRNA-155. Nat Med 2011; 17: 1275–1282.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008; 27: 2128–2136.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe–Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T . MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007; 133: 647–658.
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY . MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 14328.
Mishra PJ, Merlino G . MicroRNA reexpression as differentiation therapy in cancer. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 2119–2123.
Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, Murmann AE, Peter ME . The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 2010; 17: F19–F36.
Villadsen SB, Bramsen JB, Ostenfeld MS, Wiklund ED, Fristrup N, Gao S et al. The miR-143/-145 cluster regulates plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer 2012; 106: 366–374.
Murray MY, Rushworth SA, MacEwan DJ . Micro RNAs as a new therapeutic target towards leukaemia signalling. Cell Signal 2012; 24: 363–368.
Schotte D, Pieters R, Den Boer ML . MicroRNAs in acute leukemia: from biological players to clinical contributors. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1–12.
Babu JM, Prathibha R, Jijith VS, Hariharan R, Pillai MR . A miR-centric view of head and neck cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2011; 1816: 67–72.
Ferracin M, Querzoli P, Calin GA, Negrini M . MicroRNAs: toward the clinic for breast cancer patients. Semin Oncol 2011; 38: 764–775.
Castañeda CA, Agullo-Ortuño MT, Fresno Vara JA, Cortes-Funes H, Gomez HL, Ciruelos E . Implication of miRNA in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2011; 11: 1265–1275.
Fanini F, Vannini I, Amadori D, Fabbri M . Clinical implications of microRNAs in lung cancer. Semin Oncol 2011; 38: 776–780.
Cherni I, Weiss GJ . miRNAs in lung cancer: large roles for small players. Future Oncol 2011; 7: 1045–1055.
Gao W, Xu J, Shu Y-q . miRNA expression and its clinical implications for the prevention and diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev Respir Med 2011; 5: 699–709.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 189–198.
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Kohno S, Nakao K . MicroRNAs and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Digestion 2010; 82: 138–144.
Wu WKK, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J et al. MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: a new player enters the game. Oncogene 2010; 29: 5761–5771.
Dong Y, Wu WKK, Wu CW, Sung JJY, Yu J, Ng SSM . MicroRNA dysregulation in colorectal cancer: a clinical perspective. Br J Cancer 2011; 104: 893–898.
Wu WKK, Law PTY, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K et al. MicroRNA in colorectal cancer: from benchtop to bedside. Carcinogenesis 2011; 32: 247–253.
Nugent M, Miller N, Kerin M . MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: function, dysregulation and potential as novel biomarkers. Eur J Surg Oncol 2011; 37: 649–654.
de Krijger I, Mekenkamp LJM, Punt CJA, Nagtegaal ID . MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer metastasis. J Pathol 2011; 224: 438–447.
Schetter AJ, Harris CC . Alterations of microRNAs contribute to colon carcinogenesis. Semin Oncol 2011; 38: 734–742.
Law PTY, Wong N . Emerging roles of microRNA in the intracellular signaling networks of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 26: 437–449.
Steele CW, Oien KA, McKay CJ, Jamieson NB . Clinical potential of microRNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2011; 40: 1165.
Wang J, Sen S . MicroRNA functional network in pancreatic cancer: from biology to biomarkers of disease. J Biosci 2011; 36: 481–491.
Catto JWF, Alcaraz A, Bjartell AS, De Vere White R, Evans CP, Fussel S et al. MicroRNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer: a systematic review. Eur Urol 2011; 59: 671–681.
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP . Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 131–142.
van Zijl F, Zulehner G, Petz M, Schneller D, Kornauth C, Hau M et al. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol 2009; 5: 1169–1179.
Tsai K-W, Liao Y-L, Wu C-W, Hu L-Y, Li S-C, Chan W-C et al. Aberrant expression of miR-196a in gastric cancers and correlation with recurrence. Genes Chromosom Cancer 2012; 51: 394–401.
Ru P, Steele R, Newhall P, Phillips NJ, Toth K, Ray RB . miRNA-29b suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 11: 1166–1173.
Liu YN, Yin JJ, Abou-Kheir W, Hynes PG, Casey OM, Fang L et al. MiR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via Slug-dependent and tumorigenesis via Slug-independent mechanisms. Oncogene 2012 doi:10.1038/onc.2012.58.
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh P, Muth D et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 247–256.
Turcatel G, Rubin N, El-Hashash A, Warburton D . MIR-99a and MIR-99b modulate TGF-β induced epithelial to mesenchymal plasticity in normal murine mammary gland cells. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e31032.
Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M, Hiyoshi Y, Iwatsuki M, Tanaka Y et al. MicroRNA-200b regulates cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by directly targeting ZEB2 in gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2012: 1–9.
Schliekelman MJ, Gibbons DL, Faca VM, Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH, Zhang Q et al. Targets of the tumor suppressor miR-200 in regulation of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 7670–7682.
Korpal M, Ell BJ, Buffa FM, Ibrahim T, Blanco MA, Celia-Terrassa T et al. Direct targeting of Sec23a by miR-200s influences cancer cell secretome and promotes metastatic colonization. Nat Med 2011; 17: 1101–1108.
Eades G, Yao Y, Yang M, Zhang Y, Chumsri S, Zhou Q . miR-200a regulates SIRT1 expression and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like transformation in mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 25992–26002.
Kim T, Veronese A, Pichiorri F, Lee TJ, Jeon YJ, Volinia S et al. p53 regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition through microRNAs targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 875–883.
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Smith E, Bert AG, Wright JA, Roslan S et al. An autocrine TGF-β/ZEB/miR-200 signaling network regulates establishment and maintenance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Biol Cell 2011; 22: 1686–1698.
Yang Y, Ahn YH, Gibbons DL, Zang Y, Lin W, Thilaganathan N et al. The Notch ligand Jagged2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis through a miR-200–dependent pathway in mice. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 1373.
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, Cheung WKC, Sze J, Bian X-W et al. miR-200a-mediated downregulation of ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 391: 535–541.
Park S-M, Gaur AB, Lengyel E, Peter ME . The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 894–907.
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 593–601.
Smith AL, Iwanaga R, Drasin DJ, Micalizzi DS, Vartuli RL, Tan AC et al. The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-[beta] signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer. Oncogene 2012.
Qi J, Rice SJ, Salzberg AC, Runkle EA, Liao J, Zander DS et al. MiR-365 regulates lung cancer and developmental gene thyroid transcription factor 1. Cell cycle 2012; 11: 177–186.
Yu F, Jiao Y, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Zhu J, Cui X et al. MicroRNA 34c gene down-regulation via DNA methylation promotes self-renewal and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast tumor-initiating cells. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 465–473.
Kim NH, Kim HS, Li X-Y, Lee I, Choi H-S, Kang SE et al. A p53/miRNA-34 axis regulates Snail1-dependent cancer cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 2011; 195: 417–433.
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R, Zhao G . miR-27 promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet 2011; 204: 486–491.
Papadimitriou E, Vasilaki E, Vorvis C, Iliopoulos D, Moustakas A, Kardassis D et al. Differential regulation of the two RhoA-specific GEF isoforms Net1/Net1A by TGF-[beta] and miR-24: role in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2011.
He Y, Cui Y, Wang W, Gu J, Guo S, Ma K et al. Hypomethylation of the hsa-miR-191 locus causes high expression of hsa-mir-191 and promotes the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia 2011; 13: 841.
Shah MY, Calin GA . MicroRNAs miR-221 and miR-222: a new level of regulation in aggressive breast cancer. Genome Med 2011; 3: 56.
Stinson S, Lackner MR, Adai AT, Yu N, Kim HJ, O'Brien C et al. TRPS1 targeting by miR-221/222 promotes the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Sci Signal 2011; 4: ra41.
Dong P, Kaneuchi M, Watari H, Hamada J, Sudo S, Ju J et al. MicroRNA-194 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition of endometrial cancer cells by targeting oncogene BMI-1. Mol Cancer 2011; 10: 99.
Meng Z, Fu X, Chen X, Zeng S, Tian Y, Jove R et al. miR-194 is a marker of hepatic epithelial cells and suppresses metastasis of liver cancer cells in mice. Hepatology 2010; 52: 2148–2157.
Xiqiang L, Cheng W, Zujian C, Yi J, Yun W, Antonia K et al. MicroRNA-138 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Biochem J 2011; 440: 23–31.
Chang CJ, Hsu CC, Chang CH, Tsai LL, Chang YC, Lu SW et al. Let-7d functions as novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistant property in oral cancer. Oncol Rep 2011; 26: 1003.
Sun L, Yao Y, Liu B, Lin Z, Lin L, Yang M et al. MiR-200b and miR-15b regulate chemotherapy-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human tongue cancer cells by targeting BMI1. Oncogene 2012; 31: 432–445.
Chao A, Lin C, Lee Y, Tsai C, Wei P, Hsueh S et al. Regulation of ovarian cancer progression by microRNA-187 through targeting disabled homolog-2. Oncogene 2012; 31: 764–775.
