Abstract
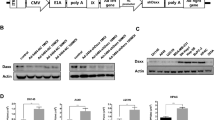
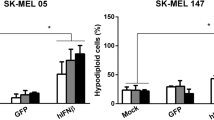
Although the combination of gene therapy and virotherapy for cancer therapy has obtained some encouraging results in vitro and in vivo over the past few years, some improvements of the vectors are still urgently needed to enhance their therapeutic effects for cancers. In order to maximize the anti-cancer activities of conditionally replicating adenoviral vectors (CRAd) vector, we for the first time generated a novel CRAd vector by inserting an expression cassette between E4 and the fiber using homologous recombination and tested this vector in melanoma cancer therapy. By using this novel vector we expressed two therapeutic transgenes, IL-24 and arresten, inserted in E1 and the region between E4 and the fiber, respectively, to test the melanoma inhibitory activities of this oncolytic virus in vitro and in vivo. The two therapeutic transgenes were successfully expressed by the novel CRAd, which was confirmed by western blotting. We then showed that this novel CRAd vector significantly suppressed the tumor growth of melanoma in vitro and in vivo compared with the control by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting angiogenesis. The novel CRAd vector generated in this study holds promise for developing more effective therapeutics for not only melanoma but also other common cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oh JY, Park MY, Kim DR, Lee JH, Shim SH, Chung JH et al. Combination gene therapy of lung cancer with conditionally replicating adenovirus and adenovirus-herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase. Int J Mol Med 2010; 25: 369–376.
Trujillo MA, Oneal MJ, McDonough S, Qin R, Morris JC . A probasin promoter, conditionally replicating adenovirus that expresses the sodium iodide symporter (NIS) for radiovirotherapy of prostate cancer. Gene Ther 2010; 17: 1325–1332.
Bortolanza S, Bunuales M, Otano I, Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza G, Ortiz-de-Solorzano C, Perez D et al. Treatment of pancreatic cancer with an oncolytic adenovirus expressing interleukin-12 in Syrian hamsters. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 614–622.
Cody JJ, Douglas JT . Armed replicating adenoviruses for cancer virotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2009; 16: 473–488.
Wong HH, Lemoine NR, Wang Y . Oncolytic Viruses for Cancer Therapy: Overcoming the Obstacles. Viruses 2010; 2: 78–106.
Tollefson AE, Ryerse JS, Scaria A, Hermiston TW, Wold WS . The E3-11.6-kDa adenovirus death protein (ADP) is required for efficient cell death: characterization of cells infected with adp mutants. Virology 1996; 220: 152–162.
Zou A, Atencio I, Huang WM, Horn M, Ramachandra M . Overexpression of adenovirus E3-11.6K protein induces cell killing by both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms. Virology 2004; 326: 240–249.
Doronin K, Toth K, Kuppuswamy M, Krajcsi P, Tollefson AE, Wold WS . Overexpression of the ADP (E3-11.6K) protein increases cell lysis and spread of adenovirus. Virology 2003; 305: 378–387.
Wang Y, Hallden G, Hill R, Anand A, Liu TC, Francis J et al. E3 gene manipulations affect oncolytic adenovirus activity in immunocompetent tumor models. Nat Biotechnol 2003; 21: 1328–1335.
Bortolanza S, Bunuales M, Alzuguren P, Lamas O, Aldabe R, Prieto J et al. Deletion of the E3-6.7K/gp19K region reduces the persistence of wild-type adenovirus in a permissive tumor model in Syrian hamsters. Cancer Gene Ther 2009; 16: 703–712.
Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB . Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene 1995; 11: 2477–24786.
Huang EY, Madireddi MT, Gopalkrishnan RV, Leszczyniecka M, Su Z, Lebedeva IV et al. Genomic structure, chromosomal localization and expression profile of a novel melanoma differentiation associated (mda-7) gene with cancer specific growth suppressing and apoptosis inducing properties. Oncogene 2001; 20: 7051–7063.
Caudell EG, Mumm JB, Poindexter N, Ekmekcioglu S, Mhashilkar AM, Yang XH et al. The protein product of the tumor suppressor gene, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7, exhibits immunostimulatory activity and is designated IL-24. J Immunol 2002; 168: 6041–6046.
Parrish-Novak J, Xu W, Brender T, Yao L, Jones C, West J et al. Interleukins 19, 20, and 24 signal through two distinct receptor complexes. Differences in receptor-ligand interactions mediate unique biological functions. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 47517–47523.
Fisher PB, Gopalkrishnan RV, Chada S, Ramesh R, Grimm EA, Rosenfeld MR et al. mda-7/IL-24, a novel cancer selective apoptosis inducing cytokine gene: from the laboratory into the clinic. Cancer Biol Ther 2003; 2: 23–37.
Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, Fisher PB . Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 2004; 22: 929–979.
Gupta P, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Sarkar D, Sauane M, Emdad L et al. mda-7/IL-24: multifunctional cancer-specific apoptosis-inducing cytokine. Pharmacol Ther 2006; 111: 596–628.
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Vozhilla N, Park ES, Gupta P, Fisher PB . Dual cancer-specific targeting strategy cures primary and distant breast carcinomas in nude mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 14034–14039.
