Abstract
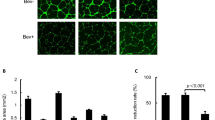
Despite optimal surgery and chemotherapy, the prognosis of ovarian cancer patients remains poor and new treatments are urgently needed. Solid tumors require the formation of new vessels for growth and metastasis. In the present study, we have used soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (sVEGF) receptors sVEGFR-1 and -3, soluble receptors Tie1 and Tie2 and their combinations in an ovarian cancer xenograft model. Human ovarian cancer cells were injected intraperitoneally into nude mice (n=42) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used for confirming tumors before gene delivery. Treatment with combined AdsVEGFR-1, AdsVEGFR-3 and AdsTie2 significantly decreased the size of the intraperitoneal tumors compared with the controls (AdLacZ; P=0.038) with significantly less microvessels and vascular area. Unexpectedly, treatment with combined AdsTie1 and AdsTie2 led to a dramatic shortening of the survival which was not observed in the groups receiving either of the soluble receptors alone (P=0.031). The only difference to other treatments was liver toxicity observed after the combined Tie receptor treatment. In conclusion, combined inhibition of VEGFR-1, VEGFR-3 and Tie2 pathways was safe and provided efficient therapy for ovarian cancer in mice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannistra SA . Cancer of the ovary. N Engl J Med 2004; 35: 2519–2529.
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E et al. Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin 2004; 54: 8–29.
Folkman J . What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 1990; 82: 4–6.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK . Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000; 407: 249–257.
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J . Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 2000; 407: 242–248.
Adams RH, Alitalo K . Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 464–478.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J . The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 2003; 9: 669–676.
Shibuya M . Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and receptor-2 in angiogenesis. J Biochem Mol Biol 2006; 39: 469–478.
Kendall RL, Wang G, Thomas KA . Identification of a natural soluble form of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, FLT-1, and its heterodimerization with KDR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 226: 324–328.
Levine RJ, Maynard SE, Qian C, Lim KH, England LJ, Yu KF et al. Circulating angiogenic factors and the risk of preeclampsia. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 672–683.
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L . VEGF receptor signaling—in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 359–371.
Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV . Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature 2005; 438: 946–953.
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, Chilov D, Lahtinen I, Kukk E et al. A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 1996; 15: 290–298.
Achen MG, Jeltsch M, Kukk E, Makinen T, Vitali A, Wilks AF et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) is a ligand for the tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (Flk1) and VEGF receptor 3 (Flt4). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 548–553.
Tammela T, Zarkada G, Wallgard E, Murtomaki A, Suchting S, Wirzenius M et al. Blocking VEGFR-3 suppresses angiogenic sprouting and vascular network formation. Nature 2008; 454: 656–660.
Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Acheson A, Compton DL, Jain V et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell 1996; 87: 1161–1169.
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C et al. Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 1997; 277: 55–60.
Valenzuela DM, Griffiths JA, Rojas J, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Zhou H et al. Angiopoietins 3 and 4: diverging gene counterparts in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 1904–1909.
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S et al. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 1996; 87: 1171–1180.
Holopainen T, Huang H, Chen C, Kim KE, Zhang L, Zhou F et al. Angiopoietin-1 overexpression modulates vascular endothelium to facilitate tumor cell dissemination and metastasis establishment. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 4656–4664.
Holash J, Wiegand SJ, Yancopoulos GD . New model of tumor angiogenesis: dynamic balance between vessel regression and growth mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Oncogene 1999; 18: 5356–5362.
Tammela T, Saaristo A, Lohela M, Morisada T, Tornberg J, Norrmen C et al. Angiopoietin-1 promotes lymphatic sprouting and hyperplasia. Blood 2005; 105: 4642–4648.
Gale NW, Thurston G, Hackett SF, Renard R, Wang Q, McClain J et al. Angiopoietin-2 is required for postnatal angiogenesis and lymphatic patterning, and only the latter role is rescued by angiopoietin-1. Dev Cell 2002; 3: 411–423.
Saharinen P, Kerkela K, Ekman N, Marron M, Brindle N, Lee GM et al. Multiple angiopoietin recombinant proteins activate the Tie1 receptor tyrosine kinase and promote its interaction with Tie2. J Cell Biol 2005; 169: 239–243.
Sallinen H, Anttila M, Narvainen J, Koponen J, Hamalainen K, Kholova I et al. Antiangiogenic gene therapy with soluble VEGFR-1, -2, and -3 reduces the growth of solid human ovarian carcinoma in mice. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 278–284.
Sallinen H, Anttila M, Narvainen J, Orden MR, Ropponen K, Kosma VM et al. A highly reproducible xenograft model for human ovarian carcinoma and application of MRI and ultrasound in longitudinal follow-up. Gynecol Oncol 2006; 103: 315–320.
Bhardwaj S, Roy H, Karpanen T, He Y, Jauhiainen S, Hedman M et al. Periadventitial angiopoietin-1 gene transfer induces angiogenesis in rabbit carotid arteries. Gene Ther 2005; 12: 388–394.
Pajusola K, Aprelikova O, Armstrong E, Morris S, Alitalo K . Two human FLT4 receptor tyrosine kinase isoforms with distinct carboxy terminal tails are produced by alternative processing of primary transcripts. Oncogene 1993; 8: 2931–2937.
Takayama K, Ueno H, Nakanishi Y, Sakamoto T, Inoue K, Shimizu K et al. Suppression of tumor angiogenesis and growth by gene transfer of a soluble form of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor into a remote organ. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 2169–2177.