Zheng F, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Liu YH, Liu TH, Chen SP et al. The putative tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut 2012; 61: 278–289.
Peng X, Guo W, Liu T, Wang X, Xa Tu, Xiong D et al. Identification of miRs-143 and -145 that is associated with bone metastasis of prostate cancer and involved in the regulation of EMT. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e20341.
Kumarswamy R, Mudduluru G, Ceppi P, Muppala S, Kozlowski M, Niklinski J et al. MicroRNA‐30a inhibits epithelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition by targeting Snai1 and is downregulated in non‐small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 2012; 130: 2044–2053.
Xiang X, Zhuang X, Ju S, Zhang S, Jiang H, Mu J et al. miR-155 promotes macroscopic tumor formation yet inhibits tumor dissemination from mammary fat pads to the lung by preventing EMT. Oncogene 2011; 30: 3440–3453.
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, Inoue N, Machida H, Nakayama T et al. MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Transl Med 2011; 9: 30.
Saini S, Majid S, Yamamura S, Tabatabai L, Suh SO, Shahryari V et al. Regulatory role of miR-203 in prostate cancer progression and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 5287.
Li Q, Chen Z, Cao X, Xu J, Xu J, Chen Y et al. Involvement of NF-κB/miR-448 regulatory feedback loop in chemotherapy-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Diff 2010; 18: 16–25.
Vetter G, Saumet A, Moes M, Vallar L, Le Béchec A, Laurini C et al. miR-661 expression in SNAI1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to breast cancer cell invasion by targeting Nectin-1 and StarD10 messengers. Oncogene 2010; 29: 4436–4448.
Dahl KDC, Dahl R, Kruichak JN, Hudson LG . The epidermal growth factor receptor responsive miR-125a represses mesenchymal morphology in ovarian cancer cells. Neoplasia 2009; 11: 1208.
Singh A, J Settleman . EMT cancer stem cells and drug resistance: an emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010; 29: 4741–4751.
Gill J, Langer E, Lindsley R, Cai M, Murphy T, Kyba M et al. Snail and the miR-200 family act in opposition to regulate EMT and germ layer fate restriction in differentiating ES cells. Stem cells 2011; 29: 764–776.
Scaffidi P, Misteli T . In vitro generation of human cells with cancer stem cell properties. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 1051–1061.
Xia MH . Great potential of microRNA in cancer stem cell. J Cancer Mol 2008; 4: 79–89.
Jia Y, Liu H, Zhuang Q, Xu S, Yang Z, Li J et al. Tumorigenicity of cancer stem-like cells derived from hepatocarcinoma is regulated by microRNA-145. Oncol Rep 2012; 27: 1865–1872.
Yang Y-P, Chien Y, Chiou G-Y, Cherng J-Y, Wang M-L, Lo W-L et al. Inhibition of cancer stem cell-like properties and reduced chemoradioresistance of glioblastoma using microRNA145 with cationic polyurethane-short branch PEI. Biomaterials 2012; 33: 1462–1476.
Yu XF, Zou J, Bao ZJ, Dong J . miR-93 suppresses proliferation and colony formation of human colon cancer stem cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17: 4711.
de Antonellis P, Medaglia C, Cusanelli E, Andolfo I, Liguori L, De Vita G et al. MiR-34a targeting of Notch ligand Delta-like 1 impairs CD15+/CD133+ tumor-propagating cells and supports neural differentiation in medulloblastoma. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e24584.
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li L et al. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS ONE 2009; 4: e6816.
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X, Calhoun-Davis T, Li H et al. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med 2011; 17: 211–215.
Yu Y, Kanwar SS, Patel BB, Oh P-S, Nautiyal J, Sarkar FH et al. MicroRNA-21 induces stemness by downregulating transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFβR2) in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33: 68–76.
Zhang J, Luo N, Luo Y, Peng Z, Zhang T, Li S . microRNA-150 inhibits human CD133-positive liver cancer stem cells through negative regulation of the transcription factor c-Myb. Int J Oncol 2011; 40: 747–756.
Zhu Y, Yu F, Jiao Y, Feng J, Tang W, Yao H et al. Reduced miR-128 in breast tumor–initiating cells induces chemotherapeutic resistance via Bmi-1 and ABCC5. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 7105–7115.
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A, Williams S, Otsuki A, Nuovo G et al. Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and self-renewal. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 9125–9130.