Su Z, Emdad L, Sauane M, Lebedeva IV, Sarkar D, Gupta P et al. Unique aspects of mda-7/IL-24 antitumor bystander activity: establishing a role for secretion of MDA-7/IL-24 protein by normal cells. Oncogene 2005; 24: 7552–7566.
Gupta P, Walter MR, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Emdad L, Randolph A et al. BiP/GRP78 is an intracellular target for MDA-7/IL-24 induction of cancer-specific apoptosis. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 81–91.
Sauane M, Gupta P, Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, Sarkar D, Randolph A et al. N-glycosylation of MDA-7/IL-24 is dispensable for tumor cell-specific apoptosis and ‘bystander’ antitumor activity. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11869–11877.
Emdad L, Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, Gupta P, Sauane M, Dash R et al. Historical perspective and recent insights into our understanding of the molecular and biochemical basis of the antitumor properties of mda-7/IL-24. Cancer Biol Ther 2009; 8: 391–400.
Cunningham CC, Chada S, Merritt JA, Tong A, Senzer N, Zhang Y et al. Clinical and local biological effects of an intratumoral injection of mda-7 (IL24; INGN 241) in patients with advanced carcinoma: a phase I study. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 149–159.
Fisher PB, Sarkar D, Lebedeva IV, Emdad L, Gupta P, Sauane M et al. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 (mda-7/IL-24): novel gene therapeutic for metastatic melanoma. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2007; 224: 300–307.
Dent P, Yacoub A, Hamed HA, Park MA, Dash R, Bhutia SK et al. MDA-7/IL-24 as a cancer therapeutic: from bench to bedside. Anticancer Drugs 2010; 21: 725–731.
Colorado PC, Torre A, Kamphaus G, Maeshima Y, Hopfer H, Takahashi K et al. Anti-angiogenic cues from vascular basement membrane collagen. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 2520–2526.
Long MY, Li HH, Xu JY, Lai DM, Weng ZH . Inhibitory effects of transfection of arresten gene on liver metastasis from colorectal cancer in nude mice. Ai Zheng 2008; 27: 1039–1043.
Zhang ZL, Zou WG, Luo CX, Li BH, Wang JH, Sun LY et al. An armed oncolytic adenovirus system, ZD55-gene, demonstrating potent antitumoral efficacy. Cell Res 2003; 13: 481–489.
Zhang Z, Zou W, Wang J, Gu J, Dang Y, Li B et al. Suppression of tumor growth by oncolytic adenovirus-mediated delivery of an antiangiogenic gene, soluble Flt-1. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 553–562.
Zhao L, Dong A, Gu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang W et al. The antitumor activity of TRAIL and IL-24 with replicating oncolytic adenovirus in colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 1011–1022.
Anderson RD, Haskell RE, Xia H, Roessler BJ, Davidson BL . A simple method for the rapid generation of recombinant adenovirus vectors. Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1034–1038.
Liu S, Mao Q, Zhang W, Zheng X, Bian Y, Wang D et al. Genetically modified adenoviral vector with the protein transduction domain of Tat improves gene transfer to CAR-deficient cells. Biosci Rep 2009; 29: 103–109.
Addison CL, Bramson JL, Hitt MM, Muller WJ, Gauldie J, Graham FL . Intratumoral coinjection of adenoviral vectors expressing IL-2 and IL-12 results in enhanced frequency of regression of injected and untreated distal tumors. Gene Ther 1998; 5: 1400–1409.
Huang X, Lin T, Gu J, Zhang L, Roth JA, Stephens LC et al. Combined TRAIL and Bax gene therapy prolonged survival in mice with ovarian cancer xenograft. Gene Ther 2002; 9: 1379–1386.
Inoue S, Branch CD, Gallick GE, Chada S, Ramesh R . Inhibition of Src kinase activity by Ad-mda7 suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor expression in prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 707–715.
Ramesh R, Mhashilkar AM, Tanaka F, Saito Y, Branch CD, Sieger K et al. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7/interleukin (IL)-24 is a novel ligand that regulates angiogenesis via the IL-22 receptor. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 5105–5113.
Nyberg P, Xie L, Sugimoto H, Colorado P, Sund M, Holthaus K et al. Characterization of the anti-angiogenic properties of arresten, an alpha1beta1 integrin-dependent collagen-derived tumor suppressor. Exp Cell Res 2008; 314: 3292–32305.
Sudhakar A, Nyberg P, Keshamouni VG, Mannam AP, Li J, Sugimoto H et al. Human alpha1 type IV collagen NC1 domain exhibits distinct antiangiogenic activity mediated by alpha1beta1 integrin. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2801–2810.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the ‘Innovation Funds of Graduate Programs, Shaanxi Normal University’ (2009CXB009) and research Grants to H.X from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30872993 and No.31070137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, L., Liu, S., Mao, Q. et al. A novel conditionally replicating adenoviral vector with dual expression of IL-24 and arresten inserted in E1 and the region between E4 and fiber for improved melanoma therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 19, 247–254 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2011.84
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2011.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Optimizing oncolytic virotherapy in cancer treatment
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2019)
-
Oncolytic virotherapy for urological cancers
Nature Reviews Urology (2016)
-
Potent anti-tumour activity of a novel conditionally replicating adenovirus for melanoma via inhibition of migration and invasion
British Journal of Cancer (2014)
-
Therapeutic Improvement of a Stroma-Targeted CRAd by Incorporating Motives Responsive to the Melanoma Microenvironment
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2013)