Makinen T, Jussila L, Veikkola T, Karpanen T, Kettunen MI, Pulkkanen KJ et al. Inhibition of lymphangiogenesis with resulting lymphedema in transgenic mice expressing soluble VEGF receptor-3. Nat Med 2001; 7: 199–205.
Veikkola T, Jussila L, Makinen T, Karpanen T, Jeltsch M, Petrova TV et al. Signalling via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 is sufficient for lymphangiogenesis in transgenic mice. EMBO J 2001; 20: 1223–1231.
Lin P, Buxton JA, Acheson A, Radziejewski C, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD et al. Antiangiogenic gene therapy targeting the endothelium-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 8829–8834.
Hedman M, Hartikainen J, Syvanne M, Stjernvall J, Hedman A, Kivela A et al. Safety and feasibility of catheter-based local intracoronary vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer in the prevention of postangioplasty and in-stent restenosis and in the treatment of chronic myocardial ischemia: phase II results of the Kuopio Angiogenesis Trial (KAT). Circulation 2003; 107: 2677–2683.
Puumalainen AM, Vapalahti M, Agrawal RS, Kossila M, Laukkanen J, Lehtolainen P et al. Beta-galactosidase gene transfer to human malignant glioma in vivo using replication-deficient retroviruses and adenoviruses. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 1769–1774.
Yla-Herttuala S, Rosenfeld ME, Parthasarathy S, Glass CK, Sigal E, Witztum JL et al. Colocalization of 15-lipoxygenase mRNA and protein with epitopes of oxidized low density lipoprotein in macrophage-rich areas of atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 6959–6963.
Yamamoto S, Konishi I, Mandai M, Kuroda H, Komatsu T, Nanbu K et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in epithelial ovarian neoplasms: correlation with clinicopathology and patient survival, and analysis of serum VEGF levels. Br J Cancer 1997; 76: 1221–1227.
Hata K, Nakayama K, Fujiwaki R, Katabuchi H, Okamura H, Miyazaki K . Expression of the angopoietin-1, angopoietin-2, Tie2, and vascular endothelial growth factor gene in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2004; 93: 215–222.
Jendreyko N, Popkov M, Rader C, Barbas III CF . Phenotypic knockout of VEGF-R2 and Tie-2 with an intradiabody reduces tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 8293–8298.
Raikwar SP, Temm CJ, Raikwar NS, Kao C, Molitoris BA, Gardner TA . Adenoviral vectors expressing human endostatin-angiostatin and soluble Tie2: enhanced suppression of tumor growth and antiangiogenic effects in a prostate tumor model. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 1091–1100.
Siemeister G, Schirner M, Weindel K, Reusch P, Menrad A, Marme D et al. Two independent mechanisms essential for tumor angiogenesis: inhibition of human melanoma xenograft growth by interfering with either the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor pathway or the Tie-2 pathway. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 3185–3191.
Zadeh G, Reti R, Koushan K, Baoping Q, Shannon P, Guha A . Regulation of the pathological vasculature of malignant astrocytomas by angiopoietin-1. Neoplasia 2005; 7: 1081–1090.
Hata K, Udagawa J, Fujiwaki R, Nakayama K, Otani H, Miyazaki K . Expression of angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, and Tie2 genes in normal ovary with corpus luteum and in ovarian cancer. Oncology 2002; 62: 340–348.
Zhang L, Yang N, Park JW, Katsaros D, Fracchioli S, Cao G et al. Tumor-derived vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulates angiopoietin-2 in host endothelium and destabilizes host vasculature, supporting angiogenesis in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3403–3412.
Dumont DJ, Gradwohl G, Fong GH, Puri MC, Gertsenstein M, Auerbach A et al. Dominant-negative and targeted null mutations in the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase, tek, reveal a critical role in vasculogenesis of the embryo. Genes Dev 1994; 8: 1897–1909.
Sato TN, Tozawa Y, Deutsch U, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fujiwara Y, Gendron-Maguire M et al. Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature 1995; 376: 70–74.
Kuhnert F, Tam BY, Sennino B, Gray JT, Yuan J, Jocson A et al. Soluble receptor-mediated selective inhibition of VEGFR and PDGFRbeta signaling during physiologic and tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 10185–10190.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Seija Sahrio, Ms Sari Järveläinen, Ms Tiina Koponen, Ms Anneli Miettinen and Ms Helena Kemiläinen for skilful technical assistance. This study was supported by the Finnish Academy, EU Lymphangiogenomics network (LSHG-CT-2004-503573), Kuopio University Hospital (EVO grant 5185), the Finnish Medical Foundation, the Foundation of Finnish Cancer Institute, the Cancer Foundation of Northern Savo, the Finnish Cultural Foundation of Northern Savo, the Research Foundation of Orion Corporation and the Emil Aaltonen Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sallinen, H., Anttila, M., Gröhn, O. et al. Cotargeting of VEGFR-1 and -3 and angiopoietin receptor Tie2 reduces the growth of solid human ovarian cancer in mice. Cancer Gene Ther 18, 100–109 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2010.56
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2010.56
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A TMVP1-modified near-infrared nanoprobe: molecular imaging for tumor metastasis in sentinel lymph node and targeted enhanced photothermal therapy
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2023)
-
Brain and Testis Accumulation of Regorafenib is Restricted by Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP/ABCG2) and P-glycoprotein (P-GP/ABCB1)
Pharmaceutical Research (2015)
-
Serum angiopoietin-2 and soluble VEGFR-2 levels predict malignancy of ovarian neoplasm and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
BMC Cancer (2014)