Bitarte N, Bandres E, Boni V, Zarate R, Rodriguez J, Gonzalez-Huarriz M et al. MicroRNA-451 is involved in the self-renewal, tumorigenicity, and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer stem cells. Stem Cells 2011; 29: 1661–1671.
Gal H, Pandi G, Kanner AA, Ram Z, Lithwick-Yanai G, Amariglio N et al. MIR-451 and imatinib mesylate inhibit tumor growth of glioblastoma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 376: 86–90.
Shi L, Zhang S, Feng K, Wu F, Wan Y, Wang Z et al. MicroRNA-125b-2 confers human glioblastoma stem cells resistance to temozolomide through the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Int J Oncol 2012; 40: 119.
Shi L, Zhang J, Pan T, Zhou J, Gong W, Liu N et al. MiR-125b is critical for the suppression of human U251 glioma stem cell proliferation. Brain Res 1312: 120–126.
Schraivogel D, Weinmann L, Beier D, Tabatabai G, Eichner A, Zhu JY et al. CAMTA1 is a novel tumour suppressor regulated by miR-9/9* in glioblastoma stem cells. EMBO J 2011; 30: 4309–4322.
Jeon HM, Sohn YW, Oh SY, Kim SH, Beck S, Kim S et al. ID4 Imparts chemoresistance and cancer stemness to glioma cells by derepressing miR-9*–mediated suppression of SOX2. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3410.
Tellez CS, Juri DE, Do K, Bernauer AM, Thomas CL, Damiani LA et al. EMT and stem cell–like properties associated with miR-205 and miR-200 epigenetic silencing are early manifestations during carcinogen-induced transformation of human lung epithelial cells. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3087–3097.
Lo W-L, Yu C-C, Chiou G-Y, Chen Y-W, Huang P-I, Chien C-S et al. MicroRNA-200c attenuates tumour growth and metastasis of presumptive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. J Pathol 2011; 223: 482–495.
Iliopoulos D, Lindahl-Allen M, Polytarchou C, Hirsch HA, Tsichlis PN, Struhl K . Loss of miR-200 inhibition of Suz12 leads to polycomb-mediated repression required for the formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells. Mol Cell 2010; 39: 761–772.
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 1487–1495.
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho R, Lobo N, Dalerba P, Qian D et al. Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 2009; 138: 592–603.
Meng F, Glaser SS, Francis H, DeMorrow S, Han Y, Passarini JD et al. Functional analysis of microRNAs in human hepatocellular cancer stem cells. J Cell Mol Med 2012; 16: 160–173.
Wang Y, Yu Y, Tsuyada A, Ren X, Wu X, Stubblefield K et al. Transforming growth factor-β regulates the sphere-initiating stem cell-like feature in breast cancer through miRNA-181 and ATM. Oncogene 2010; 30: 1470–1480.
Ji J, Yamashita T, Budhu A, Forgues M, Jia H-L, Li C et al. Identification of microRNA-181 by genome-wide screening as a critical player in EpCAM-positive hepatic cancer stem cells. Hepatology 2009; 50: 472–480.
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong C et al. let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 2007; 131: 1109–1123.
Yang X, Lin X, Zhong X, Kaur S, Li N, Liang S et al. Double-negative feedback loop between reprogramming factor LIN28 and microRNA let-7 regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase 1–positive cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 9463–9472.
Hwang-Verslues W, Chang P, Wei P, Yang C, Huang C, Kuo W et al. miR-495 is upregulated by E12/E47 in breast cancer stem cells, and promotes oncogenesis and hypoxia resistance via downregulation of E-cadherin and REDD1. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2463–2474.
Ma S, Tang KH, Chan YP, Lee TK, Kwan PS, Castilho A et al. miR-130b promotes CD133+ liver tumor-initiating cell growth and self-renewal via tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. Cell Stem Cell 2010; 7: 694–707.
Li WQ, Li YM, Tao BB, Lu YC, Hu GH, Liu HM et al. Downregulation of ABCG2 expression in glioblastoma cancer stem cells with miRNA-328 may decrease their chemoresistance. Med Sci Monit 2010; 16: HY27.
Yu F, Deng H, Yao H, Liu Q, Su F, Song E . Mir-30 reduction maintains self-renewal and inhibits apoptosis in breast tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene 2010; 29: 4194–4204.
Wong P, Iwasaki M, Somervaille TCP, Ficara F, Carico C, Arnold C et al. The miR-17-92 microRNA polycistron regulates MLL leukemia stem cell potential by modulating p21 expression. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 3833–3842.
Garzia L, Andolfo I, Cusanelli E, Marino N, Petrosino G, De Martino D et al. MicroRNA-199b-5p impairs cancer stem cells through negative regulation of HES1 in medulloblastoma. PLoS ONE 2009; 4: e4998.
Xia H, Cheung WKC, Ng SS, Jiang X, Jiang S, Sze J et al. Loss of brain-enriched miR-124 enhances the stem-like traits and invasiveness of glioma cells. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 9962–9971.
Silber J, Lim D, Petritsch C, Persson A, Maunakea A, Yu M et al. miR-124 and miR-137 inhibit proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells and induce differentiation of brain tumor stem cells. BMC Med 2008; 6: 14.
Mani S, Guo W, Liao M, Eaton E, Ayyanan A, Zhou A et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008; 133: 704–715.
Han M, Wang Y, Liu M, Bi X, Bao J, Zeng N et al. MiR‐21 regulates EMT phenotype and HIF‐1α expression in third‐sphereforming breast cancer stem cell‐like cells. Cancer Sci 2012; 103: 1058–1064.
Chang CJ, Chao CH, Xia W, Yang JY, Xiong Y, Li CW et al. p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties through modulating miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 317–323.
Guttilla I, Phoenix K, Hong X, Tirnauer J, Claffey K, White B . Prolonged mammosphere culture of MCF-7 cells induces an EMT and repression of the estrogen receptor by microRNAs. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012; 132: 75–85.
Iliopoulos D, Polytarchou C, Hatziapostolou M, Kottakis F, Maroulakou IG, Struhl K et al. MicroRNAs differentially regulated by Akt isoforms control EMT and stem cell renewal in cancer cells. Sci Signal 2009; 2: ra62-.
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Kong D, Banerjee S, Ahmad A et al. Over-expression of FoxM1 leads to epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 2011; 112: 2296–2306.
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Kong D, Li Y, Ahmad A et al. Notch-1 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition consistent with cancer stem cell phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett 2011; 307: 26–36.
Xia H, Cheung WKC, Sze J, Lu G, Jiang S, Yao H et al. miR-200a regulates epithelial-mesenchymal to stem-like transition via ZEB2 and ¦Â-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 36995.
Garzon R, Marcucci G, Croce CM . Targeting microRNAs in cancer: rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010; 9: 775–789.
Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M et al. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with/‘antagomirs/’. Nature 2005; 438: 685–689.
Elmen J, Lindow M, Schutz S, Lawrence M, Petri A, Obad S et al. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2008; 452: 896–899.
Ebert MS, Neilson JR, Sharp PA . MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat Methods 2007; 4: 721–726.
Ebert MS, Sharp PA . MicroRNA sponges: progress and possibilities. RNA 2010; 16: 2043–2050.
Choi WY, Giraldez AJ, Schier AF . Target protectors reveal dampening and balancing of Nodal agonist and antagonist by miR-430. Sci STKE 2007; 318: 271.
Zhang S, Chen L, Jung E, Calin G . Targeting microRNAs with small molecules: from dream to reality. Clin Pharmacol Therapeut 2010; 87: 754–758.
Gumireddy K, Young DD, Xiong X, Hogenesch JB, Huang Q, Deiters A . Small-molecule inhibitors of microRNA miR-21 function. Angewandte Chemie Int Edit 2008; 47: 7482–7484.
Bader AG, Brown D, Winkler M . The promise of microRNA replacement therapy. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 7027–7030.
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang H-W et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 2009; 137: 1005–1017.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the SingHealth Foundation, National Medical Research Council, Biomedical Research Council of Singapore and The Singapore Millennium Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, H., Hui, K. MicroRNAs involved in regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells as molecular targets for cancer therapeutics. Cancer Gene Ther 19, 723–730 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.58
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.58
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Induction of metastasis, cancer stem cell phenotype, and oncogenic metabolism in cancer cells by ionizing radiation
Molecular Cancer (2017)
-
Upregulation of microRNA-4417 and Its Target Genes Contribute to Nickel Chloride-promoted Lung Epithelial Cell Fibrogenesis and Tumorigenesis
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometrial cancer: connecting PI3K, estrogen signaling, and microRNAs
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2016)
-
SPOCK1 as a potential cancer prognostic marker promotes the proliferation and metastasis of gallbladder cancer cells by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
Molecular Cancer (2015)
-
Sequence variation among members of the miR-200 microRNA family is correlated with variation in the ability to induce hallmarks of mesenchymal-epithelial transition in ovarian cancer cells
Journal of Ovarian Research (2